Clinical efficacy and safety of programmed death protein-1 inhibitor combined with TS regimen in the treatment of peritoneal metastasis of advanced gastric cancer
-
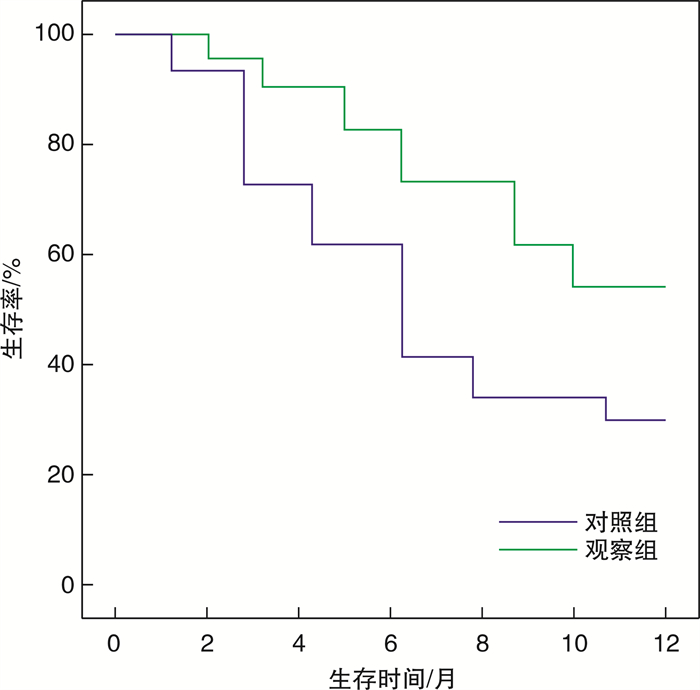
摘要: 目的 研究程序性死亡蛋白-1(programmed death protein-1, PD-1)抑制剂(信迪利单抗)联合TS方案(紫杉醇+替吉奥)治疗进展期胃癌腹膜腔转移患者的临床效果及安全性。方法 回顾性分析2019年8月-2021年12月本院收治的80例进展期胃癌腹膜腔转移患者的临床资料, 将其根据治疗方式分为对照组和观察组, 每组各40例。对照组采用TS方案治疗, 观察组患者在对照组的基础上再给予PD-1抑制剂治疗。比较两组患者的临床疗效、治疗前后肿瘤标志物[糖类抗原(CA199)、癌胚抗原(CEA)]水平。观察治疗前、治疗1、2个疗程后的病灶直径水平, 对比两组患者治疗期间的不良反应发生情况。治疗结束后对两组患者随访1年, 观察随访期间的生存情况。结果 观察组总有效率高于对照组(87.50%vs 65.00%, P < 0.05)。治疗后, 两组患者的血清CA199、CEA水平均低于治疗前(P < 0.05), 且观察组患者的血清CA199、CEA水平低于对照组(P < 0.05)。与治疗前比较, 治疗1、2个疗程后两组患者的病灶直径水平均降低(P < 0.05), 观察组患者治疗1、2个疗程后病灶直径水平低于对照组(P < 0.05)。观察组患者的胃肠道反应、白细胞减少、贫血、甲状腺功能减退、手足综合征等不良反应发生率与对照组比较, 差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。观察组患者的生存率高于对照组(55.00%vs 30.00%, P=0.024)。结论 PD-1抑制剂联合TS方案可明显提高进展期胃癌腹膜腔转移患者的临床疗效, 下调肿瘤标志物水平, 缩小病灶, 更有利于提高的患者生存率且安全性佳。
-
关键词:
- 程序性死亡蛋白-1抑制剂 /
- 紫杉醇 /
- 替吉奥 /
- 胃癌 /
- 腹膜腔转移
Abstract: Objective To study the clinical efficacy and safety of programmed death protein-1(PD-1) inhibitor(Xindilimab) combined with TS regimen(taxol+gimeracil and oteracil porassium capsules) in the treatment of peritoneal metastasis of advanced gastric cancer.Methods Clinical data of 80 patients with advanced gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis admitted to our hospital from August 2019 to December 2021 were retrospectively analyzed, and they were divided into control group and observation group according to treatment methods, with 40 cases in each group. The control group was treated with TS regimen, and the patients in the observation group were treated with PD-1 inhibitor on the basis of the control group. The clinical efficacy, levels of tumor markers[carbohydrate antigen(CA199), carcinoembryonic antigen(CEA)]before and after treatment were compared between the two groups. The diameter of the lesion was observed before and after 1 and 2 courses of treatment. The adverse reactions of the two groups during treatment were compared. After treatment, the patients in the two groups were followed up for 1 year to observe their survival during the follow-up period.Results The total effective rate of the observation group was higher than that of the control group(87.50% vs 65.00%, P < 0.05). After treatment, the levels of serum CA199 and CEA in the two groups were lower than those before treatment(P < 0.05), and the levels of serum CA199 and CEA in the observation group were lower than those in the control group(P < 0.05). Compared with before treatment, the lesion diameter of the two groups decreased after one course of treatment and two courses of treatment(P < 0.05). After one course of treatment and two courses of treatment, the lesion diameter in the observation group was lower than that in the control group(P < 0.05). There was no significant difference between the observation group and the control group in the incidence of gastrointestinal reactions, leukopenia, anemia, hypothyroidism, hand foot syndrome and other adverse reactions(P>0.05). The survival rate in the observation group was higher than that in the control group(55.00% vs 30.00%, P=0.024).Conclusion PD-1 inhibitor combined with TS regimen can significantly improve the clinical efficacy of patients with peritoneal metastasis of advanced gastric cancer, reduce the level of tumor markers, shrink the focus, and is more conducive to improving the survival rate of patients with good safety. -

-
表 1 两组患者的临床资料比较
例(%),X±S 临床资料 对照组
(n=40)观察组
(n=40)χ2/t/Z P 性别 0.220 0.639 男 25(62.50) 27(67.50) 女 15(37.50) 13(32.50) 年龄/岁 57.89±15.78 58.24±14.69 0.103 0.918 BMI 22.45±1.13 22.36±1.09 0.363 0.718 肿瘤位置 0.202 0.653 胃体 17(42.50) 19(47.50) 胃窦 23(57.50) 21(52.50) 表 2 两组患者的临床疗效比较
例(%) 组别 例数 CR PR SD PD ORR DCR 对照组 40 2(5.00) 24(60.00) 14(35.00) 0 26(65.00) 40(100.00) 观察组 40 4(10.00) 31(77.50) 5(12.50) 0 35(87.50) 40(100.00) χ2 5.591 0.000 P 0.018 1.000 表 3 两组患者治疗前后肿瘤标志物水平比较
X±S 组别 例数 CA199/(U/mL) CEA/(ng/mL) 治疗前 治疗后 治疗前 治疗后 对照组 40 76.78±10.25 57.05±8.481)5 20.85±4.25 16.01±3.941) 观察组 40 77.15±11.36 47.56±6.541) 21.18±4.51 12.39±3.571) 组间 F=11.971 P=0.001 F=7.051 P=0.010 时间点 F=232.104 P < 0.001 F=104.122 P < 0.001 组间·时间点 F=9.298 P < 0.001 F=8.743 P=0.004 与治疗前比较,1)P < 0.05。 表 4 两组患者治疗前、治疗1、2个疗程后病灶直径比较
cm,X±S 组别 例数 治疗前 治疗1个疗程后 治疗2个疗程后 对照组 40 5.14±0.61 4.71±0.411) 3.59±0.341) 观察组 40 5.21±0.57 4.23±0.351) 2.89±0.311) 组间 F=65.371 P < 0.001 时间点 F=245.572 P < 0.001 组间·时间点 F=15.436 P < 0.001 与治疗前比较,1)P < 0.05。 表 5 两组患者不良反应发生情况比较
例(%) 组别 例数 胃肠道反应 白细胞减少 贫血 甲状腺功能减退 手足综合征 对照组 40 11(27.50) 9(22.50) 12(30.00) 13(32.50) 10(25.00) 观察组 40 14(35.00) 8(20.00) 10(25.00) 12(30.00) 8(20.00) χ2 0.524 0.075 0.251 0.058 0.287 P 0.469 0.785 0.617 0.809 0.592 -
[1] Wong MCS, Huang JJ, Chan PSF, et al. Global incidence and mortality of gastric cancer, 1980-2018[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2021, 4(7): e2118457. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.18457
[2] Pan YY, Zheng Y, Yang J, et al. A new biomarker for the early diagnosis of gastric cancer: gastric juice-and serum-derived SNCG[J]. Future Oncol, 2022, 18(28): 3179-3190. doi: 10.2217/fon-2022-0253
[3] Ye ZY, Yu PF, Cao Y, et al. Prediction of peritoneal cancer index and prognosis in peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer using NLR-PLR-DDI score: a retrospective study[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2022, 14: 177-187. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S343467
[4] Sindayigaya R, Dogan C, Demtroder CR, et al. Clinical outcome for patients managed with low-dose cisplatin and doxorubicin delivered as pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy for unresectable peritoneal metastases of gastric cancer[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2022, 29(1): 112-123. doi: 10.1245/s10434-021-10860-y
[5] 陈智成, 朱可心, 赵金莉, 等. CT影像组学预测合并腹膜转移晚期胃癌新辅助化疗初期疗效的研究[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2022, 38(3): 420-436. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1671.2022.03.017
[6] Vatandoust S, Bright T, Roy AC, et al. Phase 1 trial of intraperitoneal paclitaxel in combination with intravenous cisplatin and oral capecitabine in patients with advanced gastric cancer and peritoneal metastases(IPGP study)[J]. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol, 2022, 18(4): 404-409. doi: 10.1111/ajco.13659
[7] Yamashita S, Abe H, Kunita A, et al. Programmed cell death protein 1/programmed death ligand 1 but not HER2 is a potential therapeutic target in gastric neuroendocrine carcinoma[J]. Histopathology, 2021, 78(3): 381-391. doi: 10.1111/his.14230
[8] 卫春燕, 宋丽丽. 信迪利单抗联合改良DCF方案治疗晚期胃癌的临床研究[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2022, 19(14): 1970-1974. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2022.14.023
[9] Zaanan A, Bouche O, Benhaim L, et al. Gastric cancer: French intergroup clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatments and follow-up(SNFGE, FFCD, GERCOR, UNICANCER, SFCD, SFED, SFRO)[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2018, 50(8): 768-779. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2018.04.025
[10] 中国抗癌协会胃癌专业委员会. 胃癌诊治难点中国专家共识(2020版)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2020, 40(8): 869-904.
[11] 国家卫生健康委员会. 胃癌诊疗规范(2018年版)[J]. 中华消化病与影像杂志(电子版), 2019, 9(3): 118-144.
[12] Ippolito D, Maino C, Ragusi M, et al. Immune response evaluation criteria in solid tumors for assessment of atypical responses after immunotherapy[J]. World J Clin Oncol, 2021, 12(5): 323-334. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v12.i5.323
[13] Qiu HB, Cao SM, Xu RH. Cancer incidence, mortality, and burden in China: a time-trend analysis and comparison with the United States and United Kingdom based on the global epidemiological data released in 2020[J]. Cancer Commun, 2021, 41(10): 1037-1048. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12197
[14] Chen ZX, Li J, Liu WB, et al. Elemene-containing hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy combined with chemotherapy for elderly patients with peritoneal metastatic advanced gastric cancer[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2022, 10(5): 1498-1507. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i5.1498
[15] Nakamura M, Ojima T, Katsuda M, et al. Phase 1 study of combined chemotherapy of nab-paclitaxel, S-1, and oxaliplatin for gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis(NSOX study)[J]. Oncology, 2021, 99(1): 57-61. doi: 10.1159/000509396
[16] Ishikawa M, Iwasa S, Nagashima K, et al. Retrospective comparison of nab-paclitaxel plus ramucirumab and paclitaxel plus ramucirumab as second-line treatment for advanced gastric cancer focusing on peritoneal metastasis[J]. Invest New Drugs, 2020, 38(2): 533-540. doi: 10.1007/s10637-019-00822-3
[17] 叶再生, 曾奕, 魏晟宏, 等. 阿帕替尼联合奥沙利铂和替吉奥在胃癌腹膜转移转化治疗中的安全性及近期疗效观察[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志, 2021, 24(3): 240-247.
[18] Shitara K, van Cutsem E, Bang YJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab or pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy vs chemotherapy alone for patients with first-line, advanced gastric cancer: the KEYNOTE-062 phase 3 randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2020, 6(10): 1571-1580. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.3370
-




 下载:
下载: