Theoretical analysis on treatment of autoimmune gastritis from "Deficiency and Stagnation of Qi"
-
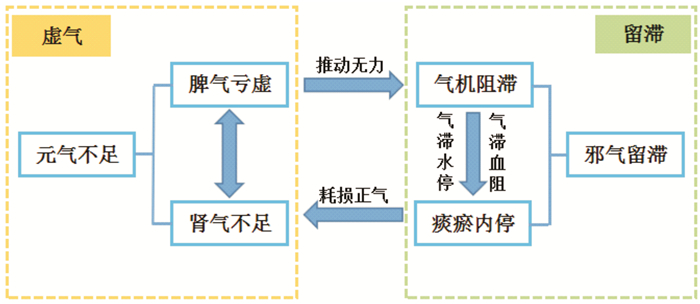
摘要: “虚气留滞”是王永炎院士将《仁斋直指方》和自身临床经验相结合构建的中医理论,“虚气”指元气亏虚,即脾气亏虚和肾气不足;“留滞”指邪气留滞,即气滞、痰凝、血瘀。“虚气留滞”用于描述脾气亏虚、肾气不足,致使气滞、痰凝、血瘀等邪气留滞的病理状态,与自身免疫性胃炎(AG)的发生、发展密切相关。脾气亏虚是AG的始动病机,脾气亏虚,推动无力,则气机阻滞;气滞水停,气滞血阻,则痰瘀内生;痰瘀阻滞,耗损正气,则肾气不足,最终形成了AG的一系列病机演变。AG早期以脾气亏虚、气滞胃脘为基本病机,病理表现为胃底腺黏膜处多灶性淋巴细胞浸润,部分壁细胞向腔内突出,方用香砂六君子汤加减化裁。AG活动期以脾气亏虚、痰瘀阻滞为基本病机,病理表现为胃底腺黏膜弥漫性淋巴细胞浸润,胃底腺萎缩和壁细胞消失,肠嗜铬样细胞增生,肠上皮化生,假幽门腺形成,胰腺腺泡化生等,方用香砂六君子汤合丹参饮加减化裁。AG晚期以脾肾气虚、痰瘀阻滞为主要病机,病理表现为胃底腺显著减少甚至消失,肠嗜铬样细胞显著增生,可伴类息肉病变甚至并发肿瘤,方用附子理中汤合丹参饮加减化裁。Abstract: Deficiency and stagnation of Qi is a Chinese medicine theory constructed by Academician WANG Yongyan by combining Renzhai Zhizhi Fang with his own clinical experience. "Deficient Qi" refers to the deficiency of vitality, that is, the deficiency of spleen and kidney Qi. "Stasis" refers to the retention of evil Qi, namely Qi stagnation, phlegm coagulation and blood stasis. "Deficiency and stagnation of Qi" is used to describe the pathological state of Qi stagnation, phlegm coagulation, blood stasis and other evil Qi stagnation caused by deficiency of spleen Qi or deficiency of kidney Qi, which is closely related to the occurrence and development of autoimmune gastritis(AG). Qi deficiency is the initial pathogenesis of AG. If Qi stagnates and water stops, and Qi stagnates and blood is blocked, phlegm and blood stasis are endogenous. Phlegm and blood stasis block, deplete the vital energy, and the kidney Qi is insufficient, which finally forms a series of pathogenesis evolution of AG. In the early stage of AG, the basic pathogenesis was spleen Qi deficiency and Qi stagnation in the gastric cavity. The pathological manifestation was multifocal lymphocyte infiltration at the mucosa of the gastric fundus gland, and some parietal cells protruded into the cavity. The prescription was reduced with Xiangsha Liujunzi decoction. In the middle stage of AG, the basic pathogenesis is deficiency of spleen Qi and stagnation of phlegm and blood stasis. The pathological manifestations are diffuse lymphocytic infiltration of gastric fundus gland mucosa, atrophy of gastric fundus gland and disappearance of parietal cells, proliferation of enterochromaffin like cells, intestinal epithelial metaplasia, formation of pseudopyloric gland, and pancreatic acinar metaplasia. The prescription is Xiangsha Liujunzi decoction and Danshen decoction. In the late stage of AG, spleen and kidney Qi deficiency and phlegm stasis block are the main pathogenesis. The pathological manifestation is that the gastric fundus gland is significantly reduced or even disappeared, and the enterochromaffin like cells are significantly proliferated. Polypoid lesions and even tumors can be accompanied. The prescription is Fuzi Lizhong decoction and Danshen decoction.
-

-
[1] Venerito M, Sulzer S, Jechorek D. Clinical management of autoimmune gastritis[J]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr, 2022, 147(8): 451-459. doi: 10.1055/a-1520-3562
[2] Kamada T, Maruyama Y, Monobe Y, et al. Endoscopic features and clinical importance of autoimmune gastritis[J]. Dig Endosc, 2022, 34(4): 700-713. doi: 10.1111/den.14175
[3] 吴胜男, 孙为豪. 自身免疫性胃炎发病机制的研究进展[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 42(1): 147-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJYK202201029.htm
[4] Lenti MV, Rugge M, Lahner E, et al. Autoimmune gastritis[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2020, 6(1): 1-19. doi: 10.1038/s41572-019-0135-7
[5] 靳蕊, 张文, 李景南. 自身免疫性胃炎的研究进展[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2021, 41(1): 66-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NMYX202201021.htm
[6] 尹朝, 齐明, 王倩. 自身免疫性胃炎研究进展[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2020(4): 322-325. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20190616-00416
[7] Lenti MV, Miceli E, Cococcia S, et al. Determinants of diagnostic delay in autoimmune atrophic gastritis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 50(2): 167-175. doi: 10.1111/apt.15317
[8] Rustgi SD, Bijlani P, Shah SC. Autoimmune gastritis, with or without pernicious anemia: epidemiology, risk factors, and clinical management[J]. Therap Adv Gastroenterol, 2021, 14: 17562848211038771.
[9] Livzan MA, Gaus OV, Mozgovoi SI, et al. Chronic Autoimmune Gastritis: Modern Diagnostic Principles[J]. Diagnostics(Basel), 2021, 11(11): 2113.
[10] Asfuroglu Kalkan E, Kalkan C, Gumussoy M, et al. Prevalence and predictors of colonoscopic findings in patients with autoimmune gastritis[J]. J Investig Med, 2022, 70(1): 73-78. doi: 10.1136/jim-2021-001911
[11] Notsu T, Adachi K, Mishiro T, et al. Prevalence of autoimmune gastritis in individuals undergoing medical checkups in Japan[J]. Intern Med, 2019, 58(13): 1817-1823. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.2292-18
[12] Hall SN, Appelman HD. Autoimmune gastritis[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2019, 143(11): 1327-1331. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2019-0345-RA
[13] 莫方正, 郭哲宇, 周斌. 周斌微观辨证治疗自身免疫性胃炎经验[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2021, 36(2): 869-872. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY202102066.htm
[14] 梁春耕, 李静波, 肖定洪, 等. 69例自身免疫性胃炎证候分布规律的单中心回顾性横断面研究[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2022, 30(7): 495-499. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2022.07.06
[15] 古金晓, 于海青, 李伟荣, 等. 基于"虚气留滞"病机探讨心脑同治理论[J]. 环球中医药, 2022, 15(5): 792-796. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HQZY202205011.htm
[16] 黎莉莉, 刘冲冲, 董笑克, 等. 基于"虚气留滞"理论探讨颈动脉斑块的病机[J]. 环球中医药, 2021, 14(5): 855-859. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HQZY202105019.htm
[17] 杨梦, 胡思远, 李琳, 等. 基于"虚气留滞"理论探讨慢性肾衰竭"微炎症状态"的病机及中药防治进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28(16): 229-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSFX202216029.htm
[18] 谭丽, 马羽, 官杰, 等. 冯兴中基于"虚气流滞"论治帕金森病经脑深部电刺激术后[J]. 中医杂志, 2022, 63(17): 1625-1630. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZYZ202217006.htm
[19] 官杰, 冯兴中. 基于"虚气流滞"学说论糖尿病微血管病变的防治[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志, 2020, 26(8): 1065-1067. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYJC202008012.htm
[20] (宋)杨士瀛. 仁斋直指[M]. 北京: 中医古籍出版社, 2016: 326-326.
[21] 高维, 郭蓉娟, 王永炎. 论七情致病"虚气留滞"病因病机新认识[J]. 环球中医药, 2019, 12(10): 1490-1494. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HQZY201910007.htm
[22] (清)喻昌. 医门法律[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社, 2002: 77-77.
[23] (明)赵献可. 医贯[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2005: 117-117.
[24] Weise F, Vieth M, Reinhold D, et al. Gastric cancer in autoimmune gastritis: a case-control study from the German centers of the staR project on gastric cancer research[J]. United European Gastroenterol J, 2020, 8(2): 175-184.
[25] Massironi S, Zilli A, Elvevi A, et al. The changing face of chronic autoimmune atrophic gastritis: an updated comprehensive perspective[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2019, 18(3): 215-222.
[26] (清)程杏轩. 医述十六卷[M]. 合肥: 安徽科学技术出版社, 1983: 746-746.
[27] (清)王清任. 医林改错[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1991: 43-43.
[28] 张瑞贤. 本草名著集成[M]. 北京: 华夏出版社, 1998: 1102-1102.
[29] (清)陈士铎. 本草新编[M]. 太原: 山西科学技术出版社, 2011: 11-11.
[30] (明)张介宾. 景岳全书[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社, 1994: 400-400.
-




 下载:
下载: