Study on the role of circularCUX1 in the mechanism of drug resistance mediated by programmed death factor 1 ligand in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
-
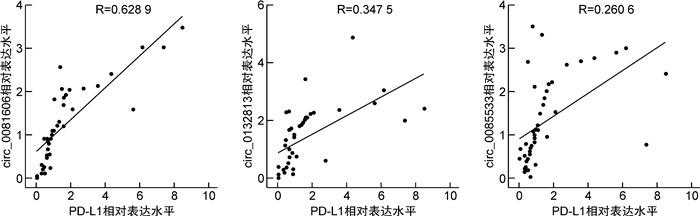
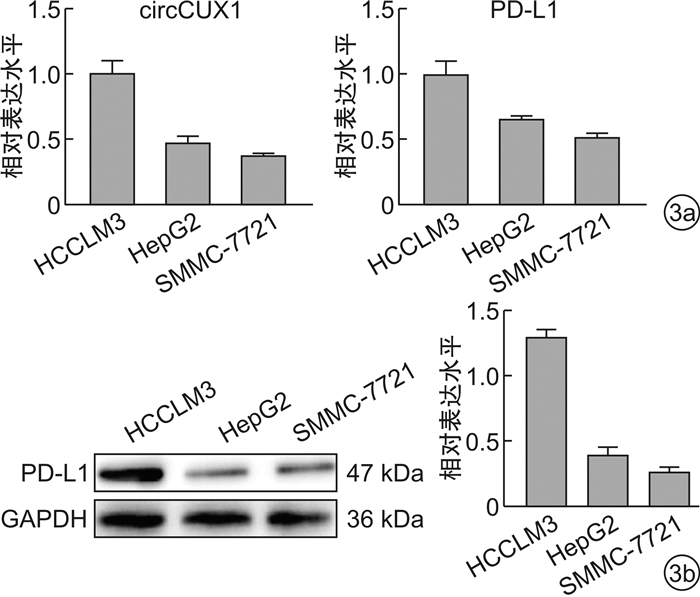
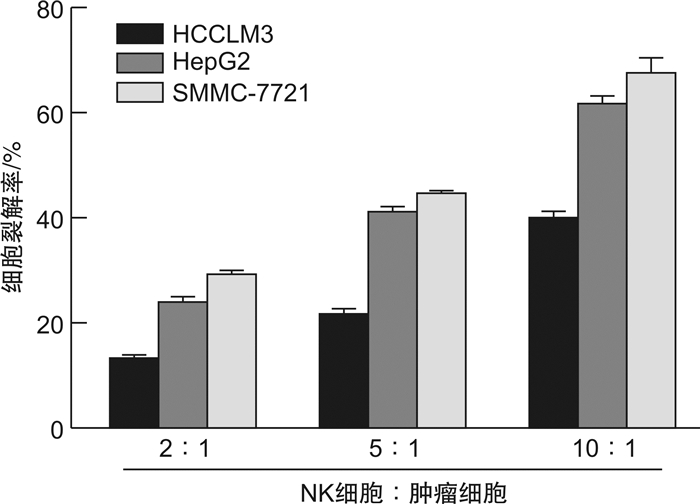
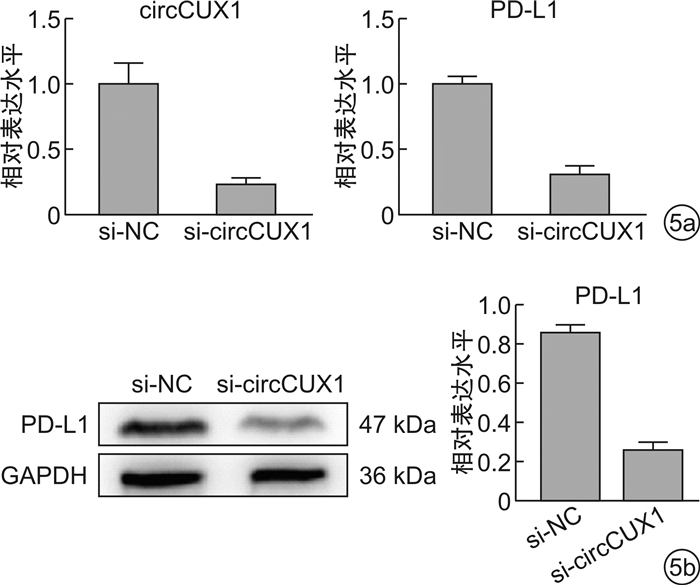
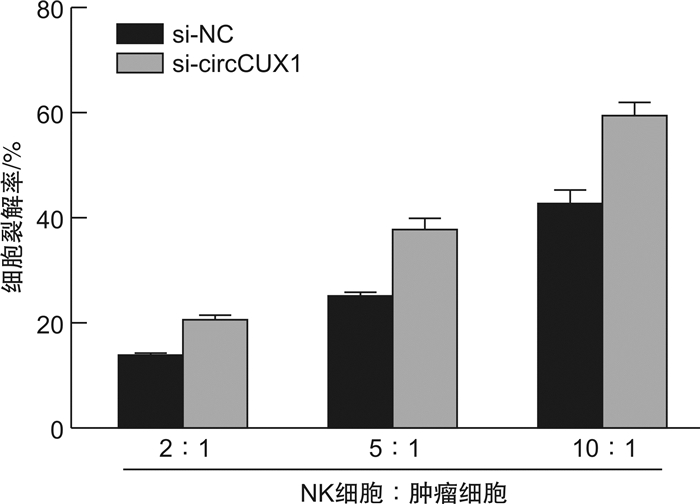
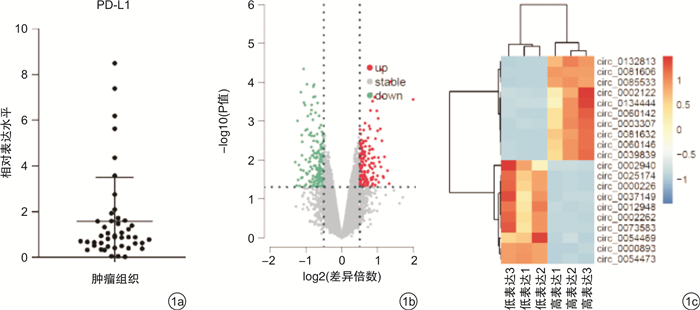
摘要: 目的 探究circularCUX1(circCUX1)对肝癌细胞免疫逃逸的作用及其相关机制。方法 收集45例肝癌切除肿瘤组织,qRT-PCR检测肿瘤组织程序性死亡因子1配体(PD-L1)的表达水平,circRNA-seq分析PD-L1高表达和低表达肿瘤组织中circRNA的差异表达,并比较circCUX1与PD-L1表达的相关性。在细胞实验中采用qRT-PCR和Western blot检测HCCLM3、HepG2、SMMC-7721细胞circCUX1和PD-L1的表达水平,通过NK细胞毒性实验检测对NK细胞的敏感性。将HCCLM3细胞分为si-NC组(转染si-NC)和si-circCUX1组(转染si-circCUX1),检测两组细胞circCUX1和PD-L1的表达水平以及对NK细胞的敏感性。结果 在肝癌患者肿瘤组织中,与PD-L1低表达肿瘤组织比较,PD-L1高表达肿瘤组织有282个circRNA表达上调,307个circRNA表达下调,其中circCUX1与PD-L1的表达水平呈正相关(R=0.628 9,P< 0.05)。与HepG2细胞和SMMC-7721细胞比较,HCCLM3细胞中circCUX1的表达水平升高(P< 0.05),PD-L1 mRNA和蛋白的表达水平升高(P< 0.05),其对NK细胞的敏感性降低(P< 0.05)。与si-NC组比较,circCUX1组circCUX1的表达水平降低(P< 0.05),PD-L1 mRNA和蛋白的表达水平降低(P< 0.05),其对NK细胞的敏感性增加(P< 0.05)。结论 在肝癌组织中circCUX1与PD-L1的表达呈正相关,circCUX1通过影响PD-L1表达介导肝癌细胞的免疫逃逸。
-
关键词:
- 肝细胞癌 /
- 环状RNA /
- 程序性死亡因子1配体 /
- 免疫逃逸 /
- 耐药
Abstract: Objective To explore the effect of circularCUX1(circCUX1) on the immune escape of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and its related mechanism.Methods Forty-five cases of hepatocellular carcinoma resected tumor tissues were collected, and the expression level of programmed death factor 1 ligand (PD-L1) in tumor tissues was detected by qRT-PCR. circRNA-seq was used to analyze the circRNA expression difference between the high and low expression of PD-L1, and the correlation between circCUX1 and PD-L1 expression was compared. In cell experiments, the expression levels of circCUX1 and PD-L1 in HCCLM3, HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cells were detected by qRT-PCR and Western blot, and the sensitivity to NK cells was detected by NK cell toxicity assay. HCCLM3 cells were divided into si-NC group(transfected with si-NC) and si-circCUX1 group(transfected with si-circCUX1), and the expression levels of circCUX1 and PD-L1 and their sensitivity to NK cells were detected.Results In tumor tissues of hepatocellular carcinoma patients, compared with tumor tissues with low PD-L1 expression, 282 circRNA with high PD-L1 expression were up-regulated and 307 circRNA were down-regulated, among which circCUX1 was positively correlated with PD-L1 expression level(R=0.628 9,P< 0.05). Compared with HepG2 cells and SMMC-7721 cells, the expression level of circCUX1 and the mRNA and protein expression of PD-L1 in HCCLM3 cells increased(P< 0.05), the sensitivity of HCCLM3 cells to NK cells decreased(P< 0.05). Compared with si-NC group, circCUX1 group had lower circCUX1 expression(P< 0.05), lower PD-L1 mRNA and protein expression(P< 0.05), and higher sensitivity to NK cells(P< 0.05).Conclusion circCUX1 is positively correlated with the expression of PD-L1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells, and circCUX1 mediates the immune escape of HCC cells by affecting the expression of PD-L1. -

-
[1] Arnold M, Abnet CC, Neale RE, et al. Global Burden of 5 Major Types of Gastrointestinal Cancer[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 159(1): 335-349. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.068
[2] Frager SZ, Schwartz JM. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology, screening, and assessment of hepatic reserve[J]. Curr Oncol, 2020, 27(Suppl 3): S138-S143.
[3] Lovet JM, Castet F, Heikenwalder M, et al. Immunotherapies for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2022, 19(3): 151-172. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00573-2
[4] Crouchet E, Schuster C, Baumert TF. Liver cell circuits and therapeutic discovery for advanced liver disease and cancer[J]. C R Biol, 2021, 344(3): 233-248.
[5] Man S, Luo C, Yan M, et al. Treatment for liver cancer: From sorafenib to natural products[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2021, 224: 113690. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113690
[6] Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, et al. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2019, 20(11): 675-691. doi: 10.1038/s41576-019-0158-7
[7] Chen CK, Cheng R, Demeter J, et al. Structured elements drive extensive circular RNA translation[J]. Mol Cell, 2021, 81(20): 4300-4318. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.07.042
[8] Zhu G, Chang X, Kang Y, et al. CircRNA: A novel potential strategy to treat thyroid cancer(Review)[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2021, 48(5): 201. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.5034
[9] Yang Y, Ding L, Li Y, et al. Hsa_circ_0039411 promotes tumorigenesis and progression of papillary thyroid cancer by miR-1179/ABCA9 and miR-1205/MTA1 signaling pathways[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2020, 235(2): 1321-1329. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29048
[10] Sun H, Xi P, Sun Z, et al. Circ-SFMBT2 promotes the proliferation of gastric cancer cells through sponging miR-182-5p to enhance CREB1 expression[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2018, 10: 5725-5734. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S172592
[11] Han D, Li J, Wang H, et al. Circular RNA circMTO1 acts as the sponge of microRNA-9 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma progression[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66(4): 1151-1164. doi: 10.1002/hep.29270
[12] Wu P, Fang X, Liu Y, et al. N6-methyladenosine modification of circCUX1 confers radioresistance of hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma through caspase1 pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(4): 298. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03558-2
[13] Wang Y, Niu Q, Dai J, et al. CircCUX1 promotes neuroblastoma progression and glycolysis by regulating the miR-338-3p/PHF20 axis[J]. Gen Physiol Biophys, 2021, 40(1): 17-29.
[14] Yi M, Xu L, Jiao Y, et al. The role of cancer-derived microRNAs in cancer immune escape[J]. Hematol Oncol, 2020, 13(1): 25. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00848-8
[15] Dermani FK, Samadi P, Rahmani G, et al. PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint: Potential target for cancer therapy[J]. Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(2): 1313-1325. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27172
[16] Xing R, Gao J, Cui Q, et al. Strategies to Improve the Antitumor Effect of Immunotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 26(12): 783236.
[17] Anwanwan D, Singh SK, Singh S, et al. Challenges in liver cancer and possible treatment approaches[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2020, 1873(1): 188314. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.188314
[18] Varley R, Tarazi M, Dave M, et al. Liver Transplantation for Non-Resectable Liver Metastases from Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis[J]. World J Surg, 2021, 45(11): 3404-3413. doi: 10.1007/s00268-021-06248-4
[19] Rincon-Riveros A, Morales D, Rodríguez JA, et al. Bioinformatic Tools for the Analysis and Prediction of ncRNA Interactions[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(21): 11397. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111397
[20] Patop IL, Wust S, Kadener S. Past, present, and future of circRNAs[J]. EMBO J, 2019, 38(16): e100836.
[21] Zhang X, Xu Y, Ma L, et al. Essential roles of exosome and circRNA_101093 on ferroptosis desensitization in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Cancer Commun(Lond), 2022, 42(4): 287-313.
[22] Yang H, Li X, Meng Q, et al. CircPTK2(hsa_circ_0005273) as a novel therapeutic target for metastatic colorectal cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2020, 19(1): 13. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-1139-3
[23] Yu X, Xiao W, Song H, et al. CircRNA_100876 sponges miR-136 to promote proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer by upregulating MIEN1 expression[J]. Gene, 2020, 748: 144678. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144678
[24] Huang G, Liang M, Liu H, et al. CircRNA hsa_circRNA_104348 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through modulating miR-187-3p/RTKN2 axis and activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(12): 1065. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03276-1
[25] Zhang X, Zhang J, Liu Q, et al. Circ-CUX1 Accelerates the Progression of Neuroblastoma via miR-16-5p/DMRT2 Axis[J]. Neurochem Res, 2020, 45(12): 2840-2855. doi: 10.1007/s11064-020-03132-w
[26] Li H, Yang F, Hu A, et al. Therapeutic targeting of circ-CUX1/EWSR1/MAZ axis inhibits glycolysis and neuroblastoma progression[J]. EMBO Mol Med, 2019, 11(12): e10835.
[27] Pathania AS, Prathipati P, Challagundla KB. New insights into exosome mediated tumor-immune escape: Clinical perspectives and therapeutic strategies[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2021, 1876(2): 188624. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188624
[28] Sarkar T, Dhar S, Sa G. Tumor-infiltrating T-regulatory cells adapt to altered metabolism to promote tumor-immune escape[J]. Curr Res Immunol, 2021, 2: 132-141. doi: 10.1016/j.crimmu.2021.08.002
[29] Dermani FK, Samadi P, Rahmani G, et al. PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint: Potential target for cancer therapy[J]. Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(2): 1313-1325. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27172
[30] Wang J, Zhao X, Wang Y, et al. circRNA-002178 act as a ceRNA to promote PDL1/PD1 expression in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(1): 32. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2230-9
-




 下载:
下载: