Study on clinical efficacy and mechanism of self-designed spleen-bushen and stomach formula with chemotherapy in advanced colorectal cancer patients with weak spleen and kidney deficiency
-
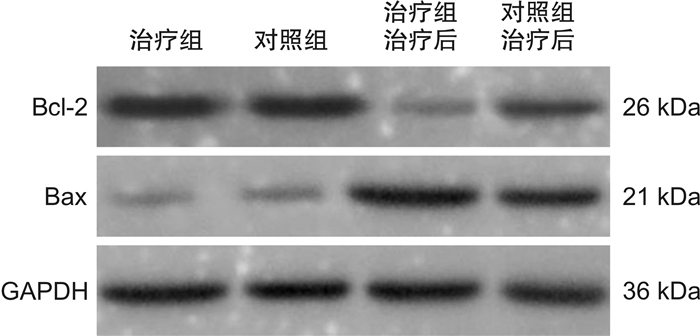
摘要: 目的 观察自拟健脾补肾和胃组方联合化疗对晚期脾肾虚弱型大肠癌患者的临床疗效、中医证候及生活质量的影响。方法 将50例脾肾虚弱型大肠癌患者随机分为治疗组和对照组。对照组给予CAPEOX联合贝伐珠单抗方案化疗,治疗组在此基础上加服自拟健脾补肾和胃组方汤剂(每日1剂,连服8周),化疗每3周重复1次,连用3个周期后观察两组的临床疗效、中医证候评分、生活质量及Bcl-2、Bax的表达情况。结果 3周期治疗后,治疗组与对照组的临床总体疗效相当;中医证候积分和中医证候疗效比较,治疗组优于对照组(P < 0.05);治疗后,两组患者Bcl-2的表达均较治疗前下降(P < 0.01),Bax的表达均较治疗前升高(P < 0.01),且治疗组的变化比对照组更明显(P < 0.05)。结论 自拟健脾补肾和胃组方能提高晚期大肠癌化疗患者的临床疗效,改善中医症状,增强机体免疫力。其可能是通过提高促凋亡蛋白Bax和降低抑凋亡蛋白Bcl-2的表达起到增加化疗疗效、改善患者生活质量的作用。Abstract: Objective To observe the clinical efficacy, traditional Chinese medicine(TCM) syndrome and quality of life of patients with spleen and kidney deficiency with chemotherapy of self-designed spleen-bushen and stomach formula in patients with advanced colorectal cancer.Methods Fifty patients with colorectal cancer were randomly divided into treatment group and control group. Patients in both groups were treated with CAPEOX combined with bevacizumab regimen for chemotherapy. The treatment group was also treated with self-designed spleen-bushen and stomach formula(one dose a day for eight weeks), and chemotherapy was repeated once every three weeks. After three consecutive cycles, the clinical efficacy, TCM syndrome score and Bcl-2 and bax expression of the two groups were observed.Results After three cycles of treatment, the overall clinical efficacy of the treatment group was comparable to the control group, the improvement of the symptoms in the treatment group was better than the control group(P < 0.05); the expression of the apoptosis regulating protein Bcl-2 decreased after treatment in both groups(P < 0.01), and the expression of the apoptosis regulating protein Bax increased(P < 0.01), and the change in the treatment group was more obvious(P < 0.05).Conclusion Self-designed spleen-bushen and stomach formula can improve the clinical effect, improve the symptoms of TCM and enhance the immunity of patients with colorectal cancer. It may enhance the efficacy of chemotherapy and improve the quality of life of patients by increasing the expression of pro-apoptotic protein Bax and decreasing the expression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2.
-
Key words:
- colorectal cancer /
- self-designed spleen-bushen and stomach formula /
- chemotherapy /
- clinical effect /
- Bax /
- Bcl-2
-

-
表 1 两组患者的临床资料比较
例,X±S 组别 例数 性别 年龄/岁 体重/kg 原发部位 病理类型 男 女 结肠癌 直肠癌 管状腺癌 黏液腺癌 印戒细胞癌 治疗组 25 17 8 60.24±7.79 54.74±4.79 10 15 19 5 1 对照组 25 16 9 60.16±6.97 54.37±4.44 9 16 20 5 0 表 2 两组患者的临床疗效比较
例 组别 例数 CR PR SD PD ORR/% DCR/% Z P 治疗组 25 0 7 14 4 28 84 -0.612 0.541 对照组 25 0 6 13 6 24 76 表 3 两组患者的中医证候评分比较
分,X±S 组别 例数 治疗前 治疗后 t P 治疗组 25 13.32±1.52 6.04±2.511)2) -1.393 < 0.001 对照组 25 13.12±1.67 9.52±3.481) -5.645 < 0.001 t 0.443 -4.058 P 0.659 < 0.001 与本组治疗前比较,1)P < 0.001;与对照组比较,2)P < 0.001。 表 4 两组患者的中医证候疗效比较
例(%) 组别 例数 临床痊愈 显效 有效 无效 总有效率/% χ2 P 治疗组 25 0 7(28) 13(52) 5(20) 801) 4.367 0.037 对照组 25 0 4(16) 9(36) 12(48) 52 与对照组比较,1)P < 0.05。 表 5 两组患者的KPS评分比较
分,X±S 组别 例数 治疗前 治疗后 t P 治疗组 25 71.60±5.54 75.60±8.701)2) 2.191 0.038 对照组 25 69.20±4.93 72.60±9.781) 1.204 0.040 t 1.618 2.292 P 0.112 0.046 与本组治疗前比较,1)P < 0.05;与对照组比较,2)P < 0.05。 表 6 两组患者的Bcl-2、Bax染色光密度值比较
X±S 组别 例数 Bcl-2 P Bax P 治疗前 治疗后 治疗前 治疗后 治疗组 25 0.78±0.05 0.41±0.03 < 0.001 0.52±0.03 0.83±0.04 < 0.001 对照组 25 0.77±0.04 0.52±0.02 0.045 0.53±0.04 0.68±0.03 0.037 P 0.801 0.038 0.725 0.046 表 7 两组患者Bcl-2、Bax表达的比较
X±S 组别 例数 Bcl-2 P Bax P 治疗前 治疗后 治疗前 治疗后 治疗组 25 0.89±0.04 0.32±0.02 < 0.001 0.26±0.01 0.79±0.03 < 0.001 对照组 25 0.88±0.03 0.37±0.03 < 0.001 0.25±0.02 0.67±0.05 < 0.001 P 0.924 0.047 0.763 0.048 -
[1] Goodarzi E, Beiranvand R, Naemi H, et al. Worldwide incidence and mortality of colorectal cancer and human development index(HDI): An ecological study[J]. World Cancer Res J, 2019, 6: e1433.
[2] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer Statistics, 2021[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(1): 7-33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21654
[3] Stoffel EM, Murphy CC. Epidemiology and Mechanisms of the Increasing Incidence of Colon and Rectal Cancers in Young Adults[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158(2): 341-353. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.055
[4] Petersson J, Bock D, Martling A, et al. Increasing incidence of colorectal cancer among the younger population in Sweden[J]. BJS Open, 2020, 4(4): 645-658. doi: 10.1002/bjs5.50279
[5] Song M, Qian C, Zhang T, et al. Salvia mitiorrhiza Bunge aqueous extract attenuates infiltration of tumor-associated macrophages and potentiates anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in colorectal cancer through modulating Cox2/PGE2 cascade[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 316: 116735. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116735
[6] 林洪生. 恶性肿瘤中医诊疗指南[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2014: 344-345.
[7] 郑筱萸. 中药新药临床研究指导原则(试行)[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2002: 5, 61.
[8] 中国抗癌协会. 新编常见恶性肿瘤诊治规范(大肠癌分册)[M]. 北京: 北京医科大学、中国协和医科大学联合出版社, 1999: 810-811.
[9] Nicholls RJ, Zinicola R, Haboubi N. Extramural spread of rectal cancer and the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual 8th edition, 2017[J]. Ann Oncol, 2019, 30(8): 1394-1395.
[10] 杨春波, 劳绍贤, 危北海, 等. 胃肠疾病中医症状评分表(中国中西医结合学会消化系统疾病专业委员会, 2010, 苏州)[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2011, 19(1): 66-68.
[11] 周际昌. 实用肿瘤内科学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2003: 47-48.
[12] Cahyadi A, Ugrasena IDG, Andarsini MR, et al. Relationship between Bax and Bcl-2 Protein Expression and Outcome of Induction Phase Chemotherapy in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2022, 23(5): 1679-1685. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.5.1679
[13] Zhao C, Ghosh B, Chakraborty T, et al. Bavachinin mitigates DMH induced colon cancer in rats by altering p53/Bcl2/BAX signaling associated with apoptosis[J]. Biotech Histochem, 2021, 96(3): 179-190. doi: 10.1080/10520295.2020.1778087
[14] Michie J, Kearney CJ, Hawkins ED, et al. The Immuno-Modulatory Effects of Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein Antagonists in Cancer Immunotherapy[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(1): 207. doi: 10.3390/cells9010207
[15] Kim HK, Kim SA, Jung EK, et al. Inhibitor of apoptosis protein Livin promotes tumor progression and chemoradioresistance in human anaplastic thyroid cancer[J]. Oncol Rep, 2021, 45(4): 18. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.7969
[16] Ramesh P, Medema JP. BCL-2 family deregulation in colorectal cancer: Potential for BH3 mimetics in therapy[J]. Apoptosis, 2020, 25: 305-320. doi: 10.1007/s10495-020-01601-9
[17] Placzek WJ, Wei J, Kitada S, et al. A survey of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 subfamily expression in cancer types provides a platform to predict the effificacy of Bcl-2 antagonists in cancer therapy[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2010, 1: e40. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2010.18
[18] Bruckheimer EM, Cho SH, Sarkiss M, et al. The Bcl-2 gene family and apoptosis[J]. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol, 1998, 62: 75-105.
[19] Socha DS, Zhao X, Bodo J, et al. Decreased BIM expression in BCL2-negative follicular lymphoma: a potential mechanism for resistance to apoptosisv[J]. Hum Pathol, 2021, 107: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2020.09.016
[20] Tang D, Lam C, Bauer N, et al. Bax and Bak knockout apoptosis-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cell lines significantly improve culture viability and titer in intensified fed-batch culture process[J]. Biotechnol Prog, 2022, 38(2): e3228. doi: 10.1002/btpr.3228
[21] Bian Y, Wang G, Zhou J, et al. Astragalus membranaceus(Huangqi)and Rhizoma curcumae(Ezhu)decoction suppresses colorectal cancer via downregulation of Wnt5/β-Catenin signal[J]. Chin Med, 2022, 17(1): 11. doi: 10.1186/s13020-021-00564-6
[22] 张国磊, 王宇立, 诸君, 等. 基于脾虚理论探讨肿瘤微环境及健脾中药的调节作用[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2023, 32(4): 534-551.
[23] Chen Z, Liu L, Gao C, et al. Astragali Radix(Huangqi): A promising edible immunomodulatory herbal medicine[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2020, 258: 112895. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112895
[24] Collignon A, Silvy F, Robert S, et al. Dendritic cell-based vaccination: powerful resources of immature dendritic cells against pancreatic adenocarcinoma[J]. Oncoimmunology, 2018, 7(12): e1504727.
-





 下载:
下载: