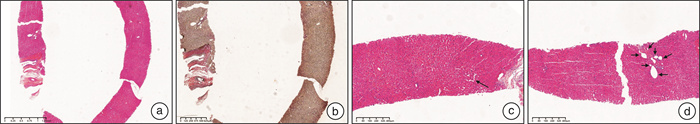
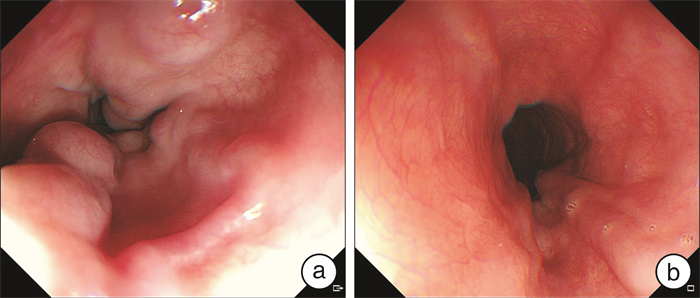
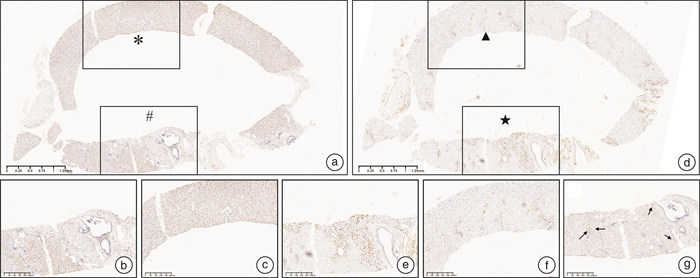
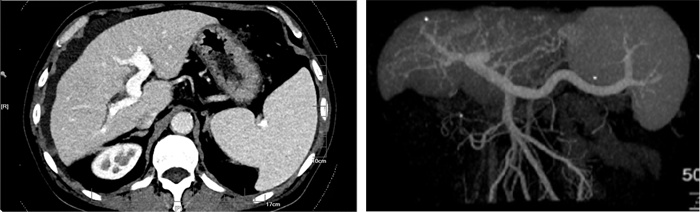
The case report: Diagnosis and treatment of porto-sinusoidal vascular disease caused by oxaliplatin
-
摘要: 奥沙利铂(oxaliplatin,OXA)为第3代铂类抗癌药,广泛应用于中晚期结直肠癌、肝癌及胃癌等的治疗,但可引起肝脏微血管病变等副作用。本文报道1例奥沙利铂引起的非肝硬化门静脉高压患者,经过肝组织病理诊断为门静脉肝窦血管病,并通过中西医结合诊治,患者临床症状与食管胃底静脉曲张得到缓解;此外,文献回顾了OXA引起门静脉肝窦血管病等肝脏微血管病变的特点。Abstract: Oxaliplatin(OXA) is a third-generation platinum-based anticancer drug, which is widely used in the treatment of colorectal cancer, liver cancer and gastric cancer. However, its use can lead to several side effects, including hepatic microvascular damage. This paper reports a case of non-cirrhotic portal hypertension caused by OXA, which was diagnosed as porto-sinusoidal vascular disease by liver histopathology. The patient was successfully treated with a combination of traditional Chinese medicine and Western medicine, leading to significant clinical improvement and alleviation of esophageal and gastric varices. In addition, the literature reviewed the characteristics of hepatic microvascular disease caused by OXA.
-

-
表 1 患者实验室检查结果
项目 2018年5月11日 2018年6月2日 2018年10月17日 2018年11月1日 肝功能 ALT/(U/L) - 23 35 39 AST/(U/L) - 28 32 43 ALP/(U/L) - 87 67 52 γ-GT/(U/L) - 50.7 56 34 TBil/(μmol/L) - 15.4 13.8 22.2 Alb/(g/L) - 42.2 42.3 41.3 血常规 WBC/(×109/L) 4.1 4.1 4.4 3.4 PLT/(×109/L) 58 55 60 55 Hb/(g/L) - 120 131 119 RBC/(×1012/L) 3.87 4.10 4.36 3.96 凝血功能 PT/s - 13.9 12.9 13.8 INR - 1.09 0.99 1.08 表 2 PSVD的诊断条件
诊断条件 肝活检病理无肝硬化,标本长度>20 mm + 符合1条门静脉高压特征性表现或符合1条PSVD特征性病理表现√ 或 肝活检病理无肝硬化,标本长度>20 mm + 符合1条门静脉高压非特征性表现和符合1条PSVD非特征性病理表现√ 表 3 PSVD的临床及病理特征
项目 门静脉高压表现 PSVD病理表现 特征性 胃、食管或异位静脉曲张√ 闭塞性门静脉病(血管壁增厚、管腔闭塞、门静脉分支消失)√ 门静脉高压性出血 结节再生性增生 影像学发现门体侧支循环√ 不完全间隔纤维化(也称为不完全间隔硬化);该特征只能通过大体肝标本而非肝活检评估 非特征性 腹水√ 门静脉支异常(增殖、动脉扩张,汇管区内与门静脉紧密相连的异常血管)√ PLT<150 000/mm3 √ 血管结构紊乱:门静脉和中央静脉分布不规则 脾脏最大长度>13 cm √ 非带状肝窦扩张√ 轻度窦周纤维化 -
[1] Hsu HT, Wu LM, Lin PC, et al. Emotional distress and quality of life during folinic acid, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer patients with and without chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A cross-sectional study[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2020, 99(6): e19029.
[2] Soveri LM, Lamminmäki A, Hänninen UA, et al. Long-term neuropathy and quality of life in colorectal cancer patients treated with oxaliplatin containing adjuvant chemotherapy[J]. Acta Oncol, 2019, 58(4): 398-406.
[3] Schouten JN, Garcia-Pagan JC, Valla DC, et al. Idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. Hepatology, 2011, 54(3): 1071-1081. doi: 10.1002/hep.24422
[4] De Gottardi A, Rautou PE, Schouten J, et al. Porto-sinusoidal vascular disease: proposal and description of a novel entity[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 4(5): 399-411. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30047-0
[5] Venook AP, Niedzwiecki D, Lenz HJ, et al. Effect of First-Line Chemotherapy Combined With Cetuximab or Bevacizumab on Overall Survival in Patients With KRAS Wild-Type Advanced or Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial[J]. JAMA, 2017, 317(23): 2392-2401.
[6] 冯允, 何裕隆. 奥沙利铂联合替吉奥的新辅助化疗方案治疗进展期胃癌的临床研究[J]. 消化肿瘤杂志, 2020, 12(4): 279-282.
[7] Yazaki T, Kawashima K, Ishimura N, et al. Oxaliplatin-related Portal Hypertension Complicated with Esophageal Varices and Refractory Massive Ascites[J]. Intern Med, 2022, 61(21): 3225-3231.
[8] Fuentes-Lacouture MC, Barrera-Garavito EC, Gomez A, et al. Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension in a Patient With Colonic Carcinoma Treated With Oxaliplatin[J]. J Med Cases, 2021, 12(3): 99-101.
[9] Morioka D, Izumisawa Y, Yamaguchi K, et al. Surgical intervention for portal hypertension caused by oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy: a case report and a review of literature regarding radiological and/or surgical interventions for oxaliplatin-associated portal hypertension[J]. Clin J Gastroenterol, 2020, 13(5): 799-805.
[10] Santini D, Tonini G, Salerno A, et al. Idiosyncratic reaction after oxaliplatin infusion[J]. Ann Oncol, 2001, 12(1): 132-133.
[11] Reiberger T, Ulbrich G, Ferlitsch A, et al. Carvedilol for primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in cirrhotic patients with haemodynamic non-response to propranolol[J]. Gut, 2013, 62(11): 1634-1641.
[12] De Mattos ÂZ, Terra C, Farias AQ, et al. Primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis: A comparison of different strategies[J]. World J Gastrointest Endosc, 2021, 13(12): 628-637. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i12.628
[13] 李煜, 陈世耀. 肝硬化门静脉高压经颈静脉肝内门体分流术的临床应用[J]. 肝博士, 2024, 1: 31.
[14] 蔡子豪, 诸葛宇征. 门静脉肝窦血管性疾病的疾病特点与诊疗进展[J]. 肝脏, 2023, 28(2): 148-151.
[15] Zhu C, Ren X, Liu D, et al. Oxaliplatin-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome[J]. Toxicology, 2021, 460: 152882. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2021.152882
[16] Toda R, Seo S, Uemoto Y, et al. Clinically relevant model of oxaliplatin-induced sinusoidal obstruction syndrome[J]. Hepatol Res, 2023, 53(2): 145-159. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13842
[17] 齐婧姝, 王宇, 刘成海. 活血化瘀法在肝硬化中医药治疗中的实践应用与发展[J]. 上海中医药杂志, 2023, 57(8): 27-32.
[18] Li ZX, Zhao ZM, Liu P, et al. Treatment of HBV Cirrhosis with FuzhengHuayu Tablet and Entecavir: Design of a Randomized, Double-Blind, Parallel and Multicenter Clinical Trial[J]. Chin J Integr Med, 2021, 27(7): 509-513. doi: 10.1007/s11655-020-3257-6
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 329
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: