Meta analysis of the efficacy of probiotics for constipation in Parkinson's disease
-
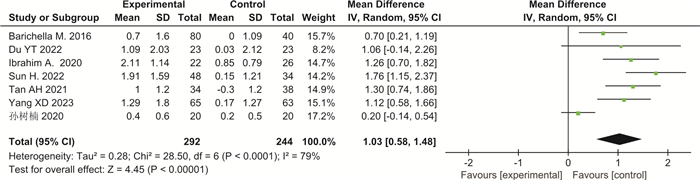
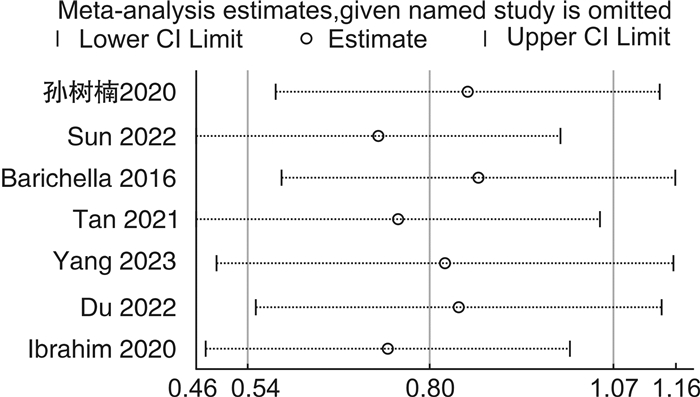
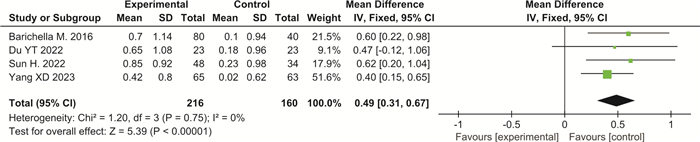
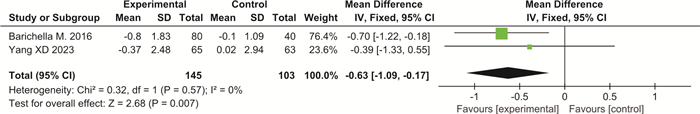
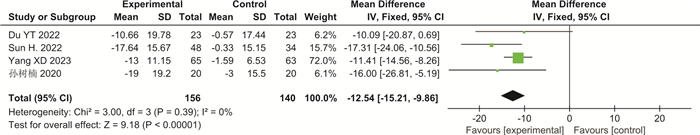
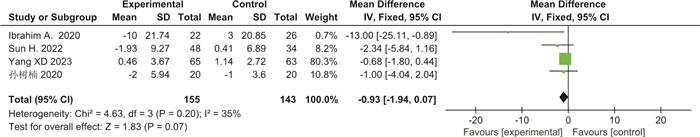
摘要: 目的 系统评价益生菌制剂治疗帕金森病(PD)相关便秘的临床疗效。方法 检索PubMed、Web of Science、Cochrane Library、Clinical Trials、Google Scholar、中国知网、维普及万方数据库,建库至2023年9月发表的PD相关便秘的随机对照试验(RCTs),通过文献筛选、评价、提取资料后,运用RevMan 5.3软件进行meta分析。结果 最终纳入7篇RCTs,共536例PD相关便秘患者。meta分析结果显示:与对照组比较,益生菌制剂可增加PD便秘患者的排便次数(SMD=1.03,95%CI:0.58~1.48,P<0.000 01,I2=79%),改善粪便性状(SMD=0.49,95%CI:0.31~0.67,P<0.000 01,I2=0),降低口服泻药使用频率(SMD=-0.63,95%CI:-1.09~-0.17,P=0.007,I2=0),提高便秘相关生活质量(SMD=-12.54,95%CI:-15.21~-9.86,P<0.000 01,I2=0),并改善PD相关焦虑抑郁评分,但对PD运动症状(UPDRS-Ⅲ)改善不明显(SMD=-0.93,95%CI:-1.94~0.07,P=0.07,I2=35%)。结论 益生菌制剂可改善PD相关便秘症状以及便秘相关生活质量,但仍需要高质量大样本RCTs进一步验证。Abstract: Objective To systematically evaluate the clinical efficacy of probiotics in the treatment of constipation in Parkinson's disease.Methods We searched PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, Clinical Trials, Google Scholar, CNKI, VIP, and WanFang database for randomized controlled trials(RCTs) of constipation in Parkinson's disease(PD) up to September 2023. After literature screening, evaluation, and data extraction, we conducted meta-analysis using RevMan 5.3 software.Results Finally, seven RCTs were included, with a total of 536 PD patients with constipation. The meta-analysis results showed that compared with the control group, probiotics significantly increased the frequency of bowel movements in PD related constipation patients(SMD=1.03, 95%CI: 0.58 to 1.48, P < 0.000 01, I2=79%), improved the stool consistency(SMD=0.49, 95%CI: 0.31 to 0.67, P < 0.000 01, I2=0), reduced the frequency of using oral laxatives(SMD=-0.63, 95%CI: -1.09 to -0.17, P=0.007, I2=0), improved the quality of life related to constipation(SMD=-12.54, 95%CI: -15.21 to -9.86, P < 0.000 01, I2=0). Probiotics also remarkably improved PD related anxiety and depression scores but did not improve PD motor symptoms(UPDRS-Ⅲ)(SMD=-0.93, 95%CI: -1.94 to 0.07, P=0.07, I2=35%).Conclusion Probiotics can alleviate symptoms of constipation in PD patients and improve the quality of life related to constipation, but further validation with high-quality and large sample size RCTs is still needed.
-
Key words:
- probiotics /
- Parkinson's disease /
- constipation /
- meta-analysis
-

-
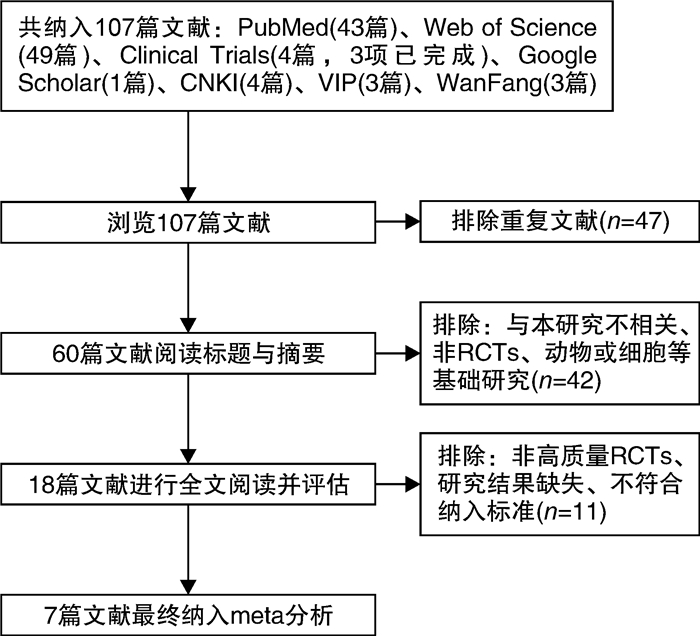
表 1 纳入RCTs研究的基本特征
纳入研究 例数 干预措施 疗程/周 观察指标 总例数 观察组 对照组 观察组 对照组 益生菌种类 益生菌含量/CFU 用法 Barichellade等[14] 120 80 40 多菌株益生菌[唾液链球菌嗜热亚种、粪肠球菌、鼠李糖乳杆菌GG、嗜酸乳杆菌、植物乳杆菌朗姆酒、副干酪乳杆菌、德氏乳杆菌保加利亚亚种和双歧杆菌(啤酒和动物乳亚种)]和益生元纤维 250×109 牛奶125 g,1次/d 安慰剂(巴氏杀菌、发酵、无纤维牛奶) 4 ①②④⑦⑪ Ibrahim等[15] 48 22 26 多菌株益生菌(乳酸杆菌和双歧杆菌) 30×109 发酵乳,3 g/次,2次/d 安慰剂(发酵乳) 8 ①②③④⑤ ⑦⑨⑩⑪ 孙树楠等[16] 40 20 20 乳双歧杆菌 - 乳酸杆菌,1袋/d - 12 ①⑥⑧⑪ Tan等[17] 72 34 38 多菌株益生菌胶囊(嗜酸乳杆菌、路氏乳杆菌、加斯里乳杆菌、鼠李糖乳杆菌、分叉双歧杆菌、长双歧杆菌、乳酸球菌、粪肠球菌) 1×1010 1次/d 安慰剂(麦芽糊精) 4 ①②⑧⑪ Sun等[11] 82 48 34 Probio-M8(动物双歧杆菌亚种乳酸Probio-M8) 30×109 Probio-M8粉2 g,1次/d 安慰剂(麦芽糊精) 12 ①②⑧⑩⑪ Du等[12] 46 23 23 多菌株益生菌胶囊(地衣芽孢杆菌、嗜酸乳杆菌、长双歧杆菌、粪肠球菌) 2.5×109地衣芽孢杆菌);1×107 (余菌株) 2粒/次,3次/d (地衣芽孢杆菌);4粒/次,2次/d (余菌株) - 12 ①②③⑥⑧ ⑩⑪ Yang等[13] 128 65 63 益生菌发酵乳(干酪乳杆菌) 1×1010 发酵乳100 mL,1次/d 安慰剂(无益生菌酸奶) 12 ①②⑦⑧ ⑩⑪ 注:①排便频率;②粪便性状;③排便费力;④排便不尽感;⑤肛门直肠堵塞感;⑥便秘症状总体评价;⑦泻药使用频率;⑧PAC-QOL;⑨GTT;⑩菌群改变;⑪ PD其他症状。 -
[1] GBD 2016 Neurology Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2019, 18(5): 459-480. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30499-X
[2] Qi S, Yin P, Wang L, et al. Prevalence of Parkinson's Disease: A Community-Based Study in China[J]. Mov Disord, 2021, 36(12): 2940-2944. doi: 10.1002/mds.28762
[3] Bloem BR, Okun MS, Klein C. Parkinson's disease[J]. Lancet, 2021, 397(10291): 2284-2303. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00218-X
[4] Claudino Dos Santos JC, Lima M, Brito G, et al. Role of enteric glia and microbiota-gut-brain axis in parkinson disease pathogenesis[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2023, 84: 101812. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101812
[5] Metta V, Leta V, Mrudula KR, et al. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson's disease: molecular pathology and implications of gut microbiome, probiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation[J]. J Neurol, 2022, 269(3): 1154-1163. doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10567-w
[6] 李晓青, 王含, 孙晓红, 等. 帕金森病消化道症状特征分析[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2021, 54(9): 928-934. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn113694-20210125-00067
[7] Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, et al. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson's disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases[J]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 1992, 55(3): 181-184. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.55.3.181
[8] Berg D, Postuma RB, Adler CH, et al. MDS research criteria for prodromal Parkinson's disease[J]. Mov Disord, 2015, 30(12): 1600-1609. doi: 10.1002/mds.26431
[9] Longstreth GF, Thompson WG, Chey WD, et al. Functional bowel disorders[J]. Gastroenterology, 2006, 130(5): 1480-1491. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.11.061
[10] 方秀才, 侯晓华译. 罗马Ⅳ: 功能性胃肠病肠-脑互动异常[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 1134.
[11] Sun H, Zhao F, Liu Y, et al. Probiotics synergized with conventional regimen in managing Parkinson's disease[J]. NPJ Parkinsons Dis, 2022, 8(1): 62. doi: 10.1038/s41531-022-00327-6
[12] Du Y, Li Y, Xu X, et al. Probiotics for constipation and gut microbiota in Parkinson's disease[J]. Parkinsonism Relat Disord, 2022, 103: 92-97. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2022.08.022
[13] Yang XD, He XQ, Xu SQ, et al. Effect of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei strain Shirota supplementation on clinical responses and gut microbiome in Parkinson's disease. [J]Food Funct, 2023, 14(15): 6828-6839. doi: 10.1039/D3FO00728F
[14] Barichella M, Pacchetti C, Bolliri C, et al. Probiotics and prebiotic fiber for constipation associated with Parkinson disease: An RCT[J]. Neurology, 2016, 87(12): 1274-1280. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003127
[15] Ibrahim A, Ali R, Manaf M, et al. Multi-strain probiotics(Hexbio)containing MCP BCMC strains improved constipation and gut motility in Parkinson's disease: A randomised controlled trial[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(12): e0244680. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244680
[16] 孙树楠, 李芳. 乳双歧杆菌对改善帕金森病患者的焦虑和抑郁症状的作用[J]. 沈阳药科大学学报, 2020, 37(4): 344-349. doi: 10.14066/j.cnki.cn21-1349/r.2020.04.009
[17] Tan AH, Lim SY, Chong KK, et al. Probiotics for Constipation in Parkinson Disease: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study[J]. Neurology, 2021, 96(5): e772-e782.
[18] Zhou Y, Chen Y, He H, et al. The role of the indoles in microbiota-gut-brain axis and potential therapeutic targets: A focus on human neurological and neuropsychiatric diseases[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2023, 239: 109690. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2023.109690
[19] Dimidi E, Christodoulides S, Scott SM, et al. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics and the Gastrointestinal Microbiota on Gut Motility and Constipation[J]. Adv Nutr, 2017, 8(3): 484-494. doi: 10.3945/an.116.014407
[20] Ma T, Xue X, Tian H, et al. Effect of the gut microbiota and their metabolites on postoperative intestinal motility and its underlying mechanisms[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21(1): 349. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04215-2
[21] Giuliani S, Santicioli P, Tramontana M, et al. Peptide N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine(FMLP)activates capsaicin-sensitive primary afferent nerves in guinea-pig atria and urinary bladder[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 1991, 102(3): 730-734. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12241.x
[22] Gill PA, van Zelm MC, Muir JG, et al. Review article: short chain fatty acids as potential therapeutic agents in human gastrointestinal and inflammatory disorders[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2018, 48(1): 15-34. doi: 10.1111/apt.14689
[23] Segers A, Desmet L, Thijs T, et al. The circadian clock regulates the diurnal levels of microbial short-chain fatty acids and their rhythmic effects on colon contractility in mice[J]. Acta Physiol(Oxf), 2019, 225(3): e13193. doi: 10.1111/apha.13193
[24] Góralczyk-Bińkowska A, Szmajda-Krygier D, Kozłowska E. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Psychiatric Disorders[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(19): 11245. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911245
[25] 肖岑昕, 黄恒青, 柯晓, 等. 粪菌移植在功能性便秘中的应用进展[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2022, 30(3): 239-243. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2022.03.13
[26] 刘友迎, 龚国忠, 代莉, 等. 功能性便秘患者肠道菌群与病情的关系分析[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2021, 29(8): 580-583. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2021.08.11
-




 下载:
下载: