Research progress of mesenchymal stem cells regulating macrophage polarization in ulcerative colitis
-
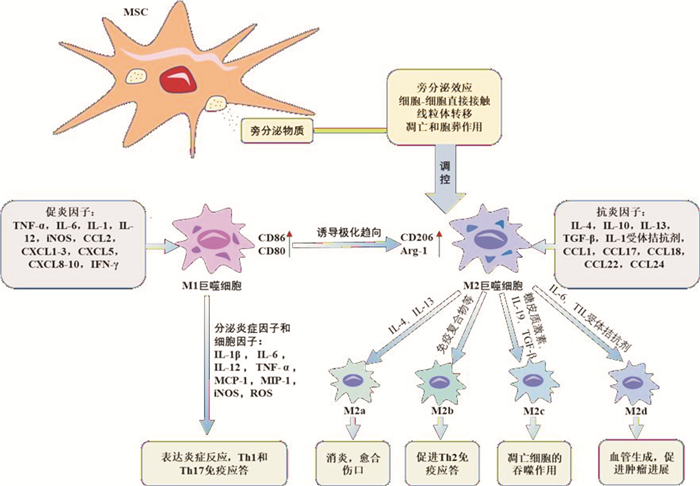
摘要: 溃疡性结肠炎(ulcerative colitis,UC)是一种常见的全球范围性的炎症性肠病。因难以治愈且易复发,治疗费用高昂,严重影响患者的生活质量。目前UC的发病机制尚不明确,临床尚无特异性治疗方案。巨噬细胞在UC病理发展中发挥了关键作用,可诱导促炎表型的M1巨噬细胞以及抗炎表型的M2巨噬细胞免疫稳态。间充质干细胞(mesenchymal stem cells,MSCs)具有多向分化潜能和免疫调节能力,可调控巨噬细胞极化,维持巨噬细胞免疫稳态,改善体内炎症环境。本文综述MSCs调控巨噬细胞极化在UC中的功能和在治疗中的作用,以及其可能的作用机制,期望为未来UC的治疗提供新的见解。Abstract: Ulcerative colitis(UC) is a common global inflammatory bowel disease that is difficult to cure and prone to recurrence, leading to high treatment costs and severely impacting patients' quality of life. The pathogenesis of UC is currently unclear, and there are no specific treatment plans in clinical practice. Macrophages play a critical role in the pathological development of UC by inducing the pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype and the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype to maintain immune homeostasis. Mesenchymal stem cells(MSCs) have multi-directional differentiation potential and immunomodulatory capabilities, and can regulate macrophage polarization to maintain immune homeostasis and improve the inflammatory environment in the body. This article summarizes the functions of MSCs in regulating macrophage polarization and their potential mechanisms of action in UC, as well as their roles in treatment, to provide new insights for future UC therapy.
-
Key words:
- mesenchymal stem cell /
- macrophage polarization /
- ulcerative colitis
-

-
表 1 M2巨噬细胞亚型特征
M2亚型 激活因子 表面标志物 分泌因子 功能作用 M2a IL-4、IL-13、真菌或蠕虫感染 IL-1受体、CD206、Arg-1、FIZZ1、Ym1/2 IL-10、IL-1受体拮抗剂、TGF-β、CCL17、CCL18、CCL22、CCL24 消除炎症、愈合伤口、杀灭寄生虫 M2b 免疫复合物、TLR/IL-1β配体 IL-6受体、IL-10受体、IL-12受体、CD86 IL-1、IL-6、IL-10、TNF-α、CCL1 增强Th2分化、加强感染、促进肿瘤进程 M2c 糖皮质激素、IL-10、TGF-β CD163、CD206、TLR-1、TLR-8、Arg-1 IL-10、TGF-β、CCL13、CCL16、CCL18 免疫抑制、凋亡细胞的吞噬作用 M2d IL-6、TLR拮抗剂 IL-10受体、IL-12受体 IL-10、IL-12、TNF-α、TGF-β、VEGF 血管生成、促进肿瘤进程 -
[1] Schlegel N, Boerner K, Waschke J. Targeting desmosomal adhesion and signalling for intestinal barrier stabilization in inflammatory bowel diseases-Lessons from experimental models and patients[J]. Acta Physiol(Oxf), 2021, 231(1): e13492. doi: 10.1111/apha.13492
[2] GBD 2017 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Collaborators. The global, regional, and national burden of inflammatory bowel disease in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 5(1): 17-30. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30333-4
[3] Pan X, Zhu Q, Pan LL, et al. Macrophage immunometabolism in inflammatory bowel diseases: From pathogenesis to therapy[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2022, 238: 108-176.
[4] Park MD, Silvin A, Ginhoux F, et al. Macrophages in health and disease[J]. Cell, 2022, 185(23): 4259-4279. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.10.007
[5] Chhibba T, Ma C. Is there room for immunomodulators in ulcerative colitis?[J]. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2020, 20(4): 379-390. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2020.1708896
[6] Eshghi F, Tahmasebi S, Alimohammadi M, et al. Study of immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in mouse model of LPS induced systemic inflammation[J]. Life Sci, 2022: 120938.
[7] Zhang M, Johnson-Stephenson TK, Wang W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome-educated macrophages alleviate systemic lupus erythematosus by promoting efferocytosis and recruitment of IL-17(+)regulatory T cell[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2022, 13(1): 484. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03174-7
[8] Kaluzna A, Olczyk P, Komosinska-Vassev K. The Role of Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells in the Pathogenesis and Development of the Inflammatory Response in Ulcerative Colitis[J]. J Clin Med, 2022, 11(2): 400. doi: 10.3390/jcm11020400
[9] Yunna C, Mengru H, Lei W, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2020, 877: 173090. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173090
[10] Du G, Xiong L, Li X, et al. Peroxisome Elevation Induces Stem Cell Differentiation and Intestinal Epithelial Repair[J]. Dev Cell, 2020, 53(2): 169-184. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.03.002
[11] Fu Y, Li J, Li M, et al. Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Inflammation-Related Tumorigenesis via Modulating Macrophages[J]. Stem Cells Int, 2022, 2022: 1617229.
[12] Cao X, Duan L, Hou H, et al. IGF-1C hydrogel improves the therapeutic effects of MSCs on colitis in mice through PGE2-mediated M2 macrophage polarization[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(17): 7697-7709. doi: 10.7150/thno.45434
[13] Yu D, Zhao Y, Wang H, et al. IL-1beta pre-stimulation enhances the therapeutic effects of endometrial regenerative cells on experimental colitis[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2021, 12(1): 324. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02392-9
[14] Zhang N, Chen Y, Huang C, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells may reduce intestinal epithelial damage in ulcerative colitis by communicating with macrophages and blocking inflammatory pathways: an analysis in silico[J]. Aging(Albany NY), 2022, 14(6): 2665-2677.
[15] Yuan Y, Ni S, Zhuge A, et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reprogram M1 Macrophage Metabolism via PHD2/HIF-1alpha Pathway in Colitis Mice[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 859806. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.859806
[16] Shin TH, Ahn JS, Oh SJ, et al. TNF-alpha Priming Elicits Robust Immunomodulatory Potential of Human Tonsil-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Alleviate Murine Colitis[J]. Biomedicines, 2020, 8(12): 561. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8120561
[17] Alvites R, Branquinho M, Sousa AC, et al. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells and Their Paracrine Activity-Immunomodulation Mechanisms and How to Influence the Therapeutic Potential[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2022, 14(2): 381. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020381
[18] Zheng Z, Wang J. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with Atractylodes macrocephala polysaccharide attenuate ulcerative colitis[J]. Bioengineered, 2022, 13(1): 824-833. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2012954
[19] Altemus J, Dadgar N, Li Y, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells' acellular product extracellular vesicles as a potential therapy for Crohn's disease[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2022, 237(7): 3001-3011. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30756
[20] Liu J, Lai X, Bao Y, et al. Intraperitoneally Delivered Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Experimental Colitis Through THBS1-Mediated Induction of IL-10-Competent Regulatory B Cells[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 853894. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.853894
[21] Li Q, Lian Y, Deng Y, et al. mRNA-engineered mesenchymal stromal cells expressing CXCR2 enhances cell migration and improves recovery in IBD[J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2021, 26: 222-236. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.07.009
[22] Kang JY, Oh MK, Joo H, et al. Xeno-Free Condition Enhances Therapeutic Functions of Human Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells against Experimental Colitis by Upregulated Indoleamine 2, 3-Dioxygenase Activity[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9(9): 2913. doi: 10.3390/jcm9092913
[23] Ortiz-Virumbrales M, Menta R, Perez LM, et al. Human adipose mesenchymal stem cells modulate myeloid cells toward an anti-inflammatory and reparative phenotype: role of IL-6 and PGE2[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020, 11(1): 462. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01975-2
[24] Shen Q, Huang Z, Yao J, et al. Extracellular vesicles-mediated interaction within intestinal microenvironment in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. J Adv Res, 2022, 37: 221-233. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.07.002
[25] An JH, Li Q, Bhang DH, et al. TNF-alpha and INF-gamma primed canine stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate experimental murine colitis[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 2115. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58909-4
[26] An JH, Li Q, Ryu MO, et al. TSG-6 in extracellular vesicles from canine mesenchymal stem/stromal is a major factor in relieving DSS-induced colitis[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(2): e220756.
[27] Qian W, Huang L, Xu Y, et al. Hypoxic ASCs-derived Exosomes Attenuate Colitis by Regulating Macrophage Polarization via miR-216a-5p/HMGB1 Axis[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2023;29(4): 602-619. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izac225
[28] Liu H, Liang Z, Wang F, et al. Exosomes from mesenchymal stromal cells reduce murine colonic inflammation via a macrophage-dependent mechanism[J]. JCI Insight, 2019, 4(24): e131273. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.131273
[29] Gan J, Sun L, Chen G, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Encapsulated Oral Microcapsules for Acute Colitis Treatment[J]. Adv Healthc Mater, 2022, 11(17): e2201105. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202201105
[30] Jiao Y, Chen X, Nong B, et al. Transplantation of Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated with Hydroactive(R)Gel promotes diabetic wound antifibrotic healing in type 2 diabetic rats[J]. J Mater Chem B, 2022, 10(40): 8330-8346. doi: 10.1039/D2TB01649D
[31] Li Y, Zhang D, Xu L, et al. Cell-cell contact with proinflammatory macrophages enhances the immunotherapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cells in two abortion models[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2019, 16(12): 908-920. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0204-6
[32] Abe Y, Ochiai D, Sato Y, et al. Prophylactic Therapy with Human Amniotic Fluid Stem Cells Improves Long-Term Cognitive Impairment in Rat Neonatal Sepsis Survivors[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(24): 9590. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249590
[33] Velarde F, Ezquerra S, Delbruyere X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated transfer of mitochondria: mechanisms and functional impact[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2022, 79(3): 177. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04207-3
[34] Lu D, Jiao X, Jiang W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells influence monocyte/macrophage phenotype: Regulatory mode and potential clinical applications[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2023, 165: 115042. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115042
[35] Yuan Y, Yuan L, Li L, et al. Mitochondrial transfer from mesenchymal stem cells to macrophages restricts inflammation and alleviates kidney injury in diabetic nephropathy mice via PGC-1alpha activation[J]. Stem Cells, 2021, 39(7): 913-928. doi: 10.1002/stem.3375
[36] Boada-Romero E, Martinez J, Heckmann BL, et al. The clearance of dead cells by efferocytosis[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2020, 21(7): 398-414. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0232-1
[37] Zheng C, Sui B, Zhang X, et al. Apoptotic vesicles restore liver macrophage homeostasis to counteract type 2 diabetes[J]. J Extracell Vesicles, 2021, 10(7): e12109. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12109
[38] Liu J, Qiu X, Lv Y, et al. Apoptotic bodies derived from mesenchymal stem cells promote cutaneous wound healing via regulating the functions of macrophages[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020, 11(1): 507. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-02014-w
[39] Ghahremani PM, Soudi S, Ghanbarian H, et al. Effect of efferocytosis of apoptotic mesenchymal stem cells(MSCs)on C57BL/6 peritoneal macrophages function[J]. Life Sci, 2018, 212: 203-212. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.09.052
-




 下载:
下载: