Correlation between ASPP2 mRNA expression and early postoperative recurrence risk in patients with liver cancer
-
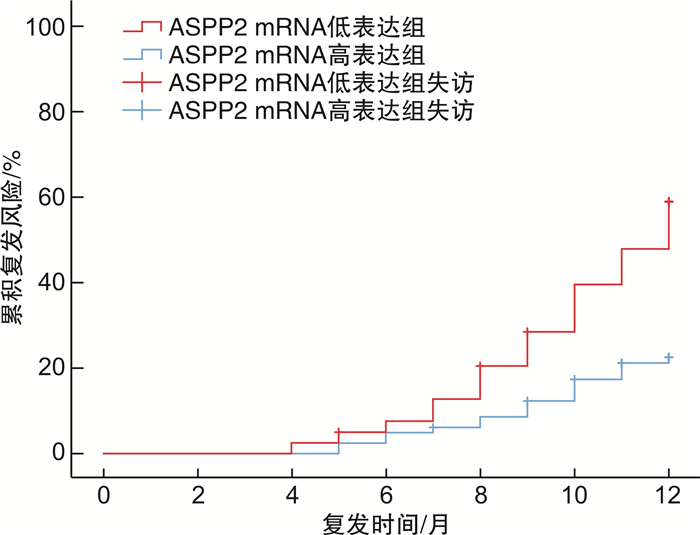
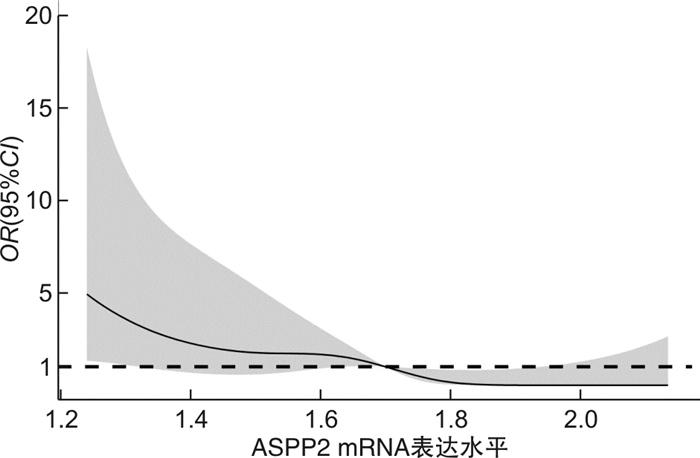
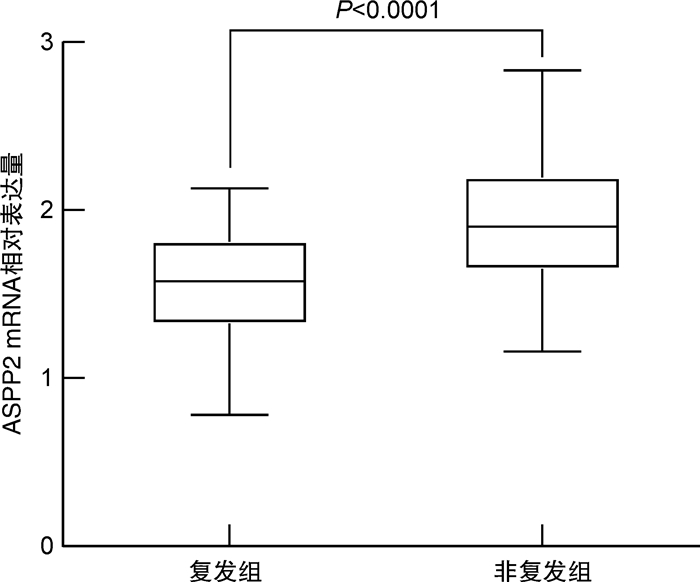
摘要: 目的 探讨p53凋亡激活蛋白2(ASPP2)mRNA表达水平与肝细胞癌(HCC)患者术后早期复发风险的相关性。方法 纳入2019年1月—2020年7月接受肝切除术的HCC患者122例,收集所有患者的临床实验室资料,采用荧光定量PCR法检测肝癌组织中ASPP2 mRNA相对表达量;随访1年,记录所有患者的复发情况,绘制生存分析曲线,分析不同ASPP2 mRNA表达水平的HCC患者术后复发风险;用多因素Cox回归分析影响HCC患者术后复发的危险因素。结果 截止2021年7月31日,共有40例患者出现复发,复发率为32.79%,据此分为复发组和非复发组,对比两组临床资料显示,复发组AFP>400 ng/mL比例、肝硬化比例、肿瘤低分化比例、白蛋白水平 < 35 g/L比例高于未复发组,ASPP2 mRNA相对表达量低于未复发组,差异有统计学意义(P< 0.05);以ASPP2表达中位数为界值,绘制生存分析曲线,显示ASPP2 mRNA低表达组患者术后复发风险明显高于ASPP2 mRNA高表达组(χ2=5.662,P=0.017);多因素Cox回归分析显示,AFP>400 ng/mL(HR=14.283)、肿瘤低分化(HR=13.269)、白蛋白水平 < 35 g/L(HR=11.279)是导致HCC术后复发的独立危险因素(P< 0.05),ASPP2 mRNA相对表达量(HR=0.020)是导致HCC术后复发的独立保护性因素(P< 0.05);限制性立方条样图显示,ASPP2 mRNA表达水平与HCC患者的早期复发风险呈显著线性关系(P>0.05)。结论 AFP>400 ng/mL、肿瘤低分化、白蛋白 < 35 g/L为HCC患者肝切除术后肿瘤复发风险的独立危险因素,ASPP2 mRNA低表达患者具有更高的术后复发风险。Abstract: Objective To investigate the correlation between the mRNA expression level of p53 apoptosis stimulating proteins of p53 (ASPP2) and the risk of early postoperative recurrence in patients with liver cancer.Methods A total of 122 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who underwent hepatectomy in our hospital from January 2019 to July 2020 were included. The clinical laboratory data of all patients were collected, and the relative expression of ASPP2 mRNA in liver cancer tissue was detected by fluorescence quantitative PCR. expression. All patients were followed up for 1 year. The recurrence of all patients was recorded, and the survival analysis curve was drawn to analyze the postoperative recurrence risk of HCC patients with different ASPP2 mRNA expression levels. Multivariate Cox regression was used to analyze the risk factors of postoperative recurrence in HCC patients.Results As of July 31, 2021, a total of 40 patients had a recurrence, and the recurrence rate was 32.79%. According to this, they were divided into a recurrence group and a non-recurrence group. A comparison of clinical data between the two groups showed that the proportion of AFP>400 ng/mL, the proportion of liver cirrhosis, the proportion of poorly differentiated tumors, and the proportion of albumin level < 35 g/L in the recurrence group were higher than those in the non-recurrence group, and the relative expression of ASPP2 mRNA was lower than that in the non-recurrence group. The difference was statistically significant (P< 0.05). By taking the median expression of ASPP2 as the cut-off value, the survival analysis curve showed that the risk of postoperative recurrence in patients with low ASPP2 mRNA expression was significantly higher than that in the high ASPP2 mRNA expression group (χ2=5.662,P=0.017); multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that AFP>400 ng/mL (HR=14.283), poorly differentiated tumor (HR=13.269), and albumin level < 35 g/L (HR=11.279) were independent risk factors for postoperative recurrence of HCC (P< 0.05). ASPP2 The relative mRNA expression (HR=0.020) was an independent protective factor leading to postoperative recurrence of HCC (P< 0.05). The restricted cubic bar plot showed that the expression level of ASPP2 mRNA was significantly linearly related to the risk of early recurrence in HCC patients (P< 0.05).Conclusion AFP>400 ng/mL, poorly differentiated tumor and albumin < 35 g/L are independent risk factors for the risk of tumor recurrence after hepatectomy in HCC patients, and patients with low ASPP2 mRNA expression have a higher risk of postoperative recurrence.
-
Key words:
- apoptosis stimulating proteins of p53 /
- hepatocellular carcinoma /
- surgery /
- prognosis /
- recurrence
-

-
表 1 两组患者临床资料比较
例,X±S 临床资料 复发组(n=40) 未复发组(n=82) P 男/女 25/15 55/27 0.618 年龄/岁 51.09±6.88 51.35±8.15 0.862 BMI 22.31±2.44 22.43±2.56 0.806 表 2 两组患者肿瘤相关特征资料比较
例,X±S 临床资料 复发组(n=40) 未复发组(n=82) P TNM分期 0.891 Ⅰ 6 14 Ⅱ 24 41 Ⅲ 10 27 肝硬化 0.029 是 24 32 否 16 50 AFP/(ng·mL-1) 0.028 ≤400 13 44 >400 27 38 Child-Pugh分级 1.000 A 20 41 B 20 41 肿瘤直径/cm 3.34±1.27 3.36±1.33 0.937 癌结节数目/个 0.647 < 3 28 54 ≥3 12 28 包膜完整 0.883 是 23 46 否 17 36 手术切缘宽度/cm 0.904 ≤1 21 44 >1 19 38 白蛋白水平/(g·L-1) 0.015 < 35 25 32 ≥35 15 50 病理分化程度 0.007 低分化 25 30 中高分化 15 52 表 3 相关因素赋值表
相关变量 序号 赋值 复发 Y 是=1,否=0 肝硬化 X1 是=1,否=0 AFP水平 X2 AFP>400 ng/mL=1, AFP≤400 ng/mL=0 白蛋白水平 X3 <35 g/L=1,≥35 g/L=0 低分化 X4 是=1,否=0 ASPP2相对表达量 X5 连续变量 表 4 HCC患者术后复发的多因素Cox回归分析
相关变量 β SE Wald χ2 P HR 95%CI 下限 上限 AFP>400 ng/mL 2.659 1.064 6.246 0.012 14.283 1.775 114.931 白蛋白<35 g/L 2.423 0.947 6.540 0.011 11.279 1.761 72.238 低分化 2.585 0.950 7.408 0.006 13.269 2.062 85.380 ASPP2相对表达量 -3.889 0.804 23.386 <0.001 0.020 0.004 0.099 肝硬化 3.153 2.054 2.357 0.125 23.408 0.418 1 310.318 常量 7.755 2.941 6.952 0.008 2 332.815 -
[1] Lin M, Chang Y, Xie F, et al. ASPP2 Inhibits the Profibrotic Effects of Transforming Growth Factor-β1 in Hepatic Stellate Cells by Reducing Autophagy[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2018, 63(1): 146-154. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4816-3
[2] Yang Y, Fu N, Wang H, et al. Leukocytes infiltration correlates intratumoral microvessel density and influence overall and late-phase disease-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2021, 100(48): e28135.
[3] Liu B, Yang L, Li XJ, et al. Expression and significance of ASPP2 in squamous carcinoma of esophagus[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2018, 34(6): 321-329. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2017.12.011
[4] 焦彦, 许萍, 时红波, 等. ASPP2在肝脏疾病中的研究进展[J]. 肝脏, 2020, 25(5): 553-555. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2020.05.036
[5] 中国抗癌协会肝癌专业委员会. 原发性肝癌的临床诊断与分期标准[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2001, 9(6): 324. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:1007-3418.2001.06.001
[6] 《原发性肝癌诊疗规范(2019年版)》编写专家委员会. 原发性肝癌诊疗规范(2019年版)[J]. 中国临床医学, 2020, 27(1): 140-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWK202002001.htm
[7] 余文昌, 张孔志, 陈示光, 等. 实体瘤反应评价标准、欧洲肝病学会和改良实体瘤反应评价标准评价原发性肝癌化疗栓塞效果一致性的比较[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2011, 45(8): 766-769. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1005-1201.2011.08.014
[8] Junaid M, Shah M, Khan A, et al. Structural-dynamic insights into the H. pylori cytotoxin-associated gene A(CagA)and its abrogation to interact with the tumor suppressor protein ASPP2 using decoy peptides[J]. J Biomol Struct Dyn, 2019, 37(15): 4035-4050. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2018.1537895
[9] Tian L, Deng Z, Xu L, et al. Downregulation of ASPP2 promotes gallbladder cancer metastasis and macrophage recruitment via aPKC-ι/GLI1 pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(11): 1115. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1145-1
[10] Yang T, Gao Y, Liu D, et al. ASPP2 enhances chemotherapeutic sensitivity through the down-regulation of XIAP expression in a p53 independent manner in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2019, 508(3): 769-774. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.11.181
[11] 李豪, 陈国勇, 魏思东, 等. 原发性肝癌患者肝切除术后复发影响因素分析[J]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2019, 11(3): 69-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZBZ201903015.htm
[12] 邓林, 孙文杰, 高知玲, 等. 中晚期原发性肝癌患者TACE术后早期复发危险因素[J]. 中国介入影像与治疗学, 2020, 17(2): 65-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JRYX202002002.htm
[13] Liu L, Wang L, Li X, et al. Effect of miR-21 on apoptosis in hepatoblastoma cell through activating ASPP2/p38 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo[J]. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol, 2019, 47(1): 3729-3736. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2019.1664561
[14] Liang B, Chen R, Song S, et al. ASPP2 inhibits tumor growth by repressing the mevalonate pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10(11): 830. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2054-7
[15] Schipper K, Drenth AP, van der Burg E, et al. Truncated ASPP2 Drives Initiation and Progression of Invasive Lobular Carcinoma via Distinct Mechanisms[J]. Cancer Res, 2020, 80(7): 1486-1497. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3607
[16] Konno T, Kohno T, Okada T, et al. ASPP2 suppression promotes malignancy via LSR and YAP in human endometrial cancer[J]. Histochem Cell Biol, 2020, 154(2): 197-213. doi: 10.1007/s00418-020-01876-8
[17] Mao J, Tan Z, Pan X, et al. ASPP2 expression predicts the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2021, 21(4): 397. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9828
[18] Wang S, Sun Y, Wang Y, et al. ASPP2 inhibits hepatitis B virus replication by preventing nucleus translocation of HSF1 and attenuating the transactivation of ATG7[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2021, 25(14): 6899-6908. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16699
-




 下载:
下载: