Key links and strategies for the diagnosis and treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with predominant diarrhea
-
摘要: 腹泻型肠易激综合征的发病率逐年增高,症状迁延不愈,目前尚缺乏改善整体症状的有效治疗药物。赵文霞教授梳理总结腹泻型肠易激综合征的关键病机为“肝失疏泄,胃肠气滞,脾气亏虚,湿浊下注”,采用柴胡疏肝散合痛泻要方加减化裁,并配合角药、对药、风药,佐以钩藤治疗,临床疗效显著。Abstract: The incidence rate of irritable bowel syndrome with predominant diarrhea(IBS-D) is increasing year by year, and its symptoms persist. Currently, there is a lack of effective therapeutic drugs to improve the overall symptoms of IBS-D. Professor ZHAO Wenxia summarized the key pathogenesis of IBS-D as follows: "Liver loss and laxity, gastrointestinal qi stagnation, spleen qi deficiency, and downward flow of dampness". In clinical practice, she used Chaihu Shugan Powder combined with Tongxie Yaofang to treat IBS-D, and combined with the use of angular drugs, paired drugs, wind drugs, and rhynchophylla for treatment, with significant clinical efficacy.
-

-
表 1 人口学基本情况
例(%) 年龄/岁 男(76例) 女(38例) 合计 17~<40 39(34.2) 8(7.0) 47(41.3) 40~<60 29(25.5) 22(19.3) 51(44.7) ≥60 8(7.0) 8(7.0) 16(14.0) 表 2 中医证型分布情况
证型 频数 占总证型比例/% 肝郁脾虚证 79 69.3 脾虚湿滞证 20 17.5 湿热壅阻证 10 8.8 寒热错杂证 4 3.5 脾肾阳虚证 1 0.9 -
[1] Ford Alexander C, Lacy Brian E, Talley Nicholas J. Irritable Bowel Syndrome[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 376(26): 2566-2578. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1607547
[2] Frandemarkas A, Törnblom H, Jakobsson S, et al. Work Productivity and Activity Impairment in Irritable Bowel Syndr ome(IBS): A Multifaceted Problem[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2018, 113(10): 1540-1549. doi: 10.1038/s41395-018-0262-x
[3] 中华医学会消化病学分会胃肠功能性疾病协作组, 中华医学会消化病学分会胃肠动力学组. 2020年中国肠易激综合征专家共识意见[J]. 中华消化杂志. 2020, 40(12): 803-818. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLYS202110007.htm
[4] Alexander C, Sperber Ami D, Corsetti Maura, et al. Irritable bowel syndrome[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10263): 1675-1688. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31548-8
[5] 张声生, 魏玮, 杨俭勤. 肠易激综合征中医诊疗专家共识意见(2017)[J]. 中医杂志, 2017, 58(18): 1614-1620. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZYZ201718024.htm
[6] Koloski NA, Jones M, Talley NJ. Evidence that independent gut-to-brain and brain-to-gut pathways operate in the irritable bowel syndrome and functional dyspepsia: a 1-year population-based prospective study[J]. Aliment Pharm Therap, 2016, 44(6): 592-600. doi: 10.1111/apt.13738
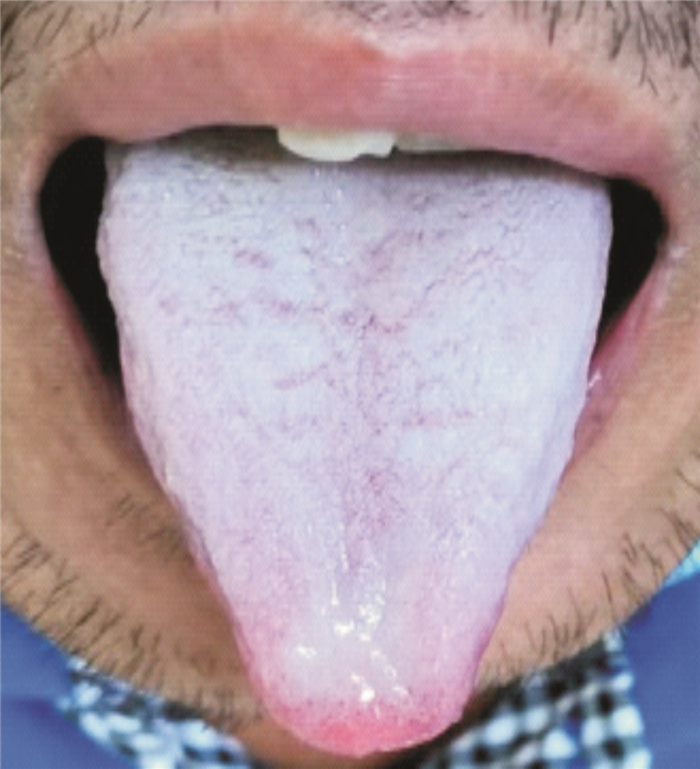
[7] 张丽慧, 赵文霞. 赵文霞重舌诊辨治脾胃肝胆病经验[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2020, 35(8): 3941-3943. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY202008037.htm
[8] 谭宗标, 董卫国. 炎症性肠病相关性腹泻的机制的研究进展[J]. 中国临床医生杂志, 2022, 50(7): 781-784. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLYS202207008.htm
[9] 杨晓, 吴复苍, 阚湘苓. 基于"内脏高敏感理论"辨治腹泻型肠易激综合征经验举隅[J]. 天津中医药大学学报, 2022, 41(6): 706-709. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZYY202206006.htm
[10] 严静, 潘以丰, 陈升捷, 等. 从风药论治腹泻型肠易激综合征经验[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2023, 31(2): 142-145. http://zxpw.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD2/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=e9b03c51-5427-422d-915a-de1520cd3ca9
[11] 张北华, 王微, 王凤云, 等. 痛泻要方干预腹泻型肠易激综合征肝郁脾虚证模型大鼠的效应评价[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2018, 33(10): 4341-4346. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY201810020.htm
[12] Zhuang X, Xiong L, Li L, et al. Alterations of gut microbiota in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 32(1): 28-38. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13471
[13] 姚思杰, 王栩芮, 张明明. 痛泻要方对肝郁脾虚型IBS-D患者的临床疗效及其机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2020, 26(12): 107-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSFX202012016.htm
[14] Wu H, Zhan K, Rao K, et al. Comparison of five diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome(IBS-D)rat models in the brain-gut-microbiota axis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2022, 149: 112811. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112811
[15] Lu Y, Chai Y, Qiu J, et al. Integrated omics analysis reveals the epigenetic mechanism of visceral hypersensitivity in IBS-D[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1062630. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1062630
[16] Altomare A, Di Rosa C, Imperia E, et al. Diarrhea Predominant-Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Effects of Different Nutritional Patterns on Intestinal Dysbiosis and Symptoms[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(5): 1506. doi: 10.3390/nu13051506
[17] Osadchiy V, Martin CR, Mayer EA. The Gut-Brain Axis and the Microbiome: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 17(2): 322-332. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.10.002
[18] Hillestad EMR, van der Meeren A, Nagaraja BH, et al. Gut bless you: The microbiota-gut-brain axis in irritable bowel syndrome[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2022, 28(4): 412-431. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i4.412
[19] Traina G. The role of mast cells in the gut and brain[J]. J Integr Neurosci, 2021, 20(1): 185-196. doi: 10.31083/j.jin.2021.01.313
[20] Ding Y, Zhang H, Liao YY, et al. Structural insights into human brain-gut peptide cholecystokinin receptors[J]. Cell Discov, 2022, 8(1): 55. doi: 10.1038/s41421-022-00420-3
[21] Wei P, Keller C, Li L. Neuropeptides in gut-brain axis and their influence on host immunity and stress[J]. Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 2020, 18: 843-851. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.02.018
[22] 张秉丽, 霍成英, 李有连, 等. 防风提取物通过5-羟色胺信号轴对腹泻型肠易激综合征大鼠结肠黏膜肥大细胞的影响[J]. 浙江中医药大学学报, 2021, 45(8): 857-865. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BHON202108009.htm
[23] 张铮铮, 张进领, 陈惠军, 等. 加味柴胡疏肝散对腹泻型肠易激综合征模型大鼠结肠黏膜胆囊收缩素的影响[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2013, 24(5): 473-475. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXY201305012.htm
-




 下载:
下载: