The effect and mechanism of ursolic acid on reducing cholesterol abundant and inducing apoptosis in colorectal cancer
-
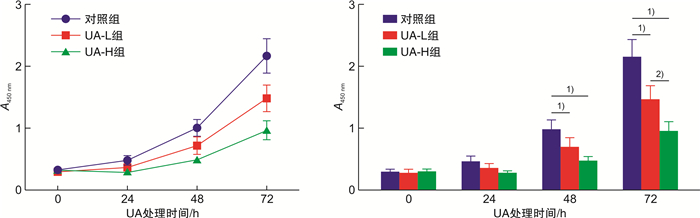
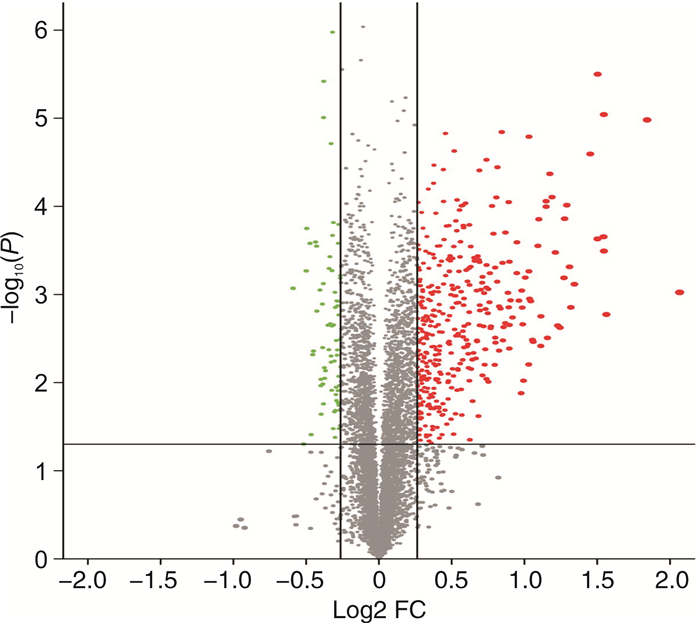
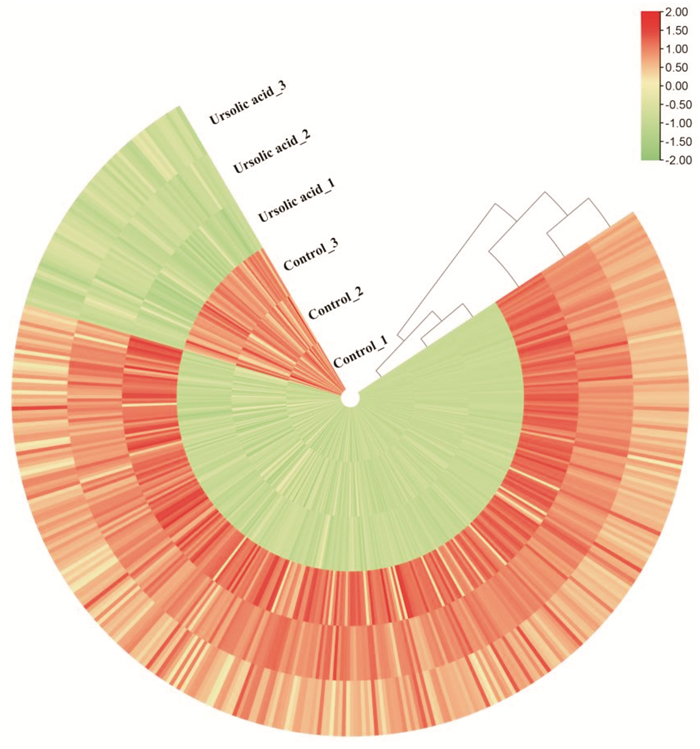
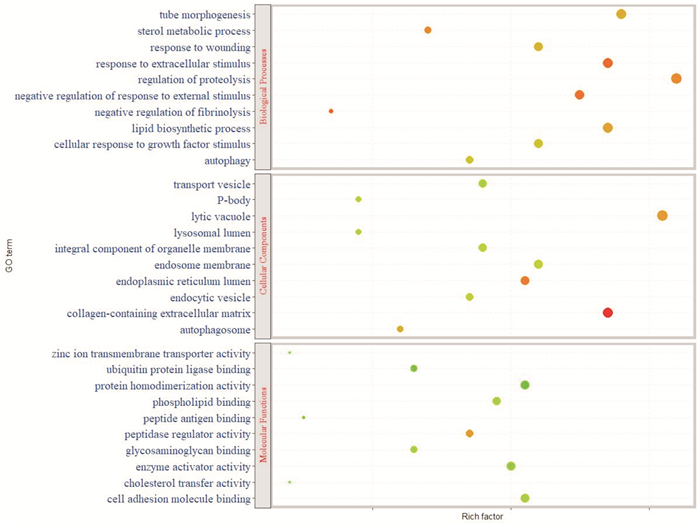
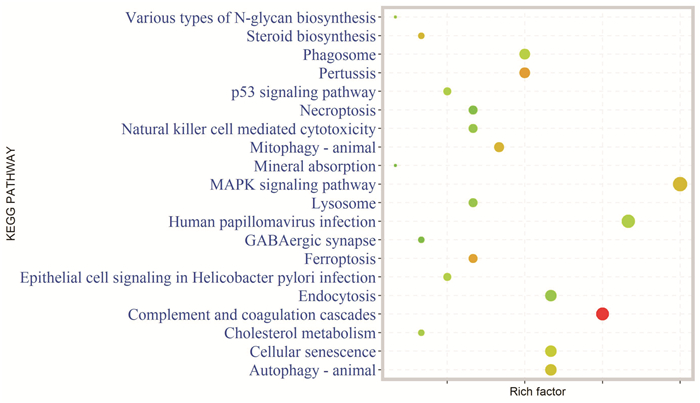
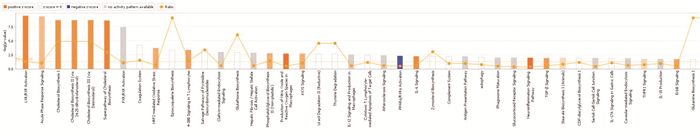
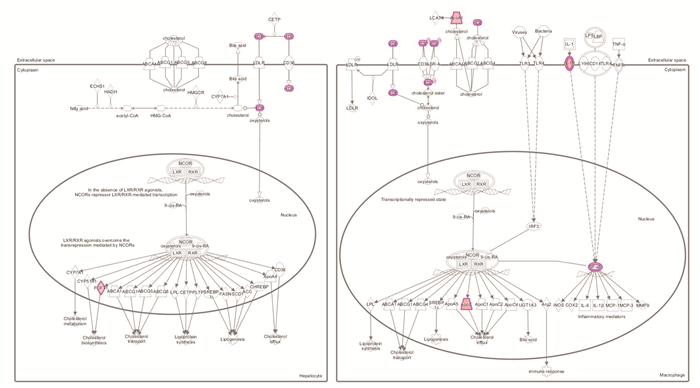
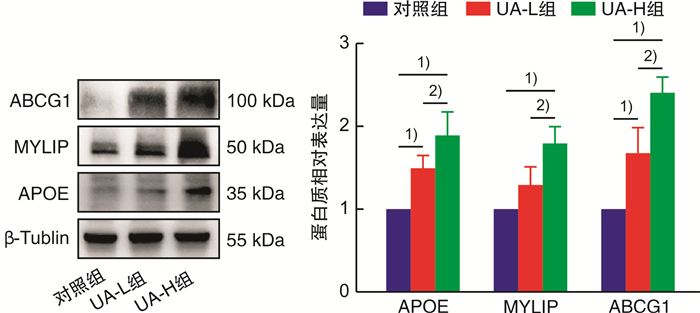
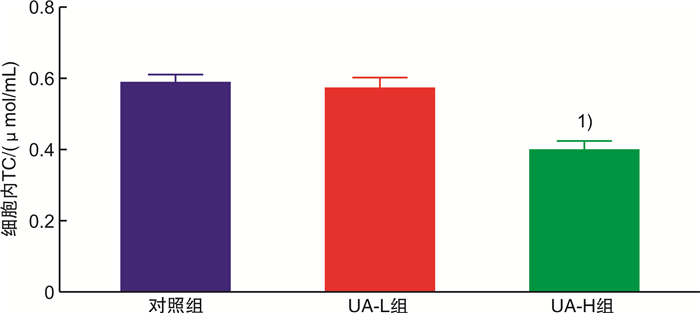
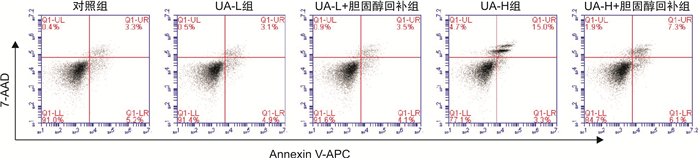
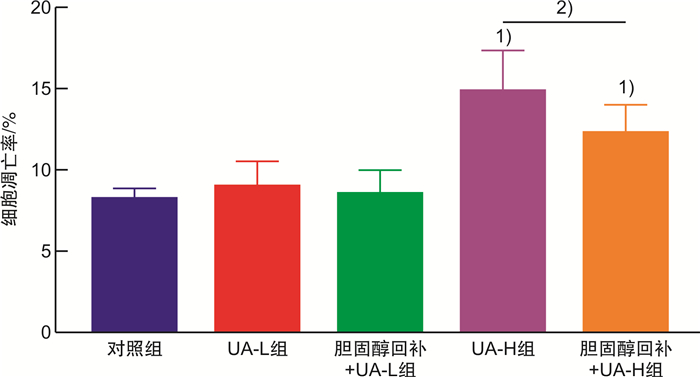
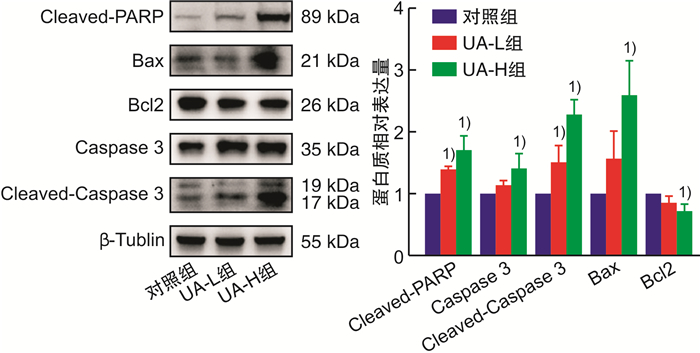
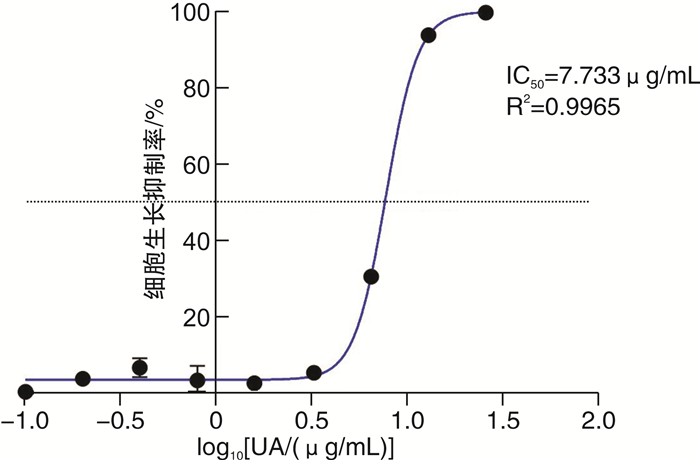
摘要: 目的 基于蛋白组学探讨熊果酸抑制结直肠癌进展的可能生物学机制。方法 以结肠癌HCT-116细胞为研究对象,通过CCK-8法检测不同浓度熊果酸对HCT-116的增殖抑制率。收集熊果酸处理组和对照组样本进行蛋白质提取、蛋白质组学测序并筛选差异蛋白。对差异蛋白进行GO和KEGG富集分析,对目标通路进一步进行GSEA富集分析验证。IPA聚焦关键信号通路,Western blot、细胞内胆固醇含量检测、流式细胞术等实验验证IPA结果。结果 熊果酸在一定范围内呈浓度依赖抑制HCT-116细胞增殖,通过非线性拟合计算出熊果酸对HCT-116细胞的IC50、IC20、IC10分别为7.733、5.926、5.072 μg/mL。选取非毒性剂量1.6 μg/mL和3.2 μg/mL进行后续实验。非毒性剂量下,熊果酸依然呈时间依赖和浓度依赖地抑制HCT-116增殖。蛋白质组学发现对照组与熊果酸处理组之间存在468个差异蛋白,对差异蛋白进行GO和KEGG富集分析显示胆固醇代谢、自噬、铁死亡等生物进程被富集,GSEA进一步发现差异蛋白在胆固醇代谢通路上显著富集(标准化富集评分=1.76,P<0.001)。IPA显示熊果酸显著激活LXR/RXR信号[Z-score=3.00,-log10(P)=9.49]。进一步实验验证结果显示,熊果酸能够上调LXR/RXR靶蛋白E3泛素连接酶MYLIP、三磷酸腺苷结合匣转运蛋白G1、载脂蛋白E的表达,降低细胞内总胆固醇含量,诱导细胞凋亡,胆固醇回补能够拮抗熊果酸所诱导的细胞凋亡。结论 熊果酸激活LXR/RXR信号增加靶蛋白E3泛素连接酶MYLIP、三磷酸腺苷结合匣转运蛋白G1、载脂蛋白E的表达,导致结直肠癌细胞内胆固醇含量降低,增殖被抑制,凋亡增加。Abstract: Objective To investigate the mechanism of ursolic acid(UA) suppresses colorectal cancer progression based on proteomics.Methods HCT-116 was selected as the study target, and the CCK-8 assay was used to detect the inhibition rates on HCT-116 after the treatment with different concentrations of UA. Extracted proteins from UA-treated and control cells were analyzed by proteomic analysis. Differential expression proteins(DEPs) were screened and then analyzed by GO and KEGG enrichment analysis. The target pathway was further verified by GSEA pathway enrichment analysis. Ingenuity pathway analysis(IPA) focused on key signaling pathways, and the results of IPA were verified by Western blot, measurement of intracellular total cholesterol level, and flow cytometry.Results UA inhibited HCT-116 cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. The IC50, IC20and IC10 of UA on HCT-116 were 7.733 μg/mL, 5.926 μg/mL and 5.072 μg/mL, respectively. Next, 1.6 μg/mL and 3.2 μg/mL UA were selected for follow-up experiments. UA inhibited HCT-116 cell proliferation in a time-and dose-dependent manner at non-toxic concentrations. Proteomics identified 468 DEPs between the control group and the UA-treated group. GO and KEGG enrichment analysis showed that the DEPs were associated with many biological processes such as cholesterol metabolism, autophagy, and ferroptosis. GSEA enrichment analysis further confirmed that the cholesterol metabolic pathway was related to the DEPs(NES=1.76, P < 0.001). IPA showed that UA significantly activated the LXR/RXR signaling(Z-score=3.00, -log10(P)=9.49). The verification experiment results showed that UA up-regulated the expression of LXR/RXR target proteins MYLIP, ABCG1, and apolipoprotein E(APOE). In addition, UA decreased the total cholesterol level and induced apoptosis in HCT-116 cells. Furthermore, cholesterol supplementation could antagonize UA-induced apoptosis.Conclusion UA activates LXR/RXR signaling and increases the expression of target proteins MYLIP, ABCG1 and APOE, which results in the decrease of cholesterol level, inhibition of proliferation, and increase of apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells.
-
Key words:
- colorectal cancer /
- ursolic acid /
- cholesterol metabolism /
- LXR/RXR signaling
-

-
[1] Cao W, Chen HD, Yu YW, et al. Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: a secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020[J]. Chin Med J(Engl), 2021, 134(7): 783-791.
[2] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(3): 145-164. doi: 10.3322/caac.21601
[3] 柴仲秋, 戴广法, 周冰. 基于定量蛋白质组学的结直肠肿瘤脾气虚证患者差异表达蛋白研究[J]. 医学信息, 2021, 34(18): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXXX202118002.htm
[4] 张喆, 李依洁, 魏玮, 等. 温肾健脾方对脾肾阳虚证腹泻型肠易激综合征大鼠模型肠组织蛋白组学的影响[J]. 中国临床保健杂志, 2021, 24(4): 507-511. doi: 10.3969/J.issn.1672-6790.2021.04.016
[5] Liu J. Pharmacology of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 1995, 49(2): 57-68. doi: 10.1016/0378-8741(95)90032-2
[6] Zheng JL, Wang SS, Shen KP, et al. Ursolic acid induces apoptosis and anoikis in colorectal carcinoma RKO cells[J]. BMC Complement Med Ther, 2021, 21(1): 52. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03232-2
[7] 何曼, 张梦, 孙强, 等. 熊果酸通过hedgehog信号通路调控结直肠癌细胞HCT116自噬的机制研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2021, 46(5): 1217-1223. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZY202105027.htm
[8] Gayathri R, Priya DK, Gunassekaran GR, et al. Ursolic acid attenuates oxidative stress-mediated hepatocellular carcinoma induction by diethylnitrosamine in male Wistar rats[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2009, 10(5): 933-938.
[9] Mandal S, Gamit N, Varier L, et al. Inhibition of breast cancer stem-like cells by a triterpenoid, ursolic acid, via activation of Wnt antagonist, sFRP4 and suppression of miRNA-499a-5p[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 265: 118854. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118854
[10] Klucken J, Buchler C, Orso E, et al. ABCG1(ABC8), the human homolog of the Drosophila white gene, is a regulator of macrophage cholesterol and phospholipid transport[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2000, 97(2): 817-822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.2.817
[11] Getz GS, Reardon CA. Apoprotein E and reverse cholesterol transport[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(11): 3479. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113479
[12] Zelcer N, Hong C, Boyadjian R, et al. LXR regulates cholesterol uptake through Idol-dependent ubiquitination of the LDL receptor[J]. Science, 2009, 325(5936): 100-104. doi: 10.1126/science.1168974
[13] Wang Y, Liu C, Hu L. Cholesterol regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer by modulating miR-33a-PIM3 pathway[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2019, 511(3): 685-692. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.02.123
[14] Gao SS, Soares F, Wang SY, et al. CRISPR screens identify cholesterol biosynthesis as a therapeutic target on stemness and drug resistance of colon cancer[J]. Oncogene, 2021, 40(48): 6601-6613. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01882-7
[15] Riscal R, Bull CJ, Mesaros C, et al. Cholesterol auxotrophy as a targetable vulnerability in clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer Discov, 2021, 11(12): 3106-3125. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0211
[16] 赵轩竹, 何国平, 梅汉玮, 等. 中医药联合化疗治疗大肠癌的临床进展[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2022, 31(14): 2036-2039. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2022.14.029
[17] 田春风, 郭宇帆, 商佳琪, 等. 熊果酸的生物活性研究进展[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志, 2022, 34(6): 1361-1365. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJHU202108004.htm
[18] Huang BL, Song BL, Xu CQ. Cholesterol metabolism in cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities[J]. Nat Metab, 2020, 2(2): 132-141. doi: 10.1038/s42255-020-0174-0
[19] Ma XY, Bai YP, Liu KX, et al. Ursolic acid inhibits the cholesterol biosynthesis and alleviates high fat diet-induced hypercholesterolemia via irreversible inhibition of HMGCS1 in vivo[J]. Phytomedicine, 2022, 103: 154233. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154233
[20] Cheng J, Liu Y, Liu YJ, et al. Ursolic acid alleviates lipid accumulation by activating the AMPK signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro[J]. J Food Sci, 2020, 85(11): 3998-4008. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15475
[21] Jia YY, Kim SY, Kim JY, et al. Ursolic acid improves lipid and glucose metabolism in high-fat-fed C57BL/6J mice by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha and hepatic autophagy[J]. Mol Nutr Food Res, 2015, 59(2): 344-354. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201400399
[22] 梁奎英, 初霞. 熊果酸对肝细胞胆固醇代谢的影响[J]. 医药导报, 2017, 36(1): 9-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYDB201701004.htm
[23] Kim GH, Kan SY, Kang H, et al. Ursolic acid suppresses cholesterol biosynthesis and exerts anti-cancer effects in hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(19): 4767. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194767
[24] Lin CY, Gustafsson JA. Targeting liver X receptors in cancer therapeutics[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2015, 15(4): 216-224. doi: 10.1038/nrc3912
[25] Liu DB, Wong CC, Fu L, et al. Squalene epoxidase drives NAFLD-induced hepatocellular carcinoma and is a pharmaceutical target[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2018, 10(437): eaap9840. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aap9840
[26] Cardwell CR, Hicks BM, Hughes C, et al. Statin use after colorectal cancer diagnosis and survival: a population-based cohort study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2014, 32(28): 3177-3183.
[27] Tavazoie MF, Pollack I, Tanqueco R, et al. LXR/ApoE activation restricts innate immune suppression in cancer[J]. Cell, 2018, 172(4): 825-840. e18.
[28] 张仁文. 胆固醇诱导HepG2细胞凋亡的研究[J]. 广东化工, 2020, 47(17): 52-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDHG202017023.htm
[29] 郭冰冰. 外源性胆固醇调控Vigilin/ERβ影响KGN细胞凋亡的机制研究[D]. 衡阳: 南华大学, 2019.
-




 下载:
下载: