Effects of Liqi Tongbian Decoction on intestinal motility and intestinal flora in rats with slow transit constipation with Qi stagnation pattern
-
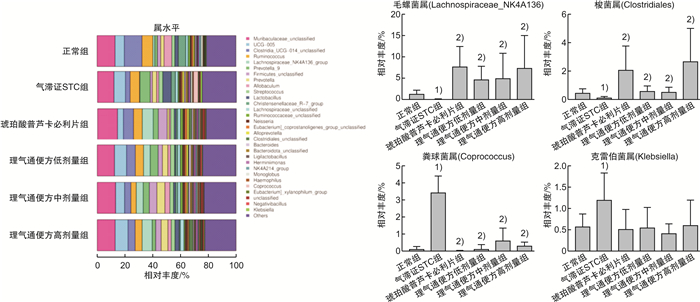
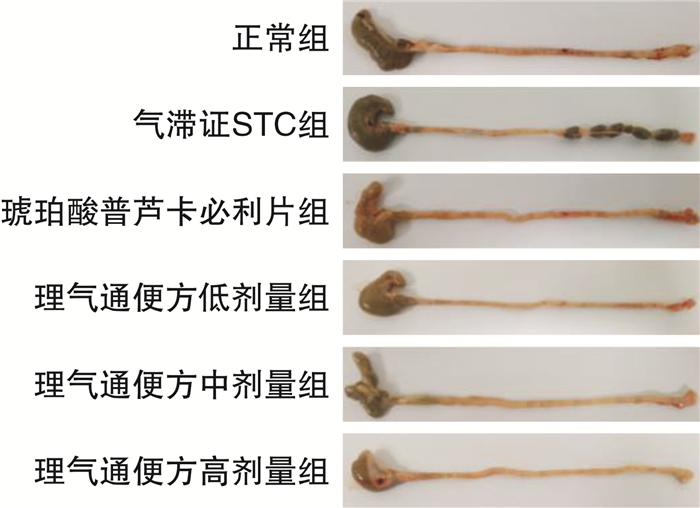
摘要: 目的 观察理气通便方对气滞证慢传输型便秘(slow transit constipation,STC)大鼠肠道动力及肠道菌群的影响。方法 以36只Wistar大鼠为研究对象,根据随机数字表法选取6只为正常组,其余大鼠采用“洛哌丁胺混悬液+夹尾刺激”复制气滞证STC大鼠模型。造模成功后,将大鼠随机分为气滞证STC模型组、琥珀酸普芦卡必利片组和理气通便方低、中、高剂量组,每组6只。正常组与气滞证STC模型组给予等容积的蒸馏水灌胃,琥珀酸普芦卡必利片组给予0.18 mg /(kg·d)混悬液灌胃,理气通便方低、中、高剂量组分别用5.15、10.30和20.60 g/kg药液灌胃。通过粪便数量、粪便含水量、小肠推进率评价理气通便方的治疗效果。采用免疫组化方法检测大鼠结肠组织中Cajal间质细胞(Cajal interstitial cell,ICC)、5-HT、5-HT3受体(5-HT3R)及5-HT4受体(5-HT4R)蛋白表达水平。采用气相色谱-质谱联用法测定短链脂肪酸(short-chain fatty acids, SCFAs)含量的变化。采用16SrDNA高通量测序分析肠道菌群的变化。结果 与正常组比较,气滞证STC模型组大鼠的粪便数量减少、粪便含水量和小肠推进率均下降(P<0.05),结肠组织中ICC、5-HT、5-HT3R及5-HT4R蛋白表达水平均降低(P<0.05),肠道菌群的丰度和多样性显著下降(P<0.05),毛螺菌属、梭菌属丰度下降(P<0.05),粪球菌属、克雷伯菌属丰度增加(P<0.05),粪便中SCFAs含量降低(P<0.05);与气滞证STC模型组比较,给药组大鼠粪便数量及含水率均增加(P<0.05),小肠推进率除理气通便方低剂量组差异无统计学意义外,其他均差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);结肠组织中ICC、5-HT、5-HT3R及5-HT4R蛋白表达水平升高,其中除了理气通便方低剂量组5-HT蛋白表达及琥珀酸普芦卡必利片组ICC、5-HT、5-HT3R蛋白表达水平差异无统计学意义外,其余均差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);琥珀酸普芦卡必利片组与理气通便方中、高剂量组能够显著提高SCFAs的总含量(P<0.05),其中显著增加了丁酸的含量;理气通便方各剂量组可提高菌群的丰度和多样性,显著增加毛螺菌属、梭菌属丰度,降低粪球菌属丰度(P<0.05)。结论 理气通便方可能通过增加ICC、5-HT及其受体的表达、调整肠道菌群结构及SCFAs的含量,从而起到治疗气滞证STC大鼠的作用。Abstract: Objective To investigate the effects of Liqi Tongbian Decoction on intestinal motility and intestinal flora in rats with slow transit constipation(STC) with Qi stagnation pattern.Methods Thirty-six Wistar rats were selected according to the random number table method, and 6 rats were selected as the normal group, and the rest of the rats were used to replicate the STC rat model of Qi stagnation pattern by using "loperamide suspension and tail clamping stimulation". After successful modelling, the rats were randomly divided into the STC model group, the prucalopride succinate tablet group, and the low, medium and high dose groups of the formula, with 6 rats in each group. The normal group and the STC model group were given equal volumes of distilled water, the prucalopride succinate tablet group was given 0.18 mg/(kg·d) suspension by gavage, and the low, medium and high dose groups of the formula were given 5.15 g/kg, 10.30 g/kg and 20.60 g/kg by gavage, respectively. The therapeutic efficacy of the formula was evaluated by the water content of faeces and the propulsion rate of small intestine, and the protein expression levels of murine Cajal interstitial cells(ICC), serotonin(5-HT), serotonin 3 receptor(5-HT3R) and serotonin 4 receptor(5-HT4R) were detected by immunohistochemistry in colon tissues, and the content of short-chain fatty acids(SCFAs) was measured by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry(GC-MS). SCFAs content changes, and 16SrDNA high-throughput sequencing was used to analyse the changes in intestinal flora.Results Compared with the normal control group, rats in the STC model group with Qi stagnation pattern showed a decrease in the number of faeces, a significant decrease in the water content of faeces and the rate of small intestinal propulsion(P < 0.05), a significant decrease in the levels of expression of the 5-HT, 5-HT3R and 5-HT4R proteins in the colonic tissues(P < 0.05), and a significant decrease in abundance and diversity of intestinal flora(P < 0.05), with a increase in the abundance of Trichoderma spp, Clostridium spp. decreased in abundance(P < 0.05), Coccidioides faecalis spp. and Klebsiella spp. increased in abundance(P < 0.05), and the content of short-chain fatty acids in the faeces was significantly reduced(P < 0.05); when compared with the STC model group of Qi stagnation pattern, the number of faeces and water content of rats in the administered group increased(P < 0.05), and the rate of propulsion of the small intestine was statistically(P < 0.05), except for no statistical difference in the low dose group of Liqi Tongbian Decoction; the middle and high dose groups of Prucalopride Succinate Tablets and Liqi Tongbian Decoction were able to increase the total content of SCFAs(P < 0.05), including a significant increase in the content of butyric acid; the dose groups of Liqi Tongbian Decoction could increase the abundance and diversity of bacterial flora, significantly increase the abundance of Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136 spp. and Clostridium spp. and decrease the abundance of Coccidioides faecalis spp. (P < 0.05).Conclusion The Liqi Tongbian Decoction may play a role in the treatment of STC with Qi stagnation pattern by increasing the expression of ICC, 5-HT and their receptors, adjusting the structure of intestinal flora and the content of SCFAs.
-

-
表 1 各组大鼠肠道动力相关指标的比较
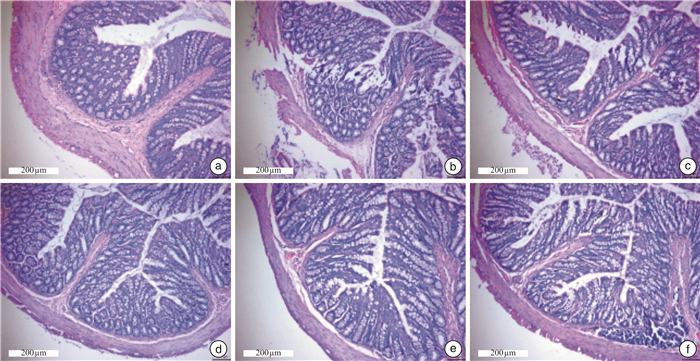
X±S 组别 例数 6 h粪便数量/个 粪便含水率/% 小肠推进率/% 正常组 6 20.33±2.52 64.27±1.33 65.40±3.60 气滞证STC组 6 8.00±1.001) 43.21±2.521) 47.13±4.921) 琥珀酸普芦卡必利片组 6 18.33±1.532) 51.52±1.872) 60.85±11.072) 理气通便方低剂量组 6 14.33±1.532) 56.90±4.592) 54.28±10.72 理气通便方中剂量组 6 16.67±1.532) 60.04±3.852) 56.26±7.022) 理气通便方高剂量组 6 18.00±2.002) 65.65±7.902) 60.25±8.292) 与正常组比较,1)P<0.05;与气滞证STC组比较,2)P<0.05。 表 2 各组大鼠结肠ICC、5-HT、5-HT3R、5-HT4R的阳性细胞面积比较
%,X±S 组别 例数 ICC 5-HT 5-HT3R 5-HT4R 正常组 6 37.77±3.27 40.74±1.84 23.85±1.96 42.56±2.41 气滞证STC组 6 31.07±1.601) 28.55±3.631) 12.94±1.251) 31.11±1.781) 琥珀酸普芦卡必利片组 6 37.91±4.822) 34.80±2.91 14.14±0.88 40.13±3.912) 理气通便方低剂量组 6 41.05±4.012) 31.69±3.04 16.58±1.932) 38.29±2.762) 理气通便方中剂量组 6 44.84±2.312) 35.78±1.852) 19.60±3.042) 40.38±2.902) 理气通便方高剂量组 6 49.73±3.572) 38.97±0.912) 22.28±1.672) 42.49±1.232) 与正常组比较,1)P<0.05;与气滞证STC组比较,2)P<0.05。 表 3 各组大鼠肠道菌群Alpha多样性的比较
X±S 组别 例数 chao1指数 shannon指数 simpson指数 正常组 6 900.00±102.15 7.99±0.14 0.990±0.002 气滞证STC组 6 729.69±104.731) 7.37±0.171) 0.983±0.0031) 琥珀酸普芦卡必利片组 6 916.21±93.392) 7.97±0.372) 0.987±0.008 理气通便方低剂量组 6 957.84±73.452) 8.11±0.162) 0.990±0.0032) 理气通便方中剂量组 6 963.82±125.452) 7.92±0.072) 0.988±0.0032) 理气通便方高剂量组 6 1 187.23±210.192) 8.30±0.222) 0.991±0.0022) 与正常组比较,1)P<0.05;与气滞证STC组比较,2)P<0.05。 表 4 各组大鼠粪便中SCFAs含量的比较
X±S SCFAs 正常组 气滞证STC组 琥珀酸普芦卡必利片组 理气通便方低剂量组 理气通便方中剂量组 理气通便方高剂量组 总SCFAs 11 810.81±1 156.33 6 934.06±627.451) 15 646.96±819.892) 7 527.09±302.75 13 680.01±447.242) 15 278.18±788.212) 乙酸 870.94±533.21 608.07±288.58 840.81±146.752) 558.83±79.75 859.37±103.692) 880.23±194.802) 丙酸 500.31±352.08 313.13±293.76 529.64±139.572) 355.25±104.08 657.56±98.352) 599.97±128.212) 异丁酸 23.41±5.42 14.05±5.711) 29.11±7.952) 18.57±5.82 25.05±8.102) 29.02±7.802) 丁酸 459.55±258.15 164.64±68.911) 1014.14±513.622) 237.98±183.92 592.77±285.082) 856.80±450.992) 戊酸 53.65±25.43 27.39±13.131) 75.26±22.942) 40.36±13.54 65.94±11.942) 75.75±25.502) 己酸 29.84±21.53 5.04±8.521) 89.16±54.132) 14.88±4.55 46.56±25.352) 67.86±37.742) 庚酸 2.31±1.92 0.72±0.961) 3.46±1.692) 1.95±0.792) 2.64±0.972) 3.55±2.092) 癸酸 1.24±0.66 0.37±0.191) 0.82±0.312) 0.91±0.332) 0.67±0.232) 0.62±0.112) 与正常组比较,1)P<0.05;与气滞证STC组比较,2)P<0.05。 -
[1] 柯晓, 王文荣. 功能性便秘的中西医结合诊疗[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2022: 8-9.
[2] Wang LF, Wu F, Hong YL, et al. Research progress in the treatment of slow transit constipation by traditional Chinese medicine[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 290: 115075. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115075
[3] Barberio B, Judge C, Savarino EV, et al. Global prevalence of functional constipation according to the Rome criteria: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 6(8): 638-648. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00111-4
[4] 刘启鸿, 柯晓, 骆云丰, 等. 基于"脑-肠-菌"轴观察理气通便方对气滞证慢传输型便秘患者的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2021, 36(6): 3324-3328. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY202106056.htm
[5] 刘启鸿, 柯晓, 骆云丰, 等. 理气通便方治疗慢传输型便秘气滞证30例随机对照试验[J]. 中医杂志, 2021, 62(7): 604-608. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZYZ202107011.htm
[6] 汤水华, 李思汉, 林翔英, 等. 理气通便方对功能性便秘气滞证大鼠脑肠肽的影响[J]. 北京中医药大学学报, 2021, 44(7): 615-624. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2157.2021.07.006
[7] 周国儿, 吴静, 黄云娟, 等. "肝郁气滞"及"肝郁脾虚"型抑郁症动物模型建立初探[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2014, 32(5): 1035-1038. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYHS201405025.htm
[8] 刘启鸿, 柯晓, 方文怡, 等. 柯晓教授治疗功能性便秘临证经验[J]. 福建中医药, 2021, 52(9): 44-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-338X.2021.09.013
[9] 张羽, 黄美祯, 潘春曲, 等. 基于"脾与线粒体相关性"探讨Cajal间质细胞功能障碍与胃食管反流关系[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志, 2022, 29(3): 6-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXYY202203002.htm
[10] 刘梦茹, 邱仁静, 李慧, 等. 运脾柔肝方对便秘型肠易激综合征大鼠SCF/c-kit信号通路的影响[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2020, 31(11): 2593-2596. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2020.11.010
[11] 张远哲, 黎豫川, 赵罗娜. 附子-肉桂对慢传输型便秘大鼠5-HT信号通路及c-Kit表达的影响[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2023, 25(3): 1111-1121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJKX202303035.htm
[12] 刘启鸿, 胡剑云, 王宁馨, 等. 5-羟色胺信号系统的研究概况[J]. 医学综述, 2021, 27(11): 2099-2103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2021.11.004
[13] 王晓燕, 张亚楠, 韩晶, 等. 电针不同腧穴对功能性腹泻大鼠多组织5-HT3R、5-HT4R的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2022, 42(22): 5566-5570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLXZ202222047.htm
[14] 吴旻娜, 王浩, 李悠然, 等. 枳术方对慢传输型便秘大鼠结肠5-HT4R及下游CaM-MLCK信号通路的影响[J]. 南京中医药大学学报, 2021, 37(6): 891-896. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJZY202106019.htm
[15] Shen L, Wang Z, Huang R, et al. Electroacupuncture Modulates 5-HT4R-Mediated cAMP/PKA Signaling to Improve Intestinal Motility Disorders in a Thy1-αSyn Parkinson's Mouse Mode[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2022, 2022: 8659462.
[16] 汤振峰, 沙静涛. 基于肠道微生态探讨针刺改善功能性便秘的研究进展[J]. 广州中医药大学学报, 2022, 39(5): 1174-1178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-REST202205031.htm
[17] 周丽, 徐派的, 张红星. 肠道菌群与常见功能性胃肠病相关性的研究进展[J]. 华中科技大学学报(医学版), 2020, 49(6): 756-760. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYX202006021.htm
[18] 庄羽骁, 杨姗莹, 龚彪, 等. 肠道微生态参与功能性便秘发生机制的研究进展[J]. 国际消化病杂志, 2021, 41(2): 84-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWXH202102003.htm
[19] 刘帅, 李红霞, 董秀山. 短链脂肪酸对肠道动力影响的研究进展[J]. 中国微生态学杂志, 2021, 33(12): 1476-1482. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWS202112021.htm
[20] 李吉磊, 王瑞昕, 赵鲁卿, 等. 厚朴排气合剂对便秘大鼠肠道分泌功能及肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2023, 31(6): 439-444, 450. https://zxyxh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2023.06.09
[21] Soret R, Chevalier J, De Coppet P, et al. Short-chain fatty acids regulate the enteric neurons and control gastrointestinal motility in rats[J]. Gastroenterology, 2010, 138(5): 1772-1782.e4.
-




 下载:
下载: