Mechanism study of steaming navel therapy in the treatment of spleen deficiency and dampness type diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome model rats
-
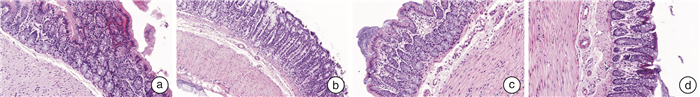
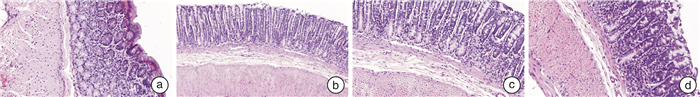
摘要: 目的 研究蒸脐疗法治疗脾虚湿盛型腹泻型肠易激综合征(diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome,IBS-D)模型大鼠的作用机制。方法 将40只SD雄性大鼠分为空白组、模型组、中药蒸脐组、西药对照组,每组各10只。采用番泻叶浸出液灌胃给药联合慢性温和束缚应激加孤养法建立大鼠IBS-D模型。造模成功后,各组采用相应的处理方法连续干预14 d,观察大鼠一般情况、体重、粪便干湿比重及腹部回缩反射(abdominal wall retraction,AWR)评分。用ELISA法测定大鼠血清、结肠、海马组织中P物质(substance P,SP)的含量,对结肠组织进行病理学观察。结果 ① 蒸脐疗法可显著改善IBS-D模型大鼠的精神状态、排便情况、粪便性状、被毛颜色等一般情况(P < 0.05)并恢复其体重的正常增长(P < 0.05);②蒸脐疗法可降低大鼠海马、血清、结肠组织中SP的含量(P < 0.01)及AWR评分(P < 0.01),调控内脏高敏性,减轻肠道炎症,从而缓解IBS-D的临床症状。结论 蒸脐疗法可能是通过调控SP水平,降低内脏高敏性,从而达到治疗脾虚湿盛型IBS-D大鼠的目的。Abstract: Objective To investigate the mechanism of steaming navel therapy in treating diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome(IBS-D) model rats with spleen deficiency and dampness.Methods Forty male SD rats were divided into a blank group, a model group, a traditional Chinese medicine navel steaming group, and a western medicine control group, with 10 rats in each group. A rat model of IBS-D was established by gavage administration of senna leaf extract combined with chronic mild restraint stress and solitary confinement. After successful modeling, each group was intervened continuously for 14 days using corresponding treatment methods, and the general condition, body weight, fecal dry wet density, and abdominal wall retraction(AWR) score of the rats were observed. The content of substance P (SP) in rat serum, colon, and hippocampus tissue was measured using the ELISA method, and perform pathological observation on colon tissue.Results ① Umbilical steaming therapy can significantly improve the general conditions such as mental state, defecation, fecal characteristics, and coat color of IBS-D model rats(P < 0.05) and restore normal weight growth(P < 0.05); ②Umbilical steaming therapy can reduce the content of SP in hippocampus, serum, and colon tissues(P < 0.01), lower the AWR score of rats(P < 0.01), regulate visceral hypersensitivity, reduce intestinal inflammation, and alleviate clinical symptoms of IBS-D.Conclusion Steaming navel therapy may achieve the goal of treating spleen deficiency and dampness excess type of IBS-D by regulating substance P and reducing visceral hypersensitivity.
-

-
表 1 各组大鼠粪便Bristol分级评分比较
分,X±S 组别 例数 造模后 治疗后 空白组 10 3.42±0.61 3.52±0.51 模型组 10 6.30±0.731) 6.53±0.50 西药对照组 10 6.10±0.771) 4.75±1.072) 中药蒸脐组 10 6.18±0.891) 4.08±0.952)3) 与空白组比较,1)P < 0.05;与模型组比较,2)P < 0.05;与西药对照组比较,3)P < 0.05。 表 2 各组大鼠造模前、造模后、治疗后体重的变化
g,X±S 组别 例数 造模前 造模后 治疗后 空白组 10 220.15±3.69 355.39±10.70 433.36±4.31 模型组 10 219.43±4.37 301.57±7.871) 383.00±6.961) 西药对照组 10 219.90±3.93 303.87±8.691) 402.77±6.251)2) 中药蒸脐组 10 218.23±4.39 304.40±7.571) 422.44±5.621)2)3) 与空白组比较,1)P < 0.05;与模型组比较,2)P < 0.05;与西药对照组比较,3)P < 0.05。 表 3 各组大鼠治疗前后粪便干湿比重比较
%,X±S 组别 例数 治疗前 治疗后 空白组 10 40.21±3.34 42.62±2.54 模型组 10 60.23±4.891) 58.13±2.33 西药对照组 10 60.34±4.351) 42.98±2.092) 中药蒸脐组 10 60.18±4.501) 35.09±1.892)3) 与空白组比较,1)P < 0.05;与模型组比较,2)P < 0.01;与西药对照组比较,3)P < 0.01。 表 4 各组大鼠治疗前AWR评分比较
分,X±S 组别 例数 20 mmHg 40 mmHg 60 mmHg 80 mmHg 空白组 10 0.47±0.10 0.89±0.12 1.56±0.20 2.50±0.71 模型组 10 1.26±0.521) 2.43±0.441) 3.12±0.911) 3.67±0.231) 西药对照组 10 1.25±0.451) 2.43±0.301) 3.11±0.491) 3.67±0.331) 中药蒸脐组 10 1.26±0.501) 2.43±0.421) 3.11±0.121) 3.67±0.451) 与空白组比较,1)P < 0.01。 表 5 各组大鼠治疗后AWR评分比较
分,X±S 组别 例数 20 mmHg 40 mmHg 60 mmHg 80 mmHg 空白组 10 0.56±0.23 0.89±0.33 1.60±0.21 2.48±0.44 模型组 10 1.30±0.191) 2.53±0.201) 3.10±0.901) 3.67±0.941) 西药对照组 10 0.46±0.122) 1.14±0.362) 1.89±0.372) 2.62±0.602) 中药蒸脐组 10 0.35±0.422)3) 0.94±0.212)3) 1.71±0.112)3) 2.10±0.342)3) 与空白组比较,1)P < 0.01;与模型组比较,2)P < 0.01;与西药对照组比较,3)P < 0.05。 表 6 各组大鼠血清、结肠、海马组织中SP含量的变化
ng/mL,X±S 组别 例数 血清 结肠组织 海马组织 空白组 10 4.02±0.56 2.01±0.40 2.32±0.32 模型组 10 6.33±0.441) 4.69±0.741) 4.76±0.121) 西药对照组 10 4.93±0.342) 1.85±0.822) 2.89±0.192) 中药蒸脐组 10 4.21±0.762)3) 1.70±0.492)3) 2.50±0.202)3) 与空白组比较,1)P < 0.01;与模型组比较,2)P < 0.01;与西药对照组比较,3)P < 0.05。 -
[1] Pimentel M, Lembo A. Microbiome and Its Role in Irritable Bowel Syndrome[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2020, 65(3): 829-839. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06109-5
[2] Black CJ, Yiannakou Y, Houghton LA, et al. Epidemiological, Clinical, and Psychological Characteristics of Individuals with Self-reported Irritable Bowel Syndrome Based on the Rome Ⅳ vs Rome ⅢCriteria[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18(2): 392-398. e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.05.037
[3] Canakis A, Haroon M, Weber HC. Irritable bowel syndrome and gut microbiota[J]. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes, 2020, 27(1): 28-35. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000523
[4] 邓长卿, 潘丽敏, 林裕辉, 等. 蒸脐疗法联合中药治疗脾胃虚弱型肠易激综合征验案举隅[J]. 中国民族民间医药, 2019, 28(11): 66-68.
[5] 谢明君, 姜劼琳, 葛来安. 中药蒸脐疗法治疗肠易激综合征的效果[J]. 中国当代医药, 2019, 26(13): 178-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4721.2019.13.054
[6] 潘丽敏, 林裕辉, 葛来安. 葛来安主任医师运用中药联合蒸脐疗法治疗脾虚湿盛型肠易激综合征(腹泻型)验案举隅[J]. 中国民族民间医药, 2019, 28(7): 61-62, 87.
[7] 谢明君, 姜劼琳, 葛来安. 加味痛泻要方配合中药蒸脐疗法治疗腹泻型肠易激综合征临床观察[J]. 中国中医药现代远程教育, 2019, 17(17): 48-50.
[8] 裴丽霞, 张伟, 宋亚芳, 等. 电针"天枢"穴对感染后肠易激综合征内脏高敏感模型大鼠结肠肥大细胞活化和P物质的影响[J]. 针刺研究, 2018, 43(7): 419-423.
[9] 李丹, 吕妍, 唐方. 腹泻型肠易激综合征大鼠模型的建立[J]. 天津中医药, 2009, 26(3): 240-242.
[10] 李忠仁. 实验针灸学[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国中医药出版社, 2007: 272-272.
[11] 付怡茗, 魏晓彤, 柏寒, 等. 电针与穴位注射法治疗腹泻型肠易激综合征小鼠模型效果的比较研究[J]. 中医药导报, 2021, 27(9): 47-51.
[12] Häuser W, Marschall U, Layer P, et al. The Prevalence, Comorbidity, Management and Costs of Irritable Bowel Syndrome[J]. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 2019, 116(27-28): 463-470.
[13] Hasan AU, Rahman A, Kobori H. Interactions between Host PPARs and Gut Microbiota in Health and Disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(2): 387.
[14] 石美凤, 葛来安. 蒸脐疗法治疗腹泻型肠易激综合征45例[J]. 江西中医药, 2020, 51(5): 40-42.
[15] Peña S, Carrasco G, Rojas P, et al. Determination of subtypes of Blastocystis sp. in Chilean patients with and without inflammatory bowel syndrome, A preliminary report[J]. Parasite Epidemiol Control, 2019, 8: e00125.
[16] 王岩, 陈朝元, 吴晖, 等. 痛泻要方对脾虚湿盛型D-IBS患者结肠粘膜VIP和SP的影响[J]. 福建中医药, 2010, 41(6): 1-4.
[17] 孔梅, 邢长永, 王莺. 痛泻要方颗粒剂干预腹泻型肠易激综合征结肠黏膜VIP、SP表达的临床研究[J]. 中药材, 2010, 33(10): 1668-1669.
-




 下载:
下载: