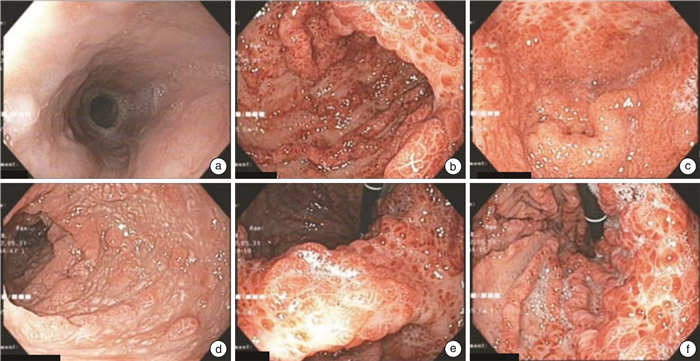
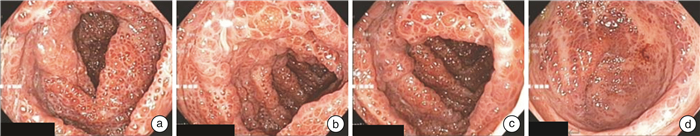
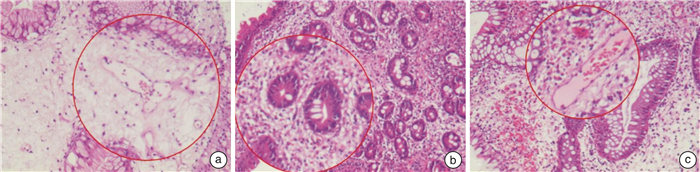
A case report of Cronkhite-Canada syndrome treated by integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine and literature review
-
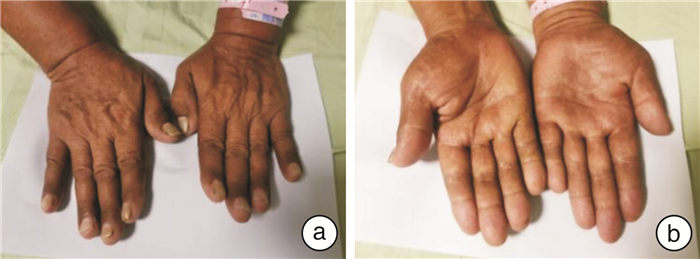
摘要: Cronkhite-Canada综合征(Cronkhite-Canada syndrome,CCS)一种临床罕见的非遗传性疾病,以胃肠道多发息肉和外胚层三联征为主要特征,临床症见消化道症状、皮肤色素沉着、脱发、爪甲脱落等。西医治疗CCS缺乏明确有效的治疗手段,多以经验性对症治疗为主。中医根据辨证论治,针对本例患者,辨证为脾虚夹痰热瘀毒滞肠证,治以健脾和胃、祛邪化积,先后予以口服清营汤和乌梅汤,经治疗2周后,患者好转出院。本文探讨中西医结合诊治1例CCS并文献复习,以供临床医师参考。
-
关键词:
- Cronkhite-Canada综合征 /
- 胃肠道息肉 /
- 中西医治疗 /
- 病例报道 /
- 文献复习
Abstract: Cronkhite-Canada syndrome(CCS) is a clinically rare nongenetic disorder that is characterized endoscopically by multiple gastrointestinal polyps and ectodermal triad. Clinical manifestations include gastrointestinal symptoms, skin pigmentation, alopecia, and nail shedding. At present, Western Medicine lacks clear and effective treatment methods for CCS, and most of them are empirical symptomatic treatment. Traditional Chinese Medicine is based on dialectical treatment for this case. The syndrome differentiation is spleen deficiency trapping phlegm, heat, stasis, and poison lingering in the intestine syndronme. The treatment is to strengthen the spleen and stomach, dispel the accumulation of evil. Oral Qingying Decoction and Wumei Decoction were given successively, after two weeks of treatment, The patient improved and was discharged. This article discusses a case of diagnosis and treatment of CCS with integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine and reviews the literature for reference by clinicians. -

-
[1] Watanabe C, Komoto S, Tomita K, et al. Endoscopic and clinical evaluation of treatment and prognosis of Cronkhite-Canada syndrome: a Japanese nationwide survey[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2016, 51(4): 327-336. doi: 10.1007/s00535-015-1107-7
[2] Slavik T, Montgomery EA. Cronkhite-Canada syndrome six decades on: the many faces of an enigmatic disease[J]. J Clin Pathol, 2014, 67(10): 891-897. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2014-202488
[3] Jha AK, Kumar A, Singh SK, et al. Panendoscopic characterization of Cronkhite-Canada syndrome[J]. Medical J Armed Forces India, 2018, 74(2): 196-200. doi: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2017.03.007
[4] Patil V, Patil LS, Jakareddy R, et al. Cronkhite-Canada syndrome: a report of two familial cases[J]. Indian J Gastroenterol, 2013.32(2): 119-122. doi: 10.1007/s12664-012-0296-8
[5] 王少墨, 王秀薇, 姚怡, 等. 王庆其治疗大肠息肉经验[J]. 中医杂志, 2016, 57(15): 1278-1280. doi: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2016.15.005
[6] 任霞, 赵智强. 赵智强教授辨治结肠腺瘤样息肉学术经验初探[J]. 浙江中医药大学学报, 2017, 41(1): 75-77. doi: 10.16466/j.issn1005-5509.2017.01.017
[7] 张旭, 韩树堂. 刘沈林教授中医治疗结肠息肉经验撷粹[J]. 天津中医药, 2021, 38(5): 581-585. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJZY202105011.htm
[8] 张华月, 李琦, 付晓伶. 乌梅化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 上海中医药杂志, 2017, 51(S1): 296-300. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHZZ2017S1078.htm
[9] Cronkhite LJ. Generalized gastrointestinal polyposis; an unusual syndrome of polyposis, pigmentation, alopecia and onychotrophia[J]. New England J Med, 1955, 252(24): 1011-1015. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195506162522401
[10] 陈鑫, 李变霞, 朱兰平, 等. 罕见的息肉病-Cronkhite-Canada综合征[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2019, 27(16): 977-983. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXHB201916002.htm
[11] 李曼, 朱明欣, 黄浩. Cronkhite-Canada综合征43例临床分析[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2010, 20(18): 2806-2808. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXDY201018024.htm
[12] Samoha S, Arber N. Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome[J]. Digestion, 2005, 71(4): 199-200. doi: 10.1159/000086134
[13] Sweetser S, Ahlquist DA, Osborn NK, et al. Clinicopathologic Features and Treatment Outcomes in Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome: Support for Autoimmunity[J]. Digest Dis Sci, 2012, 57(2): 496-502. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-1874-9
[14] Riegert-Johnson DL, Osborn N, Smyrk T, et al. Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome Hamartomatous Polyps Are Infiltrated with IgG4 Plasma Cells[J]. Digestion, 2007, 75(2-3): 96-97. doi: 10.1159/000102963
[15] Degg NL, Weil MM, Edwards A, et al. Adenoma multiplicity in irradiated Apc(Min)mice is modified by chromosome 16 segments from BALB/c[J]. Cancer Res, 2003, 63(10): 2361-2363.
[16] Boland BS, Bagi P, Valasek MA, et al. Cronkhite Canada Syndrome: Significant Response to Infliximab and a Possible Clue to Pathogenesis[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2016, 111(5): 746-748.
[17] Yu Y, Okayasu R, Weil MM, et al. Elevated breast cancer risk in irradiated BALB/c mice associates with unique functional polymorphism of the Prkdc(DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit)gene[J]. Cancer Res, 2001, 61(5): 1820-1824.
[18] Dhrubajyot I, Bandyopadhya Y, AdriJA, et al. Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome: A Rare Caus of Chronic Diarrhoea in a Young Man[J]. Case Rep Medic, 2016, 2016(3): 4210397.
[19] Okamoto K, Isomoto H, Shikuwa S, et al. A case of Cronkhite-Canada syndrome: remission after treatment with anti-Helicobacter pylori regimen[J]. Digestion, 2008, 78(2-3): 82-87.
[20] Kim MS, Jung HK, Jung HS, et al. A Case of Cronkhite-Canada syndrome showing resolution with Helicobacter pylori eradication and omeprazole[J]. Korean J Gastroenterol, 2006, 47(1): 59-64.
[21] Berzin TM, Greenberger NJ, Levy BD, et al. Clinical problem-sloving. Worth a Second Look[J]. New England J Med, 2012, 366(5): 464-469.
[22] Kurimasa A, Ouyang H, Dong LJ, et al. Catalytic subunit of DNA-dependent protein kinase: Impact on lymphocyte development and tumorigenesis[J]. Proceedings Natlional Aca Sci United States Am, 1999, 96(4): 1403-1408.
[23] Choi YJ, Lee DH, Song EJ, et al. Vitiligo: an unusual finding in Cronkhite-Canada syndrome[J]. J Dermatol, 2013, 40(10): 848-849.
[24] Taylor SA, Kelly J, Loomes DE. Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome: Sustained Clinical Response with Anti-TNF Therapy[J]. Case Rep Med, 2018, 2018: 9409732.
[25] 晁帅恒, 李修岭, 张梦婷, 等. Cronkhite-Canada综合征83例临床分析[J]. 中国临床研究, 2018, 31(3): 397-399. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCK201803028.htm
[26] Zhao R, Huang M, Banafea O, et al. Cronkhite-Canada syndrome: a rare case report and literature review[J]. Bmc Gastroenterol, 2016, 16(1): 23.
[27] Shirin H, Sima N, Amir Houshang M. Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome Associated with Metastatic Colon Cancer[J]. Case Rep Gastroenterol, 2018, 12(1): 109-115.
[28] 王浩, 范小华, 梁学敏, 等. 多学科诊治Cronkhite-Canada综合征1例[J]. 现代消化及介入诊疗, 2021, 26(3): 289-294. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDXH202103002.htm
[29] Daniel ES, Ludwig SL, Lewin KJ, et al. The Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome. An analysis of clinical and pathologic features and therapy in 55 patients[J]. Medicine, 1982, 61(5): 293-309.
[30] Anacker H. Successful treatment of Cronkhite-Canada syndrome using anti-tumor necrosis factor antibody therapy[J]. Endoscopy, 2014, 46(1): E476-E477.
[31] 王晶, 张世洋, 盛永成, 等. 白术治疗胃肠道疾病药理作用研究进展[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2018, 36(12): 2854-2858. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYHS201812008.htm
[32] 赖艳妮, 严一文, 徐培平. 基于系统药理学探索莪术有效成分的药理作用机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2017, 23(14): 177-183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSFX201714029.htm
[33] 冯娅茹, 张文婷, 李二文, 等. 三棱化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2017, 48(22): 4804-4818. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZCYO201722033.htm
[34] Chadalavada R, Brown DK, Walker AN, et al. Cronkhite-Canada syndrome: sustained remission after corticosteroid treatment[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2003, 98(6): 1444-1446.
-




 下载:
下载: