Effect of Tongxie Anchang Decoction on visceral hypersensitivity and gut microbiota in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome mice
-
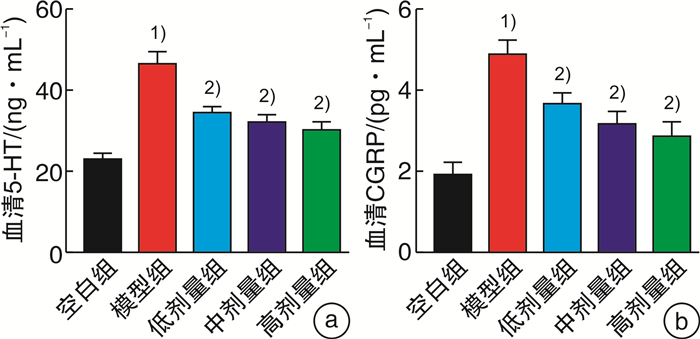
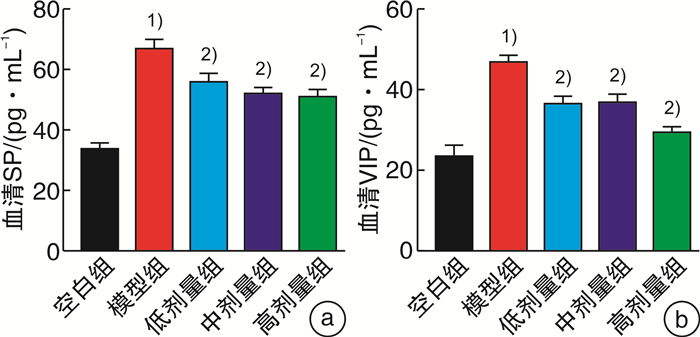
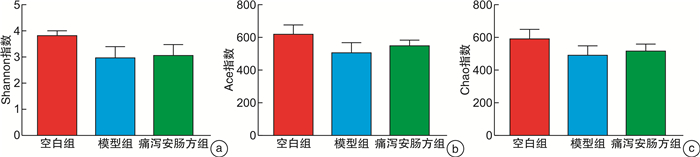
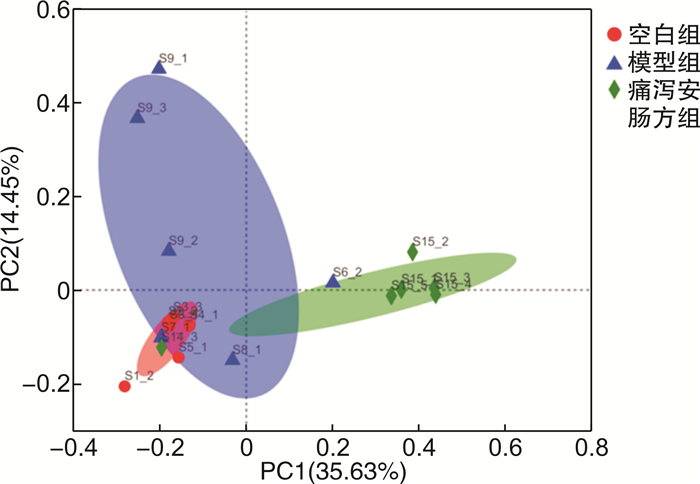
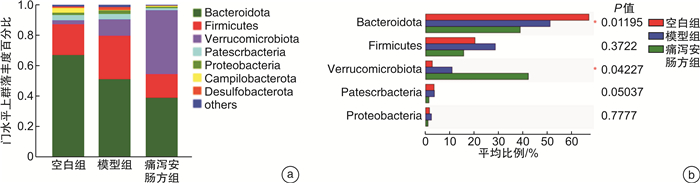
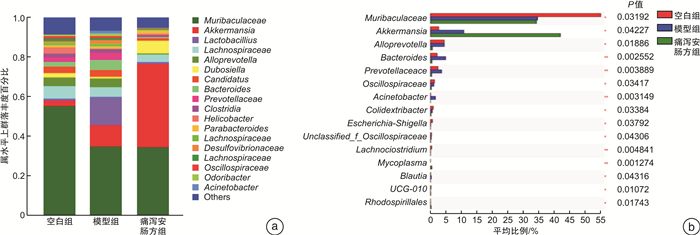
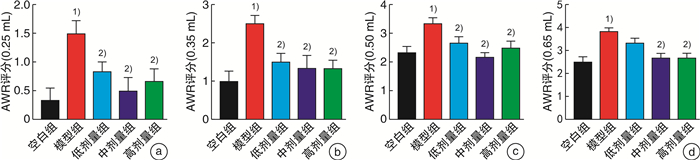
摘要: 目的 观察痛泻安肠方对腹泻型肠易激综合征(IBS-D)肝郁脾虚证小鼠内脏高敏及肠道菌群的影响。方法 30只SPF级雄性C57BL/6小鼠用随机数字表法分为空白组、模型组及痛泻安肠方低、中、高剂量组,每组各6只。除空白组小鼠外,其余各组小鼠均使用束缚应激2周联合番泻叶灌胃1周复制IBS-D肝郁脾虚证小鼠模型。造模成功后分别给予痛泻安肠方相应剂量灌胃,连续2周。比较各组小鼠腹部撤退反射(AWR)评分;甲苯胺蓝染色观察小鼠结肠肥大细胞数量;ELISA检测小鼠血清5-羟色胺(5-HT)、降钙素基因相关肽(CGRP)、血管活性肠肽(VIP)、神经肽Y(NPY)和P物质(SP)表达水平;16S rRNA高通量测序检测各组小鼠肠道菌群种类及丰富度的变化。结果 与IBS-D肝郁脾虚证模型组小鼠比较,痛泻安肠方各剂量组小鼠AWR评分呈不同程度的降低;结肠黏膜肥大细胞浸润减少;血清5-HT、CGRP、VIP、SP水平降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。16S rRNA测序分析发现,痛泻安肠方干预增加了IBS-D肝郁脾虚证小鼠肠道菌群的多样性及丰富度,增加了疣微菌门和阿克曼菌属的丰富度。结论 痛泻安肠方可以改善肝郁脾虚证IBS-D小鼠的内脏高敏感,调节肠道菌群失调。Abstract: Objective To observe the effect of Tongxie Anchang Decoction on visceral hypersensitivity and intestinal microecology in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome(IBS-D) mice.Methods Thirty SPF-grade male C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into blank group, model group, and Tongxie Anchang decoction low, medium and high dose groups, with 6 mice in each group. Except for the blank group, all the mice in each group were restrained and stressed for two weeks and gavaged with senna leaves for one week to replicate the IBS-D mouse model with liver depression and spleen deficiency. After successful modeling, each group was given the corresponding dose of Tongxie Anchang decoction by gavage for two weeks. The expression levels of serum 5-hydroxytryptamine(5-HT), calcitonin gene-related peptide(CGRP), vasoactive intestinal peptide(VIP), neuropeptide Y(NPY) and substance P(SP) were measured by ELISA. 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing was used to detect changes in the species and abundance of gut microbiota in each group of mice.Results Compared with the mice in the IBS-D group with liver depression and spleen deficiency evidence group, the AWR scores of the mice in each dose group of the Tongxie Anchang Decoction showed different degrees of reduction; mast cell infiltration in the colonic mucosa was reduced; serum 5-HT, CGRP, VIP and SP were all reduced to different degrees, and the differences were statistically significant(P < 0.05). 16S rRNA sequencing analysis revealed that the intervention of the Tongxie Anchang Decoction increased the diversity and abundance of gut microbiota in IBS-D mice with liver depression and spleen deficiency evidence, and increased the abundance of the Verrucomicrobiota and Akkermansia.Conclusion Tongxie Anchang Decoction can improve visceral hypersensitivity and alleviate gut microbiota dysbiosis in IBS-D mice with liver-depression and spleen-deficiency evidence.
-

-
表 1 粪便Bristol评分
评分/分 粪便Bristol分级标准 1 分离的硬团,如坚果,不容易通过 2 腊肠状,成块的,粪便表面凹凸 3 香肠状,表面干裂有缝 4 腊肠状或蛇状,光滑而柔软 5 软的团块,边缘清楚,容易通过 6 绒状便,边缘不清,或如泥浆状 7 水样粪,无固状物 表 2 AWR评分标准
评分/分 AWR评分标准 0 结直肠扩张刺激时小鼠情绪基本稳定 1 给予刺激时变得开始不稳定,偶尔扭动头部 2 给予刺激时腹背部肌肉轻微收缩但腹部未抬离地面 3 刺激时腹背部肌肉较强烈收缩并出现腹部抬离地面的情况 4 腹部肌肉强烈收缩,腹部呈弓形,并把腹部、会阴部抬离地面 表 3 各组小鼠Bristol粪便性状评分比较
X±S 组别 数量/只 粪便性状/分 空白组 6 4.00±0.63 模型组 6 5.00±0.631) 低剂量组 6 4.67±0.52 中剂量组 6 4.00±0.632) 高剂量组 6 4.39±0.642) 与空白组相比,1)P < 0.05;与模型组相比,2)P < 0.05。 -
[1] Bonetto S, Fagoonee S, Battaglia E, et al. Recent advances in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome[J]. Pol Arch Intern Med, 2021, 131(8): 709-715.
[2] Goodoory VC, Houghton LA, Black CJ, et al. Characteristics of, and natural history among, individuals with Rome IV functional bowel disorders[J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2022, 34(5): 1-11.
[3] Xiao L, Liu Q, Luo M, et al. Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites in Irritable Bowel Syndrome[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2021, 11(9): 1-11.
[4] Camilleri M. Diagnosis and Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Review[J]. JAMA, 2021, 325(9): 865-877. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.22532
[5] Ancona A, Petito C, Iavarone I, et al. The gut-brain axis in irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2021, 53(3): 298-305. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2020.11.026
[6] Chen Y, Chu F, Lin J, et al. The mechanisms of action of WeiChang'An Pill(WCAP)treat diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome(IBS-D)using network pharmacology approach and in vivo studies[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2021, 275(7): 1-11.
[7] Simrén M, Tornblom H, Palsson OS, et al. Visceral hypersensitivity is associated with GI symptom severity in functional GI disorders: consistent findings from five different patient cohorts[J]. Gut, 2018, 67(2): 255-262. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312361
[8] Wang C, Fang X. Inflammation and Overlap of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Functional Dyspepsia[J]. J Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2021, 27(2): 153-164. doi: 10.5056/jnm20175
[9] Gu X, Song LJ, Li LX, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum Causes Microbial Dysbiosis and Exacerbates Visceral Hypersensitivity in a Colonization-Independent Manner[J]. Front Microbiol, 2020, 11(6): 1-15.
[10] 王喜红, 薛晓轩, 裴文婧, 等. 痛泻安肠方治疗肝郁脾虚证腹泻型肠易激综合征的随机对照临床研究[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2019, 27(12): 887-892. http://zxpw.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD2/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=b7c4b45e-6c5e-4eba-811e-38dff6af6250
[11] 芮晓薇, 郑思慧, 赵方敏, 等. 痛泻要方对肝郁脾虚证IBS-D大鼠SCF/c-Kit信号系统的影响[J]. 浙江中医杂志, 2021, 56(7): 472-474. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0411-8421.2021.07.002
[12] Simren M, Tornblom H, Palsson OS, et al. Cumulative Effects of Psychologic Distress, Visceral Hypersensitivity, and Abnormal Transit on Patient-reported Outcomes in Irritable Bowel Syndrome[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 157(2): 391-402. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.04.019
[13] 赵艳钧, 杨勤. 肠易激综合征内脏高敏感的调控机制研究进展[J]. 现代消化及介入诊疗, 2020, 25(3): 407-410. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2159.2020.03.034
[14] Uranga JA, Martínez V, Abalo R. Mast Cell Regulation and Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Effects of Food Components with Potential Nutraceutical Use[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(18): 1-30.
[15] 柯少雄, 杨长青, 陈俊杰, 等. 肠易激综合征患者肠道菌群特征及其与肠黏膜肥大细胞活化的关系[J]. 山东医药, 2020, 60(2): 31-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYY202002008.htm
[16] Zhang L, Song J, Hou X. Mast Cells and Irritable Bowel Syndrome: From the Bench to the Bedside[J]. J Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2016, 22(2): 181-192. doi: 10.5056/jnm15137
[17] 任杰, 樊欣钰, 范志巍, 等. 肠康方对腹泻型肠易激综合征模型大鼠肥大细胞的影响[J]. 中医药信息, 2020, 37(3): 35-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXN202003008.htm
[18] 臧希, 窦志芳. 脑肠肽与肠易激综合征相关性研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2019, 21(12): 110-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LZXB201912033.htm
[19] 苏海霞, 付兆媛, 高永泽, 等. 5-羟色胺与腹泻型肠易激综合征相关性及中医药调控研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 22(11): 1-9.
[20] Sun H, Ma Y, An S, et al. Altered gene expression signatures by calcitonin gene-related peptide promoted mast cell activity in the colon of stress-induced visceral hyperalgesia mice[J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2021, 33(6): 1-12.
[21] 杨焱麟, 陈敏, 周彦妮, 等. P物质与肝郁脾虚型腹泻型肠易激综合征关系及中医药调控的研究进展[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2021, 39(9): 82-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYHS202109022.htm
[22] 张艳霞, 赵蓉, 吕双然, 等. 腹泻型肠易激综合征中医证候分布与VIP、SP、5-HT动态变化的相关性分析[J]. 河北中医药学报, 2022, 37(1): 17-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZYX202201005.htm
[23] 顾浩然, 徐陆周. 白石温脾汤治疗腹泻型肠易激综合征30例临床观察[J]. 湖南中医杂志, 2022, 38(3): 13-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNZO202203004.htm
[24] 杜光信, 冯群虎, 胡建文, 等. 半夏泻心汤加减治疗肠易激综合征患者腹痛的疗效及对血清5-HT、VIP、SP水平的影响[J]. 中国肛肠病杂志, 2022, 42(8): 44-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCBZ202208015.htm
[25] 王科凯, 杨焱麟, 周彦妮, 等. 痛泻要方拆方对腹泻型肠易激综合征大鼠脑肠肽的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 22(9): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QKYX202305008.htm
[26] 戴莉莉, 姜正艳, 孙志广. 肠易激综合征与肠道菌群的相关研究进展[J]. 中国临床研究, 2021, 34(9): 1261-1264. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCK202109025.htm
[27] Sciavilla P, Strati F, Di Paola M, et al. Gut microbiota profiles and characterization of cultivable fungal isolates in IBS patients[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2021, 105(8): 3277-3288.
[28] Peng Y, Zhang S, Liu Z, et al. Gut microbiota and Chinese medicine syndrome: altered fecal microbiotas in spleen(Pi)-deficient patients[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2020, 40(1): 137-143.
[29] Mei L, Zhou J, Su Y, et al. Gut microbiota composition and functional prediction in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome[J]. BMC astroenterol, 2021, 21(1): 1-12.
[30] Zhou XY, Li M, Li X, et al. Visceral hypersensitive rats share common dysbiosis features with irritable bowel syndrome patients[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22(22): 5211-5227.
[31] De Palma G, Lynch MD, Lu J, et al. Transplantation of fecal microbiota from patients with irritable bowel syndrome alters gut function and behavior in recipient mice[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2017, 9(379): 1-14.
[32] Cani PD, Depommier C, Derrien M, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila: paradigm for next-generation beneficial microorganisms[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 19(10): 625-637.
-




 下载:
下载: