Jianpi Liqi Formula improved duodenal mucosal barrier function in functional dyspepsia rats by regulating the p53/MUC2 signaling pathway
-
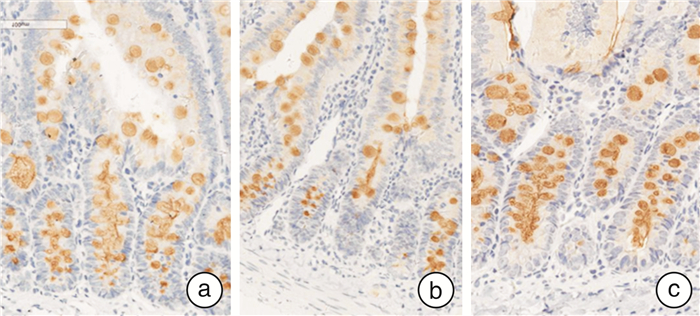
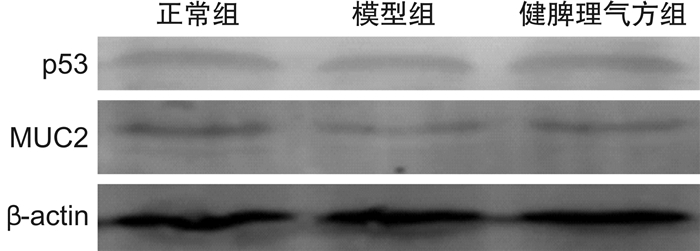
摘要: 目的 观察健脾理气方对功能性消化不良(functional dyspepsia,FD)大鼠十二指肠黏膜通透性的影响及对肿瘤蛋白p53(tumor protein p53,p53)和黏液蛋白2(mucin 2,MUC2)通路的调控作用。方法 将18只SD健康雄性大鼠随机分为正常组、模型组、健脾理气方组(6只/组),采用公认的碘乙酰胺灌胃+夹尾刺激法制备FD大鼠模型,模型制备成功后,正常组和模型组大鼠均给予0.9%氯化钠注射液灌胃,健脾理气方组给予健脾理气方水煎剂灌胃。取大鼠十二指肠组织,采用异硫氰酸荧光素-葡聚糖(FITC-Dextran)示踪法检测十二指肠上皮细胞黏膜通透性评价十二指肠肠道屏障功能,并进一步采用实时荧光定量PCR(real-time quantitative PCR,qRT-PCR)和蛋白免疫印迹(Western blot)分别检测p53、MUC2 mRNA含量和蛋白表达情况。结果 模型组大鼠十二指肠黏膜通透性增高,p53、MUC2的mRNA含量均降低,MUC2蛋白表达降低。经健脾理气方治疗后FD大鼠十二指肠黏膜通透性降低,p53 mRNA表达水平显著上升,MUC2的mRNA和蛋白表达水平明显升高。结论 健脾理气方调控p53以增加MUC2的表达,降低十二指肠黏膜通透性,从而恢复十二指肠黏膜屏障功能,可能是该方治疗FD的作用机制之一。Abstract: Objective The effect of Jianpi Liqi Formula on the permeability of duodenal mucosa in rats with functional dyspepsia(FD) and its regulatory effect on tumor protein p53(p53) and mucin 2(MUC2) pathways were observed.Methods Eighteen SD healthy male rats were randomly divided into the control group, model group, and Jianpi Liqi formula group(6 animals/group), and FD rat models were prepared by the recognized iodoacetamide gavage and tail stimulation method. Rat duodenal tissue was taken and the luciferin-dextran isothiocyanate-dextran(FITC-Dextran) tracer method was used to detect the permeability of the mucosa of duodenal epithelial cells to evaluate the duodenal intestinal barrier function, and real-time quantitative PCR(qRT-PCR) and Western Blot were used to detect p53, MUC2 mRNA content and protein expression, respectively.Results The duodenal mucosal permeability of rats in the model group increased, the mRNA content of p53 and MUC2 decreased, and the expression of MUC2 protein decreased. After treatment with Jianpi Liqi Formula, the duodenal mucosal permeability of FD rats decreased, the expression level of p53 mRNA increased significantly, and the expression level of mRNA and protein of MUC2 increased significantly.Conclusion Jianpi Liqi Formula regulates p53 to increase the expression of MUC2 and reduce the permeability of the duodenal mucosa, thereby restoring the duodenal mucosal barrier function, which may be one of the mechanisms of action of this prescription for the treatment of FD.
-
Key words:
- functional dyspepsia /
- Jianpi Liqi Formula /
- mucosal permeability /
- tumor protein p53 /
- mucin 2
-

-
表 1 各组大鼠十二指肠对FITC-Dextran的通透性
ng/(min·cm2),X±S 组别 例数 30 min 60 min 90 min 120 min 正常组 6 28.29±2.56 25.32±2.60 25.84±3.93 26.24±3.63 模型组 6 39.87±5.191) 36.82±5.761) 40.61±6.811) 45.63±10.171) 健脾理气方组 6 32.41±5.962) 29.17±6.792) 32.91±8.082) 32.77±5.913) 与正常组比较,1)P < 0.01;与模型组比较,2)P < 0.05,3)P < 0.01。 表 2 各组大鼠十二指肠p53和MUC2 mRNA相对表达量
X±S 组别 例数 p53 MUC2 正常组 6 1.01±0.15 1.00±0.13 模型组 6 0.38±0.161) 0.43±0.061) 健脾理气方组 6 0.59±0.112) 0.64±0.093) 与正常组比较,1)P < 0.01;与模型组比较,2)P < 0.05,3)P < 0.01。 表 3 各组大鼠十二指肠p53和MUC2蛋白相对表达量
X±S 组别 例数 p53 MUC2 正常组 6 0.68±0.13 0.49±0.08 模型组 6 0.64±0.17 0.31±0.081) 健脾理气方组 6 0.73±0.11 0.44±0.072) 与正常组比较,1)P < 0.01;与模型组比较,2)P < 0.05。 -
[1] Mahadeva S, Ford AC. Clinical and epidemiological differences in functional dyspepsia between the East and the West[J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2016, 28(2): 167-174. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12657
[2] Wauters L, Talley NJ, Walker MM, et al. Novel concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of functional dyspepsia[J]. Gut, 2020, 69(3): 591-600. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318536
[3] Puthanmadhom Narayanan S, O'Brien DR, Sharma M, et al. Duodenal Mucosal Barrier in Functional Dyspepsia[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 20(5): 1019-1028. e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.09.029
[4] Black CJ, Drossman DA, Talley NJ, et al. Functional gastrointestinal disorders: advances in understanding and management[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10263): 1664-1674. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32115-2
[5] 卢小芳, 张声生. 中医药治疗功能性消化不良研究进展[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2023, 31(6): 405-410. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2023.06.02
[6] 张声生, 赵鲁卿. 功能性消化不良中医诊疗专家共识意见(2017)[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2017, 32(6): 2595-2598. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY201706072.htm
[7] Zhang S, Zhao L, Wang H, et al. Efficacy of modified LiuJunZi decoction on functional dyspepsia of spleen-deficiency and qi-stagnation syndrome: a randomized controlled trial[J]. BMC Complement Altern Med, 2013, 13: 54. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-13-54
[8] 常雄飞, 沈凌宇, 张立宏, 等. 健脾理气方抑制肥大细胞改善十二指肠紧密连接蛋白表达治疗功能性消化不良的机制研究[J]. 上海中医药杂志, 2021, 55(11): 91-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHZZ202111020.htm
[9] 李小芳, 张丹, 宋大强, 等. 白术内酯Ⅰ对人胃癌细胞SGC-7901裸鼠移植瘤生长及凋亡的影响[J]. 中国医院药学杂志, 2018, 38(18): 1921-1925. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYZ201818010.htm
[10] 屈映, 李诗莹, 张书信, 等. 党参、白花蛇舌草防治结直肠癌术后复发转移的网络药理学研究[J]. 肿瘤药学, 2021, 11(6): 707-719. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LIYX202106021.htm
[11] 张明发, 沈雅琴. 和厚朴酚及厚朴酚抗结直肠癌和胃癌药理作用及其机制的研究进展[J]. 药物评价研究, 2022, 45(4): 810-816. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YWPJ202204026.htm
[12] 杨珏, 罗霄, 刘芳, 等. 基于网络药理学和分子对接分析厚朴治疗消化性溃疡的作用机制[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2021, 46(17): 4522-4530. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZY202117026.htm
[13] Stedman A, Beck-Cormier S, Le Bouteiller M, et al. Ribosome biogenesis dysfunction leads to p53-mediated apoptosis and goblet cell differentiation of mouse intestinal stem/progenitor cells[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2015, 22(11): 1865-1876.
[14] Pelaseyed T, Bergström JH, Gustafsson JK, et al. The mucus and mucins of the goblet cells and enterocytes provide the first defense line of the gastrointestinal tract and interact with the immune system[J]. Immunol Rev, 2014, 260(1): 8-20.
[15] Birchenough GM, Nyström EE, Johansson ME, et al. A sentinel goblet cell guards the colonic crypt by triggering Nlrp6-dependent Muc2 secretion[J]. Science, 2016, 352(6293): 1535-1542.
[16] 张声生, 陈贞, 许文君, 等. 基于"寒、热、虚、实"二次辨证的565例功能性消化不良证候分布特点研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2008, 23(9): 833-835. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY200809028.htm
[17] Vanheel H, Farré R. Changes in gastrointestinal tract function and structure in functional dyspepsia[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 10(3): 142-149. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035915494610_940e.html
[18] Puthanmadhom Narayanan S, O'Brien DR, Sharma M, et al. Duodenal Mucosal Barrier in Functional Dyspepsia[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 20(5): 1019-1028. e3.
[19] Wauters L, Talley NJ, Walker MM, et al. Novel concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of functional dyspepsia[J]. Gut, 2020, 69(3): 591-600.
[20] Chelakkot C, Ghim J, Ryu SH. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2018, 50(8): 1-9.
[21] Minton K. Intestinal barrier protection[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2022, 22(3): 144-145.
[22] Wauters L, Ceulemans M, Schol J, et al. The Role of Leaky Gut in Functional Dyspepsia[J]. Front Neurosci, 2022, 16: 851012.
[23] Boccellato F, Woelffling S, Imai-Matsushima A, et al. Polarised epithelial monolayers of the gastric mucosa reveal insights into mucosal homeostasis and defence against infection[J]. Gut, 2019, 68(3): 400-413.
[24] Liu Y, Yu Z, Zhu L, et al. Orchestration of MUC2-The key regulatory target of gut barrier and homeostasis: A review[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2023, 236: 123862.
[25] 吴毓谦, 汪龙德, 牛媛媛, 等. 十二指肠低度炎症在功能性消化不良中的研究进展[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2023, 31(1): 68-71, 76. https://zxyxh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2023.01.13
[26] Ford AC, Mahadeva S, Carbone MF, et al. Functional gastrointestinal disorders 3 functional dyspepsia[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10263): 1689-1702.
[27] Odenwald MA, Turner JR. Intestinal permeability defects: is it time to treat?[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 11(9): 1075-1083.
[28] Talley NJ. What Causes Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders? A Proposed Disease Model[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2020, 115(1): 41-48.
[29] Stedman A, Beck-Cormier S, Le Bouteiller M, et al. Ribosome biogenesis dysfunction leads to p53-mediated apoptosis and goblet cell differentiation of mouse intestinal stem/progenitor cells[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2015, 22(11): 1865-1876.
-




 下载:
下载: