Clinical study of Huqi Zhengxiao Decoction with lenvatinib in treating 93 patients with stage Ⅲ hepatitis B related liver cancer
-
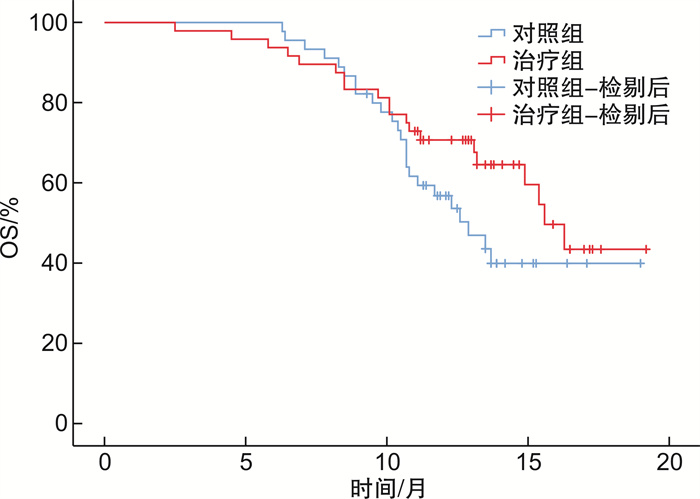
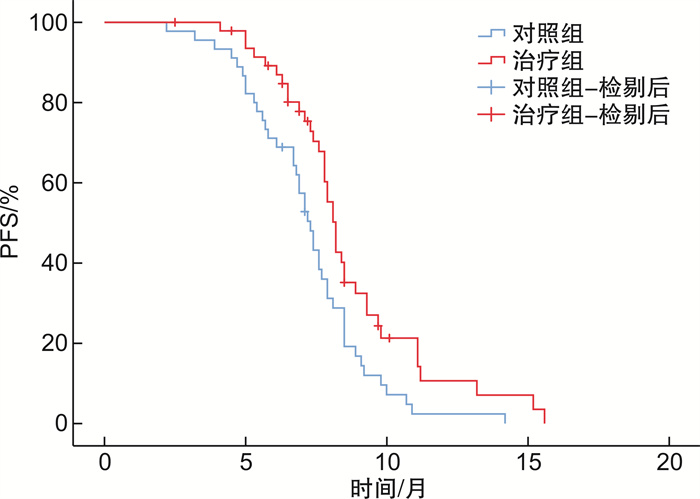
摘要: 目的 评价槲芪癥消汤联合仑伐替尼治疗Ⅲ期乙肝相关肝癌的有效性及安全性。方法 采用实用性随机对照方法,纳入Ⅲ期乙肝相关肝癌患者93例,随机分为治疗组48例,对照组45例。对照组采用仑伐替尼治疗(体重<60 kg,8 mg/次,1次/d;体重≥60 kg,12 mg/次,1次/d),治疗组在对照组用药基础上联合槲芪癥消汤中医治疗方案。两组均连续治疗24周,随访24周。主要研究终点为无进展生存期(progression-free survival,PFS),次要研究终点包括总生存期(overall survival,OS)、治疗前后生活质量症状评分、中医证候评分和安全性。结果 两组患者的基线特征差异无统计学意义,治疗组延长了Ⅲ期乙肝相关肝癌患者的PFS(8.7个月vs.7.2个月,P=0.007),OS未见显著获益(14.8个月vs.13.8个月,P=0.147)。槲芪癥消汤联合治疗能够改善患者的中医证候评分及腹胀(P=0.010)、黄疸(P=0.007)、营养改变(P=0.004)3个维度的生活质量评分,且能减少手足综合征(P=0.040)、高血压(P=0.004)及疲乏(P=0.013)等不良反应。结论 槲芪癥消汤联合仑伐替尼治疗可提高Ⅲ期乙肝相关肝癌患者的PFS,改善生活质量,且安全性良好。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the efficacy and safety of Huqi Zhengxiao Decoction(HQZX) combined with lenvatinib in the treatment of stage Ⅲ hepatitis B related liver cancer.Methods A practical randomized control method was used. Eighty-two patients with stage Ⅲ hepatitis B related liver cancer were enrolled and randomly divided into the treatment group and the control group, with 41 patients in each group. The control group was treated with lenvatinib(body weight < 60 kg, 8 mg/d, body weight ≥ 60 kg, 12 mg/d). The treatment group was treated with a combination of HQZX on the basis of the control group's medication. Both groups were treated continuously for 24 weeks and followed up for 24 weeks. The main endpoint of the study was progression free survival(PFS), while secondary endpoints included overall survival(OS), quality of life symptom score before and after treatment, Traditional Chinese Medicine syndrome score, and safety.Results There was no significant difference in baseline characteristics between the two groups. The treatment group prolonged the PFS of patients with stage Ⅲ hepatitis B related liver cancer(8.7 months vs 7.2 months, P=0.007), and OS did not benefit significantly(14.8 months vs 13.8 months, P=0.147). The combination treatment of HQZX can improve the Traditional Chinese Medicine syndrome score and the quality of life scores in the three dimensions of abdominal distension(P=0.010), jaundice(P=0.007), and nutritional changes(P=0.004) in the EORTC QLQ-HCC-18 scale. It can also reduce adverse reactions to hand and foot syndrome(P=0.040), hypertension(P=0.004) and fatigue(P=0.013).Conclusion HQZX combined with lenvatinib treatment can significantly improve the PFS of patients with stage Ⅲ hepatitis B related liver cancer, and improve the quality of life with good safety.
-

-
表 1 两组患者的临床资料比较
例(%) 临床资料 治疗组(n=48) 对照组(n=45) χ2 P 性别 0.180 0.671 男 42(87.5) 38(84.4) 女 6(12.5) 7(15.6) 年龄/岁 0.300 0.862 <65 37(77.1) 34(75.6) 65~75 11(22.9) 11(24.4) Child-Pugh分级 0.617 0.432 A级 39(81.3) 32(71.1) B级 9(18.7) 13(28.9) ECOG评分/分 1.322 0.250 1 20(41.7) 16(35.6) 2 28(58.3) 29(64.4) AFP水平/(ng/mL) 1.062 0.303 <400 27(56.3) 30(66.7) ≥400 21(43.7) 15(33.3) 分期 1.229 0.268 Ⅲa 30(62.5) 23(51.1) Ⅲb 18(37.5) 22(48.9) 前期治疗 0.764 0.739 无 13(27.1) 11(24.4) 介入治疗 31(64.6) 32(71.1) 手术治疗 4(8.3) 2(4.5) 分化程度 1.039 1.000 高 1(2.1) 0 中 3(6.3) 3(6.7) 低 4(8.3) 4(8.9) 无 40(83.3) 38(84.4) 表 2 PFS的单因素预后分析
影响因素 χ2 P 性别 0.436 0.509 年龄 3.189 0.074 Child-Pugh分级 2.221 0.136 ECOG评分 1.578 0.209 AFP水平 0.110 0.740 疾病分期 8.313 0.004 前期治疗 8.902 0.012 分化程度 2.731 0.435 是否使用中药 7.326 0.007 表 3 PFS的多因素预后分析
影响因素 OR(95%CI) P 分期(Ⅲa vs Ⅲb) 1.851(1.159~2.957) 0.010 前期治疗(介入vs无) 0.279(0.082~0.948) 0.041 前期治疗(手术vs无) 0.670(0.369~1.000) 0.050 是否使用中药(否vs是) 0.621(0.396~0.974) 0.038 表 4 两组治疗前后中医疗效比较
例 组别 例数 疗效评价 有效率/% 显效 有效 无效 治疗组 37 6 15 16 56.8 对照组 32 0 7 25 21.9 P 0.002 表 5 两组患者生活质量量表评分比较
分,X±S 维度 治疗组(n=48) 对照组(n=45) P1 P2 治疗前 治疗后 治疗前 治疗后 腹胀 45.53±33.13 26.01±22.99 47.15±31.60 41.46±29.60 0.010 0.178 躯体改变 17.89±25.11 9.76±12.90 17.89±22.79 13.82±14.39 0.050 0.095 黄疸 22.36±23.75 10.57±12.22 25.20±23.61 19.11±17.30 0.007 0.093 疼痛 19.92±19.44 17.07±17.28 22.76±22.28 18.29±16.16 0.285 0.110 发热 32.93±23.71 26.83±3.54 32.11±23.98 30.49±18.22 0.132 0.458 营养改变 39.67±20.11 35.12±17.83 35.45±16.15 32.03±15.15 0.004 0.078 疲乏 38.48±20.65 32.79±20.63 33.88±20.48 29.81±15.00 0.085 0.115 性生活改变 37.40±30.00 34.15±26.34 32.52±30.26 29.27±22.60 0.405 0.371 注:P1:治疗组治疗前后比较;P2:对照组治疗前后比较。 表 6 两组患者的不良反应比较
例(%) 不良反应 治疗组(n=48) 对照组(n=45) P 手足综合征 0.040 Ⅰ级 7(14.6) 9(20.0) Ⅱ级 1(2.1) 5(11.1) Ⅲ级 0 2(4.4) 腹泻 0.272 Ⅰ级 12(25.0) 14(31.1) Ⅱ级 6(12.5) 8(17.8) Ⅲ级 1(2.1) 1(2.2) 高血压 0.004 Ⅰ级 13(27.1) 14(31.1) Ⅱ级 2(4.2) 8(17.8) Ⅲ级 1(2.1) 4(8.9) 血清转氨酶升高 0.638 Ⅰ级 6(12.5) 5(11.1) Ⅱ级 2(4.2) 1(2.2) Ⅲ级 0 0 食欲不振 0.723 Ⅰ级 14(29.2) 16(35.6) Ⅱ级 6(12.5) 5(11.1) Ⅲ级 0 0 体重下降 0.064 Ⅰ级 5(10.4) 9(20.0) Ⅱ级 3(6.3) 6(13.3) Ⅲ级 0 0 疲乏 0.013 Ⅰ级 8(16.7) 14(31.1) Ⅱ级 2(4.9) 6(13.3) Ⅲ级 0 0 恶心呕吐 0.450 Ⅰ级 6(14.6) 6(13.3) Ⅱ级 1(2.4) 3(6.7) Ⅲ级 0 1(2.2) 蛋白尿 0.279 Ⅰ级 6(12.2) 5(11.1) Ⅱ级 2(4.2) 4(8.9) Ⅲ级 0 2(4.4) -
[1] Rumgay H, Arnold M, Ferlay J, et al. Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 77(6): 1598-1606. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.08.021
[2] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2022, 72(1): 7-33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21708
[3] Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Zeng HM, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2016[J]. J Natl Cancer Cent, 2022, 2(1): 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jncc.2022.02.002
[4] 庄克川. 中医药治疗恶性肿瘤的研究现状[J]. 光明中医, 2022, 37(13): 2466-2468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GMZY202213063.htm
[5] 王倩倩, 邱华, 朱玟霜, 等. 中医药联合靶向药物治疗原发性肝癌研究进展[J]. 医学理论与实践, 2023, 36(14): 2374-2377. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXLL202314010.htm
[6] 王贵强, 王福生, 庄辉, 等. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCGD202306006.htm
[7] 《原发性肝癌诊疗规范(2019年版)》编写专家委员会. 原发性肝癌诊疗规范(2019年版)[J]. 中国临床医学, 2020, 27(1): 140-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QLZL202222001.htm
[8] 惠友谊, 薛敬东, 高改娅, 等. 原发性肝癌中医证型及证素的文献研究[J]. 世界中医药, 2023, 18(3): 401-405. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJZA202303018.htm
[9] 邵峰, 曾普华, 曾光, 等. 628例中晚期原发性肝癌患者中医证素分布特点[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2019, 34(8): 3439-3442. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY201908023.htm
[10] 肖蕾, 欧洋, 李京, 等. 基于试验设计三要素规范化的中医实用性随机对照试验构想[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2021, 36(1): 60-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY202101011.htm
[11] Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, et al. IMbrave150 Investigators. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 382(20): 1894-1905. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1915745
-




 下载:
下载: