Predictive value of four items of inflammation for the severity of ulcerative colitis
-
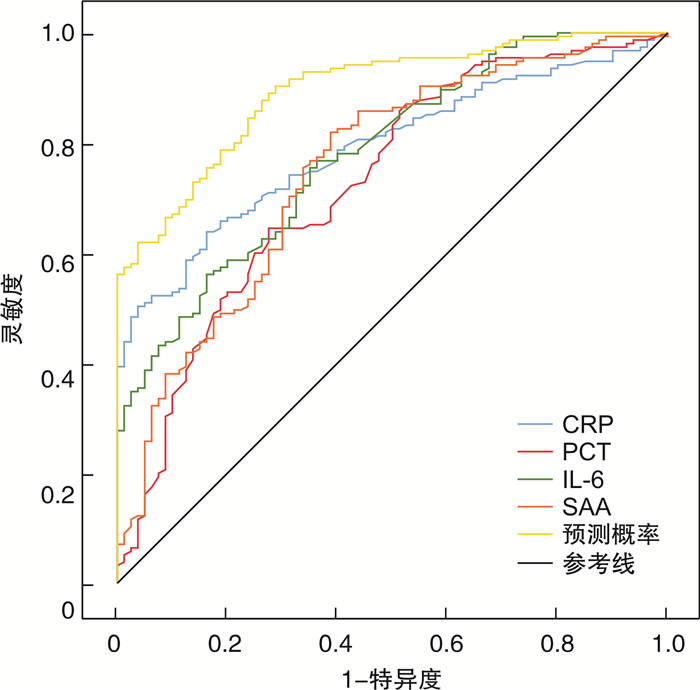
摘要: 目的 探讨炎症四项[C反应蛋白(C-reaction protein,CRP)、IL-6、血清淀粉样蛋白A(serum amyloid A,SAA)、降钙素原(procalcitonin,PCT)]在预测溃疡性结肠炎(ulcerative colitis,UC)严重程度方面的应用价值。方法 选取2020年12月—2023年12月在安徽中医药大学第一附属医院肛肠科住院治疗的UC患者为研究对象,将80例轻度患者设为对照组,155例中重度患者设为观察组。收集患者的临床资料及炎症四项数据。采用多因素logistic回归分析研究UC严重程度的影响因素,采用ROC曲线分析炎症四项对UC严重程度的预测效果。结果 观察组WBC、RBC、纤维蛋白原、CRP、IL-6、PCT、SAA均高于对照组(均P < 0.001),血清白蛋白低于对照组(P < 0.001)。多因素logistic回归分析结果显示,CRP、IL-6、PCT、SAA是UC严重程度的独立影响因素(P < 0.001)。ROC曲线分析结果显示,CRP、IL-6、PCT、SAA及四者联合预测中重度UC的AUC分别为0.791、0.728、0.781、0.751、0.895;四者联合预测中重度UC的AUC均大于CRP、IL-6、PCT、SAA单独预测的AUC(均P < 0.001)。结论 CRP、IL-6、PCT、SAA是UC严重程度的独立影响因素,且四者联合预测UC严重程度具备较高临床价值。Abstract: Objective This study will definitively determine the predictive value of inflammatory components, including C-reaction protein(CRP), procalcitonin(PCT), serum amyloid A(SAA), and IL-6, in identifying the severity of ulcerative colitis(UC).Methods This research recruited UC patients who were hospitalized in the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine from December 2020 to December 2023 of these, 155 patients with moderate severity were placed in the observation group and 80 patients with mild severity were placed in the control group. Four data sets on inflammation and general patient information were gathered. ROC curves were utilized to analyze the prediction power of the four inflammatory indicators on the severity of UC, and multifactorial logistic regression analysis was employed to investigate the factors influencing UC severity.Results Leukocyte count, erythrocyte count, fibrinogen(Fib), CRP, IL-6, PCT, and SAA were higher in the observation group than in the control group(P < 0.001), albumin(ALB) was lower in the control group(P < 0.001). The four predictor values for moderate to severe UC were 0.791, 0.728, 0.781, 0.751, and 0.895, respectively, according to ROC curve analysis, which also revealed the values for CRP, IL-6, PCT, and SAA. The AUCs of the four combined predictors of moderate to severe UC were higher than those predicted by CRP, IL-6, PCT, and SAA alone, respectively(P < 0.001).Conclusion CRP, IL-6, PCT, and SAA are the independent factors affecting the severity of UC, and the combination of the four factors has a high value in predicting the severity of UC.
-
Key words:
- ulcerative colitis /
- C-reaction protein /
- IL-6 /
- serum amyloid A /
- procalcitonin /
- predictive value
-

-
表 1 两组患者的临床资料及血清相关指标比较
X±S,例(%),M(P25,P75) 指标 观察组(n=155) 对照组(n=80) t/χ2/Z P 年龄/岁 45.55±14.98 44.46±15.35 -0.456 0.649 性别 0.108 0.743 男 81(52.26) 40(50.00) 女 74(47.74) 40(50.00) BMI 21.96±2.54 22.53±5.05 -0.295 0.768 病程/d 22.85±4.95 23.07±5.43 0.275 0.783 病变范围 5.348 0.253 直肠 23(14.84) 14(17.50) 直肠乙状结肠 32(20.64) 25(31.25) 左半结肠 38(24.52) 17(21.25) 全结肠 42(27.10) 19(23.75) 区域性结肠 20(12.90) 5(6.25) WBC/(×109/L) 8.07(6.51,9.63) 5.28(4.54,6.27) -8.957 < 0.001 RBC/(×109/L) 6.84(4.93,9.07) 4.43(3.82,4.68) -8.955 < 0.001 ESR/(mm/h) 14.09(9.12,20.03) 10.15(6.97,22.78) -1.158 0.114 Fib/(g/L) 3.46(2.12,4.75) 2.76(1.85,3.63) -3.365 < 0.001 ALB/(g/L) 33.99(30.98,37.68) 38.13(36.30,40.34) -5.438 < 0.001 CRP/(mg/L) 14.62(6.68,24.35) 5.47(3.56,8.26) -7.300 < 0.001 IL-6/(ng/L) 13.76(9.90,20.29) 8.58(4.66,12.20) -5.720 < 0.001 PCT/(μg/L) 1.43(1.15,1.68) 1.08(0.78,1.30) -7.052 < 0.001 SAA/(mg/L) 36.58(33.11,42.46) 30.11(25.85,36.21) -6.304 < 0.001 表 2 中重度UC危险因素的logistic回归分析
变量 β SE Wald χ2 P OR 95%CI CRP 0.178 0.031 32.572 < 0.001 1.195 1.124~1.270 IL-6 2.007 0.384 27.276 < 0.001 7.439 3.503~15.797 PCT 0.221 0.036 38.574 < 0.001 1.247 1.163~1.337 SAA 0.148 0.025 34.700 < 0.001 1.159 1.104~1.218 表 3 CRP、IL-6、PCT、SAA及四项联合对中重度UC的预测价值
指标 AUC 灵敏度 特异度 最佳截断值 95%CI P CRP 0.791 0.639 0.838 10.180 mg/L 0.791~0.847 < 0.001 IL-6 0.728 0.645 0.725 11.600 ng/L 0.728~0.797 < 0.001 PCT 0.781 0.768 0.637 1.135 μg/L 0.781~0.840 < 0.001 SAA 0.751 0.819 0.613 31.625 mg/L 0.751~0.818 < 0.001 四项联合 0.895 0.903 0.712 0.895~0.934 < 0.001 -
[1] 沈洪, 唐志鹏, 唐旭东, 等. 消化系统常见病溃疡性结肠炎中医诊疗指南(基层医生版)[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2019, 34(9): 4155-4160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY201909068.htm
[2] Gros B, Kaplan GG. Ulcerative Colitis in Adults: A Review[J]. JAMA, 2023, 330(10): 951-965. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.15389
[3] Lillian D, Christina H. Epidemiology and Pathogenesis of Ulcerative Colitis[J]. Gastroenterol Clin N, 2020, 49(4): 643-654. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2020.07.005
[4] Arik S, Mona S, Regina M, et al. Serum albumin levels and inflammation[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2021, 184(1): 857-862.
[5] Ishida N, Higuchi T, Miyazu T, et al. C-reactive protein is superior to fecal biomarkers for evaluating colon-wide active inflammation in ulcerative colitis[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 12431. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90558-z
[6] 吴东升, 曹晖, 张彧, 等. 基于IL-6/STAT3通路探讨芍药汤对溃疡性结肠炎Th17/Treg平衡的调节机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2023, 29(9): 46-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSFX202309006.htm
[7] 袁雪梅, 韩小琴, 韦梅, 等. 早期肝素结合蛋白联合降钙素原对重症肺炎患者的预后评估价值[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2022, 23(8): 553-556. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZLC202208002.htm
[8] Masaki W, Ryohei H, Yoshitaka U, et al. Promoting mechanism of serum amyloid a family expression in mouse intestinal epithelial cells[J]. PloS One, 2022, 17(3): e0264836. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264836
[9] Lewis JD, Chuai S, Nessel L, et al. Use of the noninvasive components of the Mayo score to assess clinical response in ulcerative colitis[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2008, 14(12): 1660-1666. doi: 10.1002/ibd.20520
[10] 王建成, 齐洪军, 郭洁洁. 溃疡性结肠炎的中医药治疗研究进展[J]. 实用中医内科杂志, 2024, 38(2): 106-109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZY202402032.htm
[11] Mariame M, Asma HL, Azzedine B, et al. Immunoanalytical characteristics of C-reactive protein and high sensitivity C-reactive protein[J]. Ann Biol Clin (Paris), 2017, 75(2): 225-229.
[12] Helena E, Birgitta G, Leena ME, et al. C-Reactive Protein Levels in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Are Modulated by the Interferon Gene Signature and CRP Gene Polymorphism rs1205[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 11: 622326. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.622326
[13] 陈佳园, 陈怡, 陈成帷, 等. 溃疡性结肠炎患者C反应蛋白/白蛋白比值与疾病活动性的相关性研究[J]. 浙江中西医结合杂志, 2022, 32(11): 1018-1021. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4561.2022.11.009
[14] Zhang J, Cao L, Sun Y, et al. The Regulatory Effects of Licochalcone A on the Intestinal Epithelium and Gut Microbiota in Murine Colitis[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(14): 4149. doi: 10.3390/molecules26144149
[15] Veselinova TV, Lyuba M, Noyko S, et al. Interleukin-6 compared to the other Th17/Treg related cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2020, 26(16): 1912-1925. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i16.1912
[16] 崔畅婉, 孙峥嵘. 溃疡性结肠炎发病机制研究进展[J]. 现代免疫学, 2019, 39(1): 77-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHMY201901015.htm
[17] 马亚南, 刘雯, 柴新梅, 等. 粪便钙卫蛋白联合CD64指数及超敏C反应蛋白在儿童细菌性肠炎诊断中的临床价值[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2023, 31(9): 691-695. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2023.09.07
[18] Cleland DA, Eranki AP. Procalcitonin[M]. Treasure Island(FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2024: 1-1.
[19] Samsudin I, Vasikaran SD. Clinical Utility and Measurement of Procalcitonin[J]. Clin Biochem Rev, 2017, 38(2): 59-68.
[20] 朱晓夏, 陈言语, 周晓俊, 等. 细菌感染与血清炎症指标间关系及其诊断价值[J]. 热带医学杂志, 2022, 22(9): 1243-1247. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDYZ202209015.htm
[21] Hou Y, Zhao W, Yang Z. Serum amyloid A(SAA)and Interleukin-6(IL-6) as the potential biomarkers for gastric cancer[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2022, 101(43): e31514.
[22] Sack GH Jr. Serum Amyloid A(SAA)Proteins[J]. Subcell Biochem, 2020, 94: 421-436.
[23] Chen R, Chen Q, Zheng J, et al. Serum amyloid protein A in inflammatory bowel disease: from bench to bedside[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2023, 9(1): 154.
-




 下载:
下载: