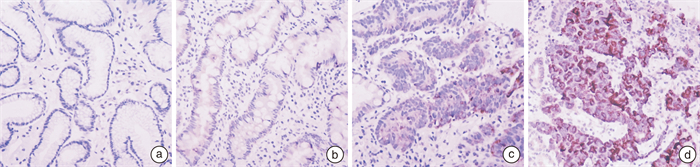
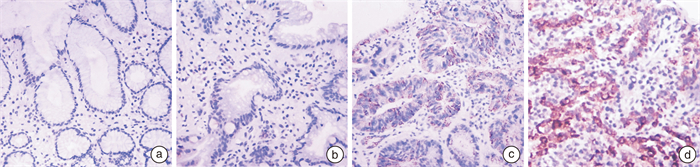
Exploring the changes and significance of IL-13Rα1 and COX-2 protein expression based on gastric "inflammation-cancer" transition
-
摘要: 目的 检测胃“炎-癌”转化各关键阶段组织样本中幽门螺杆菌(Helicobacter pylori,HP)、白介素13受体α1(interleukin-13 receptor α1,IL-13Rα1)及环氧合酶-2(cyclooxygenase-2,COX-2)等蛋白的表达,探讨其在“炎-癌”转化中的作用及意义。方法 将研究对象分为6个组:20例正常胃黏膜(N组)、50例慢性非萎缩性胃炎(CNAG组)、50例慢性萎缩性胃炎伴肠上皮化生(CAG/IM组)、50例胃黏膜低级别异型增生(LGD组)、50例胃黏膜高级别异型增生(HGD组)和50例胃癌(GC组),采用免疫组织化学EnVision两步法检测活检组织中HP、IL-13Rα1及COX-2蛋白的表达。结果 HP在N组、CNAG组、CAG/IM组、LGD组、HGD组和GC组中阳性表达率分别为15%、38%、48%、46%、42%、36%,各组间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);IL-13Rα1在各组中的阳性表达率呈逐渐上升趋势,分别为5%、18%、62%、78%、86%、92%,IL-13Rα1阳性表达与病变分级呈正相关(P < 0.01)。IL-13Rα1在CAG/IM组、LGD组、HGD组、GC组高表达,与N组、CNAG组比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01),而在CAG/IM组、LGD组、HGD组、GC组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);COX-2在各组中的阳性表达率分别为5%、4%、12%、24%、36%、84%,在GC组显著高表达,与N组、CNAG组、CAG/IM组、LGD组、HGD组比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01)。经Spearman等级相关性分析,胃癌组织中COX-2的表达与IL-13Rα1的表达呈正相关(r=0.475,P < 0.01)。结论 IL-13Rα1可能是慢性胃炎向胃上皮化生发生的早期关键分子,而COX-2可能在化生后进一步发生癌变中起作用,二者有助于胃“炎-癌”转化风险评估及病情监测。Abstract: Objective To investigate the expression of Helicobacter pylori (HP), interleukin-13 receptor α1 (IL-13Rα1), and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) proteins in tissue samples representing key stages of gastric inflammation and cancer transformation, and to explore their roles and significance in the "inflammation-cancer" transition.Methods We used immunohistochemical EnVision two-step method to detect and analyze the protein expression of HP, IL-13Rα1, and COX-2 in 270 biopsy tissue samples. These samples were categorized into six groups: normal gastric mucosa (N group, n=50), chronic non-atrophic gastritis (CNAG group, n=50), chronic atrophic gastritis with intestinal metaplasia (CAG/IM group, n=50), low-grade dysplasia of gastric mucosa (LGD group, n=50), high-grade dysplasia of gastric mucosa (HGD group, n=50), and gastric cancer (GC group, n=50).Results The positive expression rates of HP in the N, CNAG, CAG/IM, LGD, HGD, and GC groups were 15%, 38%, 48%, 46%, 42%, and 36%, respectively. There was no statistically significant difference in HP expression between the groups (P>0.05). The positive expression rates of IL-13Rα1 in each group showed a gradual increasing trend: 5%, 18%, 62%, 78%, 86%, and 92%, respectively. IL-13Rα1 expression was positively correlated with lesion grading (P < 0.01). IL-13Rα1 was highly expressed in the CAG/IM, LGD, HGD, and GC groups, showing significant differences compared to the N and CNAG groups (P < 0.01), while there was no significant difference between the CAG/IM, LGD, HGD, and GC groups (P>0.05). The positive rates of COX-2 in each group were 5%, 4%, 12%, 24%, 36%, and 84%, respectively. COX-2 was significantly overexpressed in the GC group compared to the N, CNAG, CAG/IM, LGD, and HGD groups (P < 0.01). Pearson correlation analysis revealed a positive correlation between IL-13Rα1 and COX-2 expression in gastric cancer tissue (r=0.475, P < 0.01).Conclusion IL-13Rα1 may be an early key molecule in the occurrence of gastric epithelial metaplasia in chronic gastritis, while COX-2 may play a role in further carcinogenesis after metaplasia. Both contribute to the risk assessment and disease monitoring of gastric "inflammation-cancer" transition.
-

-
表 1 HP在各组中的表达
例 组别 例数 HP 阳性率/% - + ++ +++ N组 20 17 2 1 0 15 CNAG组 50 31 8 6 5 38 CAG/IM组 50 26 12 7 5 48 LGD组 50 27 14 5 4 46 HGD组 50 29 16 2 3 42 GC组 50 32 10 6 2 36 表 2 IL-13Rα1在各组中的表达
例 组别 例数 IL-13Rα1的表达 阳性率/% - + ++ N组 20 19 1 0 5 CNAG组 50 41 6 3 18 CAG/IM组 50 19 23 8 621) LGD组 50 11 23 16 781) HGD组 50 7 10 33 861) GC组 50 4 8 38 921) 与N组和CNAG组比较,1)P < 0.001。 表 3 COX-2在各组中的表达
例 组别 例数 COX-2 阳性率/% - + ++ N组 20 19 1 0 5 CNAG组 50 48 2 0 4 CAG/IM组 50 44 5 1 12 LGD组 50 38 7 5 24 HGD组 50 32 12 6 36 GC组 50 8 11 31 841) 与N组、CNAG组、CAG/IM组、LGD组、HGD组比较,1)P < 0.001。 表 4 胃癌组织中IL-13Rα1和COX-2表达的相关性
例 IL-13Rα1 COX-2 合计 阳性 阴性 阳性 41 5 46 阴性 1 3 4 合计 42 8 50 -
[1] Freddie B, Mathieu L, Hyuna S, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(3): 229-263. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
[2] 丁霞, 李园, 沈洪. 从精准医学的视角看中医药防治慢性胃炎"炎癌转化"[J]. 北京中医药大学学报, 2023, 46(3): 315-320. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2157.2023.03.005
[3] Wadhwa V, Patel N, Grover D, et al. Interventional gastroenterology in oncology[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2023, 73(3): 286-319. doi: 10.3322/caac.21766
[4] 刘伟, 倪家慧, 张丹, 等. 中医药调控胃"炎癌转化"癌前微环境的思考与策略[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2023, 38(4): 1431-1435.
[5] 王永, 王金福, 陈洋, 等. Hp感染与胃癌患者SOX2和VEGF的相关关系及研究意义[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2018, 26(9): 728-732. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2018.09.04
[6] Yang L, Kartsonaki C, Yao P, et al. The relative and attributable risks of cardia and non-cardia gastric cancer associated with Helicobacter pylori infection in China: a case-cohort study[J]. Lancet Public Health, 2021, 6(12): 888-896. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(21)00164-X
[7] Yan L, Chen Y, Chen F, et al. Effect of Helicobacter pylori Eradication on Gastric Cancer Prevention: Updated Report From a Randomized Controlled Trial With 26.5 Years of Follow-up[J]. Gastroenterology, 2022, 163(1): 154-162. e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.03.039
[8] 杨玉霞, 马丽莉, 高燕, 等. Hp感染与胃癌及胃癌前病变组织MUC2、MUC5AC、MUC6、CD10表达的关系[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2022, 32(5): 721-725.
[9] Wang Y, Mao X, Liu Y, et al. IL-13 Genetic Susceptibility to Bullous Pemphigoid: A Potential Target for Treatment and a Prognostic Marker[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 824110. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.824110
[10] Tollenaere MA, Mølck C, Henderson I, et al. Tralokinumab Effectively Disrupts the IL-13/IL-13Rα1/IL-4Rα Signaling Complex but Not the IL-13/IL-13Rα2 Complex[J]. JID Innov, 2023, 3(5): 100214. doi: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2023.100214
[11] Yang X, Liu P, Zhao X, et al. Sulforaphane inhibits cytokine-stimulated chemokine and adhesion molecule expressions in human corneal fibroblasts: Involvement of the MAPK, STAT, and NF-κB signaling pathways[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2022, 216: 108946. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.108946
[12] Peng W, Song Y, Zhu G, et al. FGF10 attenuates allergic airway inflammation in asthma by inhibiting PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway[J]. Cell Signal, 2024, 113(Suppl C): 110964.
[13] Park MH, Kwon HJ, Kim JR, et al. Elevated Interleukin-13 Receptor Alpha 1 Expression in Tumor Cells Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Invasive Breast Cancer[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2017, 24(12): 3780-3787. doi: 10.1245/s10434-017-5907-2
[14] Ito A, Akama Y, Satoh-Takayama N, et al. Possible Metastatic Stage-Dependent ILC2 Activation Induces Differential Functions of MDSCs through IL-13/IL-13Rα1 Signaling during the Progression of Breast Cancer Lung Metastasis[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2022, 14(13): 3267-3286.
[15] Shi J, Shen X, Kang Q, et al. Loss of Interleukin-13-Receptor-Alpha-1 Induces Apoptosis and Promotes EMT in Pancreatic Cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(7): 3659-3676. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073659
[16] Salomaa T, Pemmari T, Määttä J, et al. IL-13Rα1 Suppresses Tumor Progression in Two-Stage Skin Carcinogenesis Model by Regulating Regulatory T Cells[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2021, 142(6): 1565-1575. e17.
[17] Feng T, Wang J, Cheng K, et al. IL13Rα1 prevents a castration resistant phenotype of prostate cancer by targeting hexokinase 2 for ubiquitin-mediated degradation[J]. Cancer Biol Med, 2021, 19(7): 1008-1028. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0583
[18] Choi WK, Hussein UK, Ahmed AG, et al. Co-operative roles of IL-4Rα and IL-13Rα1 in the progression of ovarian carcinomas and the survival of ovarian carcinoma patients[J]. Cancer Commun(Lond), 2023, 43(7): 850-854.
[19] Noto CN, Hoft SG, Bockerstett KA, et al. IL13 Acts Directly on Gastric Epithelial Cells to Promote Metaplasia Development During Chronic Gastritis[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 13(2): 623-642.
[20] Scott TE, Lewis CV, Zhu M, et al. IL-4 and IL-13 induce equivalent expression of traditional M2 markers and modulation of reactive oxygen species in human macrophages[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 19589. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46237-2
[21] Rong X, Huang B, Qiu S, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages induce vasculogenic mimicry of glioblastoma multiforme through cyclooxygenase-2 activation[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(51): 83976-83986. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6930
[22] 马西, 杜鹏程, 宁登, 等. IL-13、COX2和PI3K/Akt信号通路与结肠癌侵袭转移的关系[J]. 广东医学, 2020, 41(16): 1637-1641.
[23] Li X, Zhu Y, Zhao T, et al. Role of COX-2/PGE2 signaling pathway in the apoptosis of rat ovarian granulosa cells induced by MEHP[J]. Ecotox Environ Safe, 2023, 4(254): 114717.
[24] Zhang A, Zou X, Yang S, et al. Effect of NETs/COX-2 pathway on immune microenvironment and metastasis in gastric cancer[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 1(14): 1177604.
[25] Tiwari SK, Shaik AS, Shaik AP, et al. Gene expression patterns of COX-1, COX-2 and iNOS in H. Pylori infected histopathological conditions[J]. Microb Pathogenesis, 2019, 10(135): 103634.
[26] Purnama A, Lukman K, Rudiman R, et al. The prognostic value of COX-2 in predicting metastasis of patients with colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta analysis[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(10): e21051.
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 260
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: