Effect and mechanism of Buzhong Yiqi Decoction on enhancing chemosensitivity of cisplatin-resistant human gastric cancer cell line
-
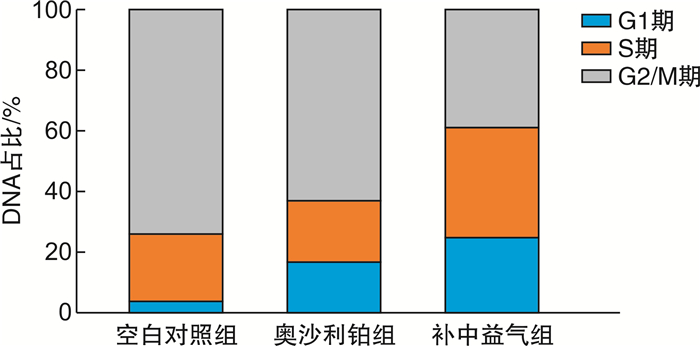
摘要: 目的 观察补中益气汤对人胃癌顺铂耐药细胞株SGC-7901CDDP奥沙利铂化疗敏感性的增强作用及机制。方法 将30株SGC-7901CDDP细胞株随机分为空白对照组、奥沙利铂组和补中益气组,每组10株,均置于DMEM高糖培养液中培养。空白对照组不添加其他药液培养,奥沙利铂组添加奥沙利铂注射液1 mL模拟化疗环境,补中益气组添加奥沙利铂注射液1 mL+补中益气汤3 mL进行培养。培养48 h后进行细胞化疗敏感性指标(细胞凋亡率、细胞迁移率、细胞周期、细胞生物学参数及化疗增敏比)及反应机制相关因子(survivin、Bcl-2、NF-κB)检测。结果 与空白对照组比较,奥沙利铂组和补中益气组的细胞凋亡率均较高(P< 0.05),且补中益气组的细胞凋亡率明显高于奥沙利铂组(P< 0.05)。在24 h和48 h两个时点,奥沙利铂组和补中益气组的划痕面积明显低于空白对照组(P< 0.05),且补中益气组的划痕面积更小(P< 0.05)。与空白对照组比较,奥沙利铂组和补中益气组细胞处于G2/M期的DNA占比明显下调,处于G1、S期的DNA占比明显上升(P< 0.05);与奥沙利铂组比较,补中益气组细胞G2/M期DNA占比明显较低,处于G1、S期的DNA占比明显较高(P< 0.05)。与空白对照组比较,奥沙利铂组和补中益气组的细胞化疗生物学参数(D0、Dq、N)均显著下降,而化疗增敏值显著上升(P< 0.05);与奥沙利铂组比较,补中益气组的细胞化疗生物学参数(D0、Dq、N)均显著下降,而化疗增敏值显著上升(P< 0.05)。与空白对照组比较,奥沙利铂组和补中益气组的survivin、Bcl-2、NF-κB表达均明显下调(P< 0.05);与奥沙利铂组比较,补中益气组的survivin、Bcl-2、NF-κB表达均明显降低(P< 0.05)。结论 补中益气汤能通过抑制细胞迁移、诱导细胞凋亡和提升人胃癌顺铂耐药细胞株的奥沙利铂化疗敏感性,其作用机制可能是补中益气汤通过下调survivin、Bcl-2、NF-κB细胞因子水平,从而提升化疗效果。
-
关键词:
- 补中益气汤 /
- 人胃癌顺铂耐药细胞株 /
- 化疗敏感性 /
- 奥沙利铂 /
- 作用机制
Abstract: Objective To observe the enhancement effect and mechanism of Buzhong Yiqi Decoction on the chemosensitivity of cisplatin-resistant human gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901CDDP to oxaliplatin.Methods Thirty SGC-7901CDDP cell lines were randomly divided into blank control group, oxaliplatin group and Buzhong Yiqi Decoction group, with 10 cells in each group, all cultured in DMEM high glucose medium. The blank control group was cultured without adding other liquid medicines. In the oxaliplatin group, 1 mL of oxaliplatin injection was added to simulate a chemotherapy environment. The Buzhong Yiqi Decoction group was supplemented with oxaliplatin injection 1 mL+Buzhong Yiqi Decoction 3 mL for culture. After 48 hours of culture, the chemosensitivity indicators(apoptosis rate, cell migration rate, cell cycle, cell biological parameters, and chemosensitization ratio) and response mechanism-related factors(survivin, Bcl-2, NF-κB) were detected.Results Compared with the blank control group, the cell apoptosis rates in the oxaliplatin group and the Buzhong Yiqi Decoction group were both higher(P< 0.05), and the cell apoptosis rate in the Buzhong Yiqi Decoction group was significantly higher than that in the oxaliplatin group(P< 0.05). At 24 h and 48 h, the scratch areas of the oxaliplatin group and the Buzhong Yiqi Decoction group were significantly lower than those of the blank control group(P< 0.05), and the Buzhong Yiqi Decoction group had a lower scratch area than the oxaliplatin group(P< 0.05). Compared with the blank control group, the proportion of DNA in the G2/M phase of the oxaliplatin group and the Buzhong Yiqi Decoction group was significantly down-regulated, and the proportion of DNA in the G1 and S phases was significantly higher(P< 0.05). Compared with the oxaliplatin group, the proportion of DNA in the G2/M phase of the Buzhong Yiqi Decoction group was significantly lower, and the proportion of DNA in the G1 and S phases was significantly higher(P< 0.05). Compared with the blank culture group, the biological parameters of cell chemotherapy(D0, Dq, N) in the oxaliplatin group and Buzhong Yiqi Decoction group were significantly decreased, while the chemotherapy sensitization value increased significantly(P< 0.05). Compared with the oxaliplatin group, the biological parameters(D0, Dq, N) of cell chemotherapy were significantly decreased, and the sensitization value was significantly increased in the Buzhong Yiqi Decoction group(P< 0.05). Compared with the blank control group, the expressions of survivin, Bcl-2, and NF-κB in the oxaliplatin group and Buzhong Yiqi Decoction group were all down-regulated(P< 0.05). Compared with the oxaliplatin group, the expressions of survivin, Bcl-2, and NF-κB in the Buzhong Yiqi Decoction group were all lower(P< 0.05).Conclusion Buzhong Yiqi Decoction can inhibit cell migration, induce cell apoptosis and improve the chemosensitivity of cisplatin-resistant human gastric cancer cell lines to oxaliplatin. The expression of Bcl-2 and NF-κB cytokines decreased, thereby enhancing the effect of chemotherapy. -

-
表 1 3组细胞凋亡率及细胞划痕面积比较
X±S 组别 株 细胞凋亡率/% 细胞划痕面积/mm2 0 24 h 48 h 空白对照组 10 -0.71±0.14 22.13±3.91 27.56±3.93 28.71±4.01 奥沙利铂组 10 32.54±3.181) 22.23±3.84 16.54±3.541) 13.68±3.391) 补中益气组 10 43.94±4.131)2) 22.29±3.79 12.18±2.941)2) 9.63±2.821)2) 与同一时点空白对照组比较,1)P < 0.05;与同一时点奥沙利铂组比较,2)P < 0.05。 表 2 3组细胞化疗生物学参数及化疗增敏值比较
X±S 组别 株 D0/% Dq/% N/% 化疗增敏值 空白对照组 10 13.49±0.17 3.32±0.21 1.28±0.10 奥沙利铂组 10 9.34±0.121) 1.65±0.141) 0.83±0.081) 1.43±0.701) 补中益气组 10 6.26±0.081)2) 0.56±0.101)2) 0.62±0.041)2) 2.18±0.121)2) 与空白对照组比较,1)P < 0.05;与奥沙利铂组比较,2)P < 0.05。 表 3 3组细胞中survivin、Bcl-2、NF-κB表达比较
μmol/L,X±S 组别 株 survivin Bcl-2 NF-κB 空白对照组 10 1.97±0.49 3.08±0.52 17.26±2.68 奥沙利铂组 10 1.34±0.301) 2.17±0.481) 14.23±2.031) 补中益气组 10 0.91±0.191)2) 1.48±0.341)2) 10.26±1.711)2) 与空白对照组比较,1)P < 0.05;与奥沙利铂组比较,2)P < 0.05。 -
[1] 中华中医药学会脾胃病分会, 中国医师协会中西医结合医师分会消化病学专业委员会. 胃黏膜定标活检技术临床应用共识(2018)[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2018, 38(12): 1496-1500. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZXJ201812022.htm
[2] 于嫔, 朱蔚远, 彭文斌, 等. 胃癌患者Hp感染与TNM分期及肿瘤恶性程度的关系分析[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2020, 28(9): 663-667. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXPW202009004.htm
[3] 王祥财, 郭蒸, 黄莉, 等. ERβ增加胃癌细胞氟尿嘧啶化疗敏感性的机制研究[J]. 赣南医学院学报, 2019, 18(5): 446-450, 454. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GNYX201905003.htm
[4] 郑勇洪, 侯凯哲. 补中益气汤治疗胃癌术后患者临床研究[J]. 新中医, 2019, 51(7): 79-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-REND201907024.htm
[5] 徐叔云, 卞如谦, 陈修, 等. 药理实验方法学[M]. 6版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2016: 1-20.
[6] Bueno MJ, Pérez de Castro I, Gómez de Cedrón M, et al. Genetic and epigenetic silencing of micro RNA-214 enhances ABL1 and BCR-ABL1 oncogene expression[J]. Cancer Cell, 2016, 13(6): 496-506.
[7] Tsujiura M, Ichikawa D, Komatsu S, et al. Circulating micro RNAs in plasma of patients with gastric cancers[J]. Br J Cancer, 2016, 102(7): 1174-1179.
[8] 戴蕾, 罗灵和, 吴黎艳, 等. miR-222、MBD2在胃癌患者中的表达及对铂类化疗敏感性的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2019, 10(6): 623-629. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YLZL201906005.htm
[9] Villagomez OV, Delgadillo DE, Marino MI, et al. Prevalence of human papillomavirus infection in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity, oropharynx and larynx[J]. Cir Cir, 2016, 84(5): 617-633.
[10] 陈渠发, 陈毅斌, 张锡迎, 等. PBK/TOPK在HCC组织中的表达与HCC对奥沙利铂敏感性的关系研究[J]. 解放军预防医学杂志, 2019, 37(3): 35-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYYX201903014.htm
[11] 邬利波. 口腔鳞状细胞癌新辅助化疗前后多药耐药相关蛋白的表达及临床疗效分析[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2016.
[12] Mengjia SX, Chen XF, Wang LP, et al. Future of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 applications: Combinations with other therapeutic regimens[J]. Chin J Cancer Res, 2018, 30(2): 157-172. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2018.02.01
[13] 王恩倩. 中医辨证护理对胃癌晚期疼痛的改善效果研究[J]. 湖南中医杂志, 2019, 35(7): 106-107, 113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNZO201907052.htm
[14] 周学文. 结直肠癌化疗患者采用补中益气汤加减治疗对其便秘症状的改善效果分析[J]. 数理医药学杂志, 2019, 32(8): 1224-1225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4337.2019.08.057
[15] 葛姗. 补中益气汤联合吉非替尼治疗肺腺癌随机平行对照研究[J]. 实用中医内科杂志, 2019, 33(6): 27-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZY201906008.htm
[16] 高文正. 补中益气汤加减对胃癌术后气虚血瘀证胃肠功能恢复的影响[J]. 天津药学, 2019, 31(2): 37-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYA201902014.htm
[17] 麦柳芳. 补中益气汤联合化疗治疗胃癌术后随机平行对照研究[J]. 实用中医内科杂志, 2019, 33(1): 36-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZY201901017.htm
[18] Terufumi K, Giichiro TW, Yoshihiko HR, et al. Immunohistological analysis of pancreatic carcinoma after vaccination with survivin 2B peptide: Analysis of an autopsy series[J]. Cancer Sci, 2019, 110(8): 2386-2395. doi: 10.1111/cas.14099
[19] Shima HE, Tsurita GH, Wada S, et al. Randomized phaseⅡtrial of survivin 2B peptide vaccination for patients with HLA-A24-positive pancreatic adenocarcinoma[J]. Cancer Sci, 2019, 110(8): 2378-2385.
[20] 于秋菊. 替吉奥胶囊对老年胃癌患者Survivin和sICAM-1及肿瘤标志物水平的影响分析[J]. 当代医学, 2019, 25(5): 135-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDYI201905058.htm
[21] 宋艳琦, 霍永利, 董笑一, 等. 浊毒1号方对胃癌前病变大鼠胃黏膜细胞凋亡及Bcl-2基因表达的影响[J]. 新中医, 2019, 51(4): 19-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-REND201904008.htm
[22] Farrow ES, Boulanger TF, Wojcik AS, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography in the assessment of mandibular invasion by squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Influence on surgical management and post-operative course[J]. Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac Chir Orale, 2016, 117(5): 339-361.
[23] 雷蕾, 张涛, 叶斌, 等. RNA干扰FLOT2基因表达下调NF-κB信号对胃癌细胞凋亡诱导作用研究[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2019, 28(6): 620-624. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WCBX201906006.htm
-




 下载:
下载: