Effect of Tongxie Yaofang combined with acupoint catgut embedding on 5-HT and SP in ulcerative colitis rats with liver stagnation and spleen deficiency
-
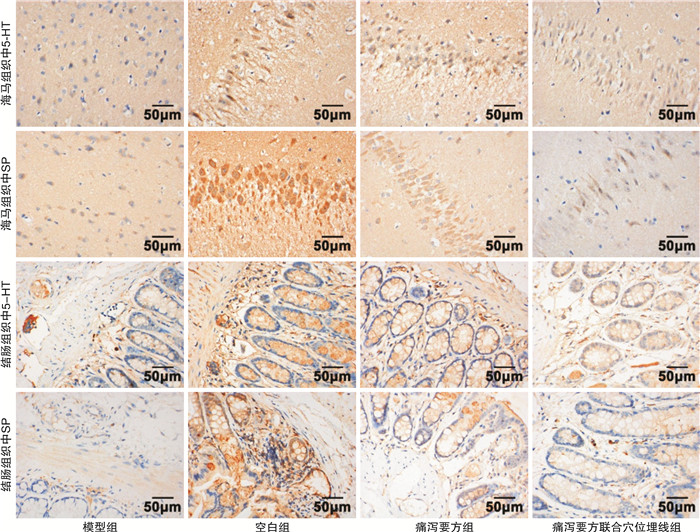
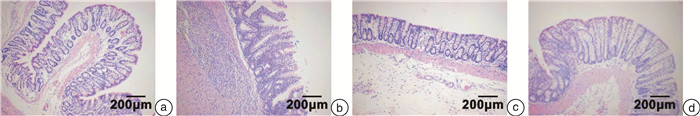
摘要: 目的 观察痛泻要方联合穴位埋线对肝郁脾虚型溃疡性结肠炎大鼠结肠、海马组织中5-羟色胺(5-hydroxytryptamine,5-HT)、神经递质P物质(neurotransmitter substance P,SP)的影响,并探讨其作用机制。方法 将48只SPF级SD雄性大鼠随机分为空白组(12只)、造模组(36只)。采用2,4,6-三硝基苯磺酸/乙醇混合剂灌肠+束缚+饮食失节+夹尾刺激制备肝郁脾虚型溃疡性结肠炎模型。将成模大鼠随机分为模型组、痛泻要方组、痛泻要方联合穴位埋线组;痛泻要方联合埋线组予以痛泻要方汤剂灌胃,连续14 d,同时于足三里、天枢、肝俞、期门、脾俞、大肠俞、膈俞各穴位处埋线,每7 d进行1次,共2次;痛泻要方组予痛泻要方汤剂灌胃;空白组和模型组予等体积纯净水进行灌胃,1次/d,干预14 d。采用苏木精-伊红染色观察结肠组织病理变化,免疫组织化学法检测大鼠结肠、海马组织中5-HT、SP的表达;ELISA法检测大鼠血清、海马组织中5-HT、SP的表达; RT-qPCR法检测结肠组织中肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、IL-6、IL-1β、IL-23含量的变化。结果 与空白组相比,余3组血清、海马及结肠组织中5-HT、SP的表达量明显增加(P < 0.05),结肠组织中TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β、IL-23的含量显著升高(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,痛泻要方组、痛泻要方联合穴位埋线组血清、海马及结肠组织中5-HT、SP的表达量明显减少(P < 0.05),结肠组织中TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β、IL-23的含量显著降低(P < 0.05)。结论 痛泻要方联合穴位埋线可以显著下调大鼠血清、海马及结肠组织中5-HT、SP的表达水平,并抑制炎性因子的表达,达到对肝郁脾虚型溃疡性结肠炎大鼠的治疗作用。Abstract: Objective To observe the effects of Tongxie Yaofang combined with acupoint catgut embedding on 5-hydroxytryptamine(5-HT) and neurotransmitter substance P(SP) in colonic and hippocampal tissues of rats with ulcerative colitis of liver depression and spleen deficiency, and to explore its mechanism.Methods Totally 48 SPF SD male rats were randomly divided into blank group(12 rats) and modeling group(36 rats). The ulcerative colitis models of liver depression and spleen deficiency pattern is established by 2, 4, 6-tritrobenzene sulfonic acid/ ethanol mixture enema combined with physical restraint, disorder diet and tail-clipping. The successfully established rat models were randomly divided into model group, Tongxie Yaofang group and Tongxie Yaofang combined with embedding group. The Tongxie Yaofang group and the combination group were treated with Tongxie Yaofang decoction by gavage for 14 days, and the combination group was also treated with acupoint embedding at"Zusanli", "Tianshu", "Ganshu", "Qimen", "Pishu", "Dachangshu"and "Geshu", seven days/time, a total of two times; and the blank group and model group were given same amount of purified water by gavage for 14 days. HE staining was used to observe the pathological changes of colon tissue and the expression of 5-HT and SP in colonic and hippocampal tissues of rats was detected by immunohistochemistry. 5-HT and SP in serum and hippocampal tissue were detected by ELISA, and tumor necrosis factor-α(TNF-α), interleukin-6(IL-6), IL-1β and IL-23 in colon tissue were detected by Real-time quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction(RT-qPCR).Results Compared with blank group, the expression levels of 5-HT and SP in serum, hippocampus and colon tissues were significantly increased(P < 0.05), and the contents of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and IL-23 in colon tissues were significantly increased(P < 0.05). Compared with model group, the expressions of 5-HT and SP in serum, hippocampus and colon tissue of Tongxie Yaofang group and Tongxie Yaofang combined with acupoint catgut group were significantly decreased(P < 0.05), and the contents of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and IL-23 in colon tissue were significantly decreased(P < 0.05).Conclusion Tongxie Yaofang combined with acupoint catgut can significantly down-regulate the expression levels of 5-HT and SP in serum, hippocampus and colon tissue, and reduce the expression of inflammatory factors, so as to treat ulcerative colitis of liver depression and spleen deficiency.
-

-
表 1 临床四诊信息与大鼠宏观表征转化
临床四诊信息 大鼠宏观表征 主症 主要依据 胃脘或胁肋胀痛,腹胀 喜蜷卧,行动迟缓 食少纳呆 体重增长缓慢,进食量少 便溏不爽 大便稀溏 次症 主要依据 情绪抑郁或急躁易怒,善太息 抓取反抗微弱或激烈 肠鸣矢气,腹痛即泻、泻后痛减 拉尾排便次数增加 舌苔白或腻 舌体多津 脉弦或细 表 2 各基因PCR引物序列
基因名称 引物序列(5′-3′) 产物长度
/ bpGAPDH F:ACAGCAACAGGGTGGTGGAC 252 R:TTTGAGGGTGCAGCGAACTT TNF-α F:CCCCTCTATTTATAATTGCACCT 167 R:CTGGTAGTTTAGCTCCGTTT IL-6 F:TCACTATGAGGTCTACTCGG 141 R:CATATTGCCAGTTCTTCGTA IL-1β F:CAGCAGCATCTCGACAAGAG 123 R:AAAGAAGGTGCTTGGGTCCT IL-23 F:CCTGCTGGACTCGGACAT 85 R:GCCCAGTAGGGAGGTATGAA 表 3 各组大鼠DAI、CMDI及TDI评分的比较
分,X±S 组别 例数 DAI CMDI TDI 空白组 9 0.53±0.17 0 0 模型组 11 2.57±0.161) 4.10±0.701) 4.16±0.381) 痛泻要方组 11 1.91±0.231)2) 2.92±0.351)2) 2.83±0.321)2) 痛泻要方联合穴位埋线组 11 1.09±0.251)2)3) 1.82±0.441)2)3) 1.77±0.341)2)3) 与空白组相比,1)P < 0.05;与模型组相比,2)P < 0.05;与痛泻要方组相比,3)P < 0.05。 表 4 各组大鼠海马组织及血清中5-HT、SP含量的比较
pg/mL,X±S 组别 例数 海马组织 血清 5-HT SP 5-HT SP 空白组 3 1.27±0.13 55.88±1.46 5.34±0.80 14.59±2.80 模型组 3 2.09±0.171) 89.11±2.901) 20.26±2.061) 32.93±1.011) 痛泻要方组 3 1.76±0.051)2) 75.33±0.901)2) 9.99±0.481)2) 26.02±0.711)2) 痛泻要方联合穴位埋线组 3 1.50±0.051)2)3) 63.96±3.451)2)3) 7.53±0.421)2)3) 21.03±1.391)2)3) 与空白组相比,1)P < 0.05;与模型组相比,2)P < 0.05;与痛泻要方组相比,3)P < 0.05。 表 5 各组大鼠海马、结肠组织中5-HT、SP表达的比较
X±S 组别 例数 海马组织 结肠组织 5-HT SP 5-HT SP 空白组 3 0.09±0.01 0.08±0.03 0.13±0.03 0.09±0.01 模型组 3 0.30±0.031) 0.30±0.021) 0.65±0.111) 0.37±0.031) 痛泻要方组 3 0.22±0.041)2) 0.23±0.011)2) 0.40±0.051)2) 0.26±0.001)2) 痛泻要方联合穴位埋线组 3 0.15±0.021)2)3) 0.13±0.011)2)3) 0.25±0.041)2)3) 0.14±0.011)2)3) 与空白组相比,1)P < 0.05;与模型组相比,2)P < 0.05;与痛泻要方组相比,3)P < 0.05。 表 6 各组大鼠结肠组织中TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β、IL-23含量的比较
pg/mL,X±S 组别 例数 TNF-α IL-6 IL-1β IL-23 空白组 3 1.30±0.38 1.07±0.37 1.22±0.22 1.15±0.24 模型组 3 7.04±0.741) 9.73±1.751) 7.90±1.361) 9.59±1.121) 痛泻要方组 3 4.25±0.351)2) 6.50±0.671)2) 5.62±1.141)2) 7.03±0.341)2) 痛泻要方联合穴位埋线组 3 3.26±0.351)2)3) 3.74±1.721)2)3) 3.77±0.491)2)3) 4.44±0.911)2)3) 与空白组相比,1)P < 0.05;与模型组相比,2)P < 0.05;与痛泻要方组相比,3)P < 0.05。 -
[1] Ordás I, Eckmann L, Talamini M, et al. Ulcerative colitis[J]. Lancet, 2012, 380(9853): 1606-1619. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60150-0
[2] Uniken Venema WT, Voskuil MD, Dijkstra G, et al. The genetic background of inflammatory bowel disease: from correlation to causality[J]. J Pathol, 2017, 241(2): 146-158. doi: 10.1002/path.4817
[3] Yu FY, Huang SG, Zhang HY, et al. Comparison of 5-hydroxytryptophan signaling pathway characteristics in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome and ulcerative colitis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22(12): 3451-3459. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i12.3451
[4] Lee D, Albenberg L, Compher C, et al. Diet in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases[J]. Gastroenterology, 2015, 148(6): 1087-1106. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.01.007
[5] Ye YL, Pang Z, Chen WC, et al. The epidemiology and risk factors of inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2015, 8(12): 22529-22542.
[6] 吴开春, 梁洁, 冉志华, 等. 炎症性肠病诊断与治疗的共识意见(2018年·北京)[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2018, 38(9): 796-813.
[7] Harbord M, Eliakim R, Bettenworth D, et al. Third European evidence-based consensus on diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis. part 2: current management[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2017, 11(7): 769-784. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx009
[8] 李宏军, 李国萍, 李宏岩. 穴位埋线治疗溃疡性结肠炎临床观察[J]. 中国针灸, 2006, 26(4): 261-263. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0255-2930.2006.04.010
[9] 朱莹, 袁伟建, 白晓明. 穴位埋线对溃疡性结肠炎淋巴细胞凋亡调控蛋白的影响[J]. 中医杂志, 2007, 48(6): 526-528. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1668.2007.06.016
[10] 朱向东, 李兰珍, 段永强, 等. 痛泻要方对溃疡性结肠炎大鼠结肠组织病理形态及血清中相关因子含量的影响[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志, 2013, 20(4): 41-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5304.2013.04.015
[11] 胡政. 痛泻要方对肝郁脾虚型UC模型大鼠VIP、TGF-β含量的影响[D]. 长沙: 湖南中医药大学, 2016.
[12] 郭义. 实验针灸学[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社, 2008: 414-417.
[13] 黄继汉, 黄晓晖, 陈志扬, 等. 药理试验中动物间和动物与人体间的等效剂量换算[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2004, 9(9): 1069-1072. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YLZL200409025.htm
[14] 郑筱萸. 中药新药临床研究指导原则: 试行[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2002: 365-365.
[15] 方肇勤. 大鼠/小鼠辨证论治实验方法学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 99-101.
[16] 李玉波. 抑郁症肝郁脾虚证大鼠模型的建立及其生物学基础研究[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2014.
[17] Murano M, Maemura K, Hirata I, et al. Therapeutic effect of intracolonically administered nuclear factor kappa B(p65) antisense oligonucleotide on mouse dextran sulphate sodium(DSS)-induced colitis[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2000, 120(1): 51-58.
[18] Ekstrom GM. Oxazolone-induced colitis in rats: effects of budesonide, cyclosporin A, and 5-aminosalicylic acid[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 1998, 33(2): 174-179. doi: 10.1080/00365529850166914
[19] Dieleman LA, Palmen MJ, Akol H, et al. Chronic experimental colitis induced by dextran sulphate sodium(DSS)is characterized by Th1 and Th2 cytokines[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 1998, 114(3): 385-391.
[20] 龙丹, 朱莹. 从伏毒论治溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南京中医药大学学报, 2022, 38(6): 550-553.
[21] 张声生, 沈洪, 郑凯, 等. 溃疡性结肠炎中医诊疗专家共识意见(2017)[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2017, 32(8): 3585-3589.
[22] 王钰嘉, 于千惠, 卢雨微, 等. 穴位埋线联合艾灸对溃疡性结肠炎大鼠结肠组织IL-6/JAK/STAT3信号通路的影响[J]. 针刺研究, 2022, 47(6): 525-530. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XCYJ202206009.htm
[23] 梁玉杰, 张元澧, 朱立鸣. 从肝郁脾虚论治溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2012, 23(7): 1768-1769. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZGY201207081.htm
[24] 张莉华, 方步武. 脑肠轴及其在胃肠疾病发病机制中的作用[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志, 2007, 13(2): 199-201.
[25] 李夏, 王凤云, 吴皓萌, 等. 基于脑-肠互动功能探讨痛泻要方治疗腹泻性肠易激综合征机制的研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2020, 26(20): 229-234.
[26] 罗琦. 基于心胃相关理论组方中药对IBS模型大鼠脑肠轴CRH及肥大细胞的干预作用[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学, 2012.
[27] 王佳俊, 袁健梅, 王立映, 等. 基于脑肠轴研究黄连厚朴汤治疗小鼠溃疡性结肠炎的作用机制[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2022, 47(11): 3038-3048.
[28] Mashaghi A, Marmalidou A, Tehrani M, et al. Neuropeptide substance P and the immune response[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2016, 73(22): 4249-4264.
[29] 臧希. 痛泻要方调控脑肠肽5-HT、SP、NPY治疗IBS肝郁脾虚证的疏肝止泻机制研究[D]. 太原: 山西中医药大学, 2020.
[30] Chen ML, Gao L, Chen P, et al. Serotonin-exacerbated DSS-induced colitis is associated with increase in MMP-3 and MMP-9 expression in the mouse colon[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2016, 2016: 5359768.
[31] 任天华, 吕敏敏, 安晓萌, 等. 溃疡性结肠炎患者结肠黏膜5-HT信号通路的变化特点[J]. 国际消化病杂志, 2019, 39(3): 222-227.
[32] Karagiannides I, Pothoulakis C. Substance P, obesity, and gut inflammation[J]. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes, 2009, 16(1): 47-52.
[33] 王佳俊, 任敉宏, 李勇, 等. SP/NK-1R系统对溃疡性结肠炎的双重调节及中医药调控的研究进展[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2022, 40(12): 112-118, 295.
[34] Dai LY, Perera DS, Burcher E, et al. Hemokinin-1 and substance P stimulate production of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in human colonic mucosa via both NK1 and NK2 tachykinin receptors[J]. Neuropeptides, 2020, 82: 102061.
[35] 娄余, 肖运婷, 朱莹, 等. 基于NF-κB信号通路的溃结宁膏穴位敷贴对溃疡性结肠炎大鼠结肠黏膜炎症反应的影响[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志, 2021, 28(4): 75-80.
[36] 丁凌辉, 贾育新, 成映霞, 等. 参苓白术散对脾虚湿困型溃疡性结肠炎大鼠结肠IL-13, IL-23及COX-2, CREB表达的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2018, 24(11): 67-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSFX201811012.htm
[37] 叶虹玉. 痛泻要方对IBS模型肠运动作用与脑—肠轴调控关系的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江中医药大学, 2015.
[38] 张旭飞, 蒋志滨, 高洁, 等. 基于5-HT信号系统探讨痛泻要方治疗肝郁脾虚型溃疡性结肠炎的作用机制[J]. 中医学报, 2021, 36(10): 2116-2121.
[39] 张薇, 葛文静, 王慧森, 等. 痛泻要方加减引经药防风对肠易激综合征大鼠水液代谢和5-HT系统的调控作用[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2020, 26(11): 56-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSFX202011009.htm
[40] 胡莹, 郑依玲, 梅全喜, 等. 痛泻要方破壁饮片对腹泻型肠易激综合征大鼠脑肠肽的影响[J]. 中药材, 2020, 43(7): 1726-1731. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYCA202007036.htm
[41] Cui WQ, Sun WS, Xu F, et al. Spinal serotonin 1A receptor contributes to the analgesia of acupoint catgut embedding by inhibiting phosphorylation of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor GluN1 subunit in complete Freund's adjuvant-induced inflammatory pain in rats[J]. J Pain, 2019, 20(1): 16. e1-16.16. e16.
[42] Salazar-Colocho P, Del Rio J, Frechilla D. Serotonin 5-hT1A receptor activation prevents phosphorylation of NMDA receptor NR1 subunit in cerebral ischemia[J]. J Physiol Biochem, 2007, 63(3): 203-211.
-




 下载:
下载: