Effect of electroacupuncture combined with Tuina at Shenque acupoint on gut microbiota in patients with functional constipation
-
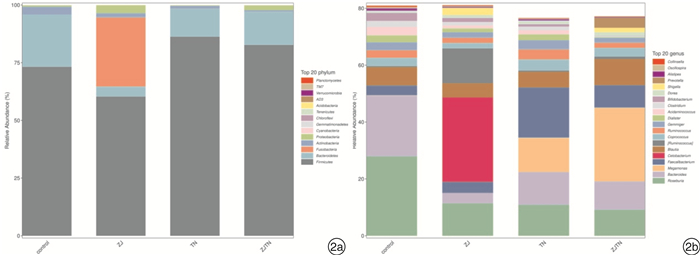
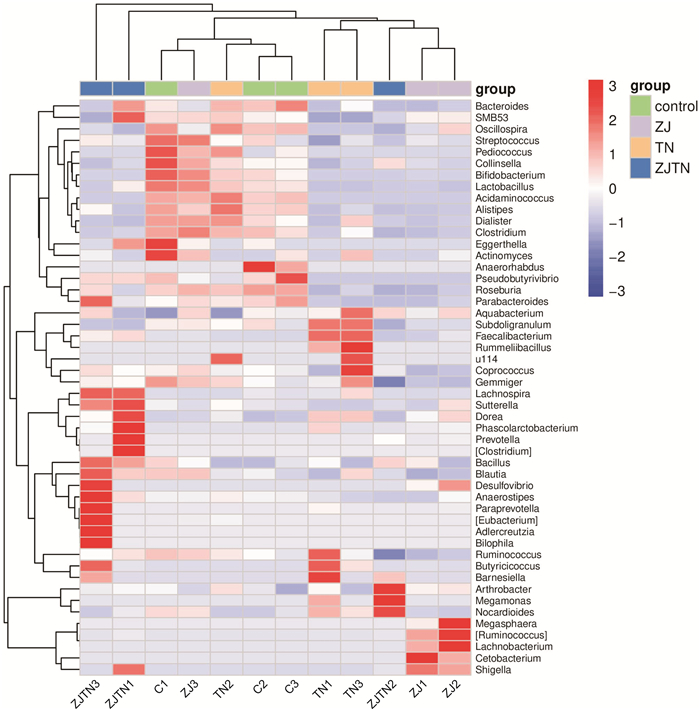
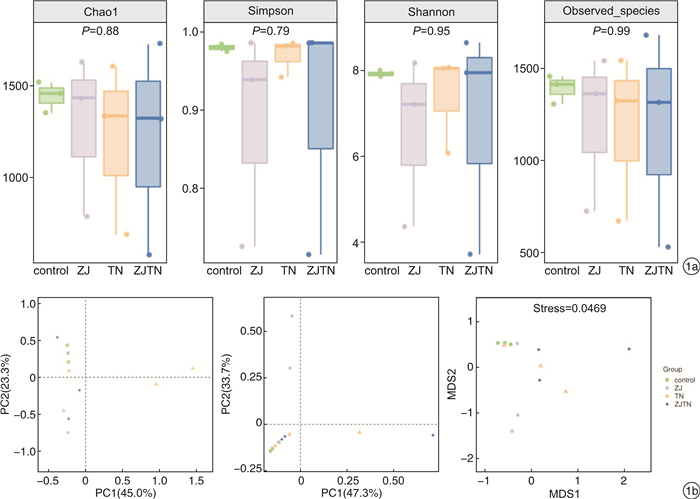
摘要: 目的 探讨神阙穴电针联合推拿对功能性便秘患者肠道菌群的影响。方法 选取于西南医科大学附属中医医院就诊的功能性便秘患者80例,采用随机分组原则分为对照组、神阙穴电针组、推拿组、神阙穴电针联合推拿组,每组20例。对照组不给予治疗,神阙穴电针组给予电针神阙穴治疗,推拿组给予腹部推拿治疗,神阙穴电针联合推拿组给予电针神阙穴及腹部推拿治疗,对比治疗后临床疗效,并采集粪便样本进行16S rDNA基因测序。结果 经过治疗后,神阙穴电针联合推拿组总有效率、大便性状改善率明显较高(P< 0.05);肠道菌群微生物中,对照组患者罗氏菌属(Roseburia)、拟杆菌(Bacteroides)丰度较高,神阙穴电针联合推拿组患者罗氏菌属(Roseburia)、拟杆菌(Bacteroides)、巨单胞菌属(Megamonas)、粪杆菌属(Faecalibacterium)、布劳特氏菌属(Blautia)相对丰度增加。结论 采用神阙穴电针联合推拿治疗功能性便秘患者具有较好的治疗效果,并具有调控患者肠道微生物菌群结构的作用。Abstract: Objective To investigate the effect of Shenque acupoint acupuncture combined with Tuina on the gut microbiota of patients with functional constipation.Methods Eighty patients with functional constipation attending our hospital were selected and divided into control group, Shenque acupoint acupuncture group, Tuina group and Shenque acupoint acupuncture combined with Tuina group with 20 cases in each group using the randomized grouping principle. The control group was not given treatment, the Shenque acupoint acupuncture group was given electroacupuncture of Shenque acupoints, the Tuina group was given abdominal Tuina treatment, and the Shenque acupoint acupuncture combined with Tuina group was given electroacupuncture of Shenque acupoints and abdominal Tuina treatment, and the clinical efficacy was compared after treatment, and stool samples were collected for 16S rDNA gene sequencing.Results After treatment, the total phase rate and stool trait improvement rate were significantly higher in the Shenque acupoint acupuncture combined with Tuina group(P< 0.05); Among the gut microbiota, the abundances ofRoseburiaandBacteroideswere higher in the control group, and the relative abundances ofRoseburia,Bacteroides,Megamonas,FaecalibacteriumandBlautiawere increased in the Shenque acupoint acupuncture combined with Tuina group.Conclusion The treatment of patients with functional constipation using Shenque acupoint electroacupuncture combined with Tuina has a good therapeutic effect and has the effect of regulating the structure of the gut microbiota of patients.
-
Key words:
- functional constipation /
- electroacupuncture /
- Tuina /
- Shenque acupoint /
- gut microbiota
-

-
表 1 各组研究对象基本资料比较
X±S 组别 例数 性别/例 平均年龄/岁 平均病程/年 男 女 对照组 20 8 12 52.70±12.71 10.85±5.69 神阙穴电针组 20 10 10 53.70±15.08 11.80±6.94 推拿组 20 7 13 54.25±12.10 12.10±5.80 神阙穴电针+推拿组 20 9 11 48.40±9.54 9.54±5.62 表 2 各组临床疗效分析
例 组别 例数 疗效 总有效率/% P 治愈 显效 有效 无效 对照组 20 神阙穴电针组 20 2 9 6 3 85.0 推拿组 20 2 8 6 4 80.0 0.020 神阙穴电针+推拿组 20 3 11 4 2 90.0 表 3 各组患者大便性状改善率比较
例 组别 例数 大便转正常例数 非正常大便例数 改善率/% 对照组 20 神阙穴电针组 20 15 5 75.0 推拿组 20 14 6 70.0 神阙穴电针+推拿组 20 17 3 85.01) 与推拿组比较,1)P < 0.05。 -
[1] 张慧田, 马兴婷. 增液承气汤联合粪菌移植对慢性功能性便秘的疗效[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2021, 29(1): 53-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXPW202101013.htm
[2] Forootan M, Bagheri N, Darvishi M. Chronic constipation: A review of literature[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2018, 97(20): e10631.
[3] Van Mill MJ, Koppen IJN, Benninga MA. Controversies in the management of functional constipation in children[J]. Curr Gastroenterol Rep, 2019, 21(6): 23. doi: 10.1007/s11894-019-0690-9
[4] 张子迪, 王锐卿, 刘敬萱, 等. 基于数据挖掘探讨电针治疗周围神经病的临床应用特点[J]. 针刺研究, 2021, 46(3): 240-247. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XCYJ202103014.htm
[5] 汪洋, 王玉娟, 武九龙, 等. 电针对PSD大鼠行为学及神经营养因子和炎症因子的影响[J]. 南京中医药大学学报, 2021, 37(2): 263-269. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJZY202102020.htm
[6] 司原成, 任晨晨, 陈波, 等. 吴茱萸透皮贴剂贴敷神阙穴对营养性肥胖小鼠脂质代谢及肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2021, 36(2): 715-718. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY202102024.htm
[7] 方燕平, 黄于婷, 陈典, 等. 推拿治疗功能性便秘有效性和安全性的系统评价和Meta分析[J]. 中国针灸, 2021, 41(6): 691-698. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZE202106033.htm
[8] 刘友迎, 龚国忠, 代莉, 等. 功能性便秘患者肠道菌群与病情的关系分析[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2021, 29(8): 580-583. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2021.08.11
[9] 刘芳铭. 基于罗马Ⅳ标准的功能性便秘患者的肛门-直肠动力研究[D]. 大连: 大连医科大学, 2017.
[10] 沈洪, 张露, 叶柏. 便秘中医诊疗专家共识意见(2017)[J]. 北京中医药, 2017, 36(9): 771-776, 784. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJZO201709001.htm
[11] 张欣宇, 孙冰, 孙滨滨, 等. 基于"肝主疏泄"理论探讨从肝论治功能性便秘[J]. 北京中医药, 2020, 39(12): 1248-1251. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJZO202012009.htm
[12] 夏洪芳. 加味六磨汤方贴敷神阙穴联合四磨汤口服液治疗抗精神病药物所致便秘临床研究[J]. 新中医, 2020, 52(20): 131-134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-REND202020039.htm
[13] Zheng H, Liu ZS, Zhang W, et al. Acupuncture for patients with chronic functional constipation: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2018, 30(7): e13307. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13307
[14] 李丽芬. 电针足三里对功能性肠病双向调节效应的实验观察[D]. 福州: 福建中医药大学, 2019.
[15] Favretto DC, Pontin B, Moreira TR. Effect of the consumption of a cheese enriched with probiotic organisms(Bifidobacterium lactis bi-07) in improving symptoms of constipation[J]. Arq Gastroenterol, 2013, 50(3): 196-201. doi: 10.1590/S0004-28032013000200035
[16] Mearin F, Lacy BE, Chang L, et al. Bowel disorders[J]. Gastroenterology, 2016, S0016-5085(16)00222-5.
[17] Parthasarathy G, Chen J, Chen X, et al. Relationship between microbiota of the colonic mucosa vs feces and symptoms, colonic transit, and methane production in female patients with chronic constipation[J]. Gastroenterology, 2016, 150(2): 367-379.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.10.005
[18] Dimidi E, Christodoulides S, Scott SM, et al. Mechanisms of action of probiotics and the gastrointestinal microbiota on gut motility and constipation[J]. Adv Nutr, 2017, 8(3): 484-494. doi: 10.3945/an.116.014407
[19] Mancabelli L, Milani C, Lugli GA, et al. Unveiling the gut microbiota composition and functionality associated with constipation through metagenomic analyses[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 9879. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10663-w
[20] Xu Z, Liu T, Zhou Q, et al. Roles of Chinese medicine and gut microbiota in chronic constipation[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2019, 2019: 9372563.
-




 下载:
下载: