Evaluation value of hepatic venous pressure gradient on gastrointestinal bleeding in decompensated cirrhosis patients
-
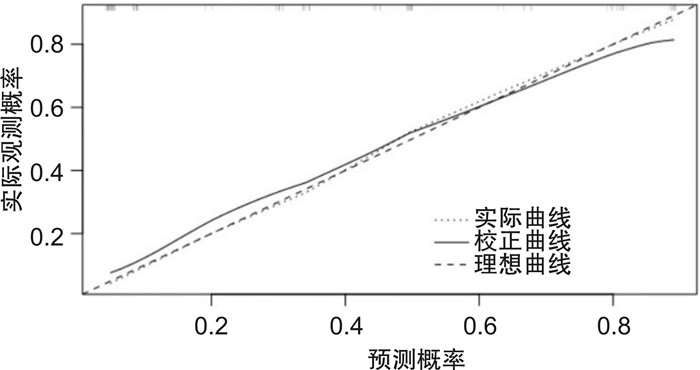
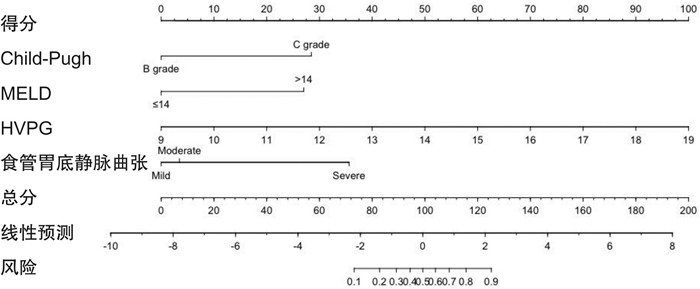
摘要: 目的 探讨肝静脉压力梯度对肝硬化失代偿期患者消化道出血的评估价值。方法 纳入2020年1月—2021年6月在我院就诊的112例肝硬化失代偿期患者作为研究对象,分析肝静脉压力梯度与患者临床特征的相关性,所有患者按随访1年内是否发生消化道出血分为消化道出血组和无消化道出血组,比较两组患者的临床资料以及肝静脉压力梯度;多因素logistic回归分析获得肝硬化失代偿期患者消化道出血的独立预测因素,重点分析肝静脉压力梯度与患者消化道出血的相关性;基于多因素分析结果建立预测肝硬化失代偿期患者消化道出血风险的列线图模型,绘制校准曲线以验证列线图模型的预测效能。结果 肝静脉压力梯度与肝硬化失代偿期患者性别、食管胃底静脉曲张程度、Child-Pugh分级以及终末期肝病模型(model for end-stage liver disease,MELD)评分有一定的相关性(P < 0.05);消化道出血组男性占比、重度食管胃底静脉曲张占比、凝血酶原活动度≤75%、Child-Pugh分级C级占比、MELD评分>14分占比以及肝静脉压力梯度明显高于无消化道出血组(P < 0.05);多因素logistic回归分析显示,食管胃底静脉曲张程度、Child-Pugh分级、MELD评分以及肝静脉压力梯度为肝硬化失代偿期患者发生消化道出血的独立预测因素(P < 0.05);基于多因素分析结果获得的独立预测因素为:食管胃底静脉曲张程度、Child-Pugh分级、MELD评分以及肝静脉压力梯度,结合各自影响权重建立预测肝硬化失代偿期患者消化道出血风险的列线图模型,校准曲线显示,肝硬化失代偿期患者消化道出血风险的预测值与实际观测值符合度良好(P>0.05)。结论 肝静脉压力梯度可用于准确评估肝硬化失代偿期患者消化道出血风险,基于独立预测因素建立的列线图模型具有较高的预测价值。Abstract: Objective To explore the value of hepatic venous pressure gradient in the evaluation of gastrointestinal bleeding in decompensated cirrhosis patients.Methods One hundred and twelve decompensated liver cirrhosis patients who were treated in our hospital from January 2020 to June 2021 were included as the study subjects. The correlation between the hepatic venous pressure gradient and the clinical characteristics of the patients was analyzed. All patients were divided into the digestive tract bleeding group and the no digestive tract bleeding group according to whether digestive tract bleeding occurred within the follow-up one year. The general clinical data and hepatic venous pressure gradient of patients between the two groups were compared. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to obtain independent predictors of digestive tract bleeding in decompensated cirrhosis patients, the analysis was focused on the correlation between hepatic venous pressure gradient and digestive tract bleeding. A nomogram model was established to predict the risk of digestive tract bleeding in decompensated cirrhosis patients based on the results of multivariate analysis, and a calibration curve was drawn to verify the predictive efficiency of the nomogram model.Results There was a certain correlation between the hepatic venous pressure gradient and the sex, the degree of esophageal and gastric fundus varices, Child-Pugh grade and model for end-stage liver disease(MELD) score of decompensated cirrhosis patients(P < 0.05). The proportion of male, severe esophageal and gastric varices, prothrombin activity =75%, Child-Pugh grade C, MELD score>14, and hepatic venous pressure gradient of patients in the gastrointestinal bleeding group were significantly higher than those in the non gastrointestinal bleeding group(P < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that the degree of esophageal and gastric fundus varices, Child-Pugh grade, MELD score and hepatic vein pressure gradient were independent predictors of gastrointestinal bleeding in decompensated cirrhosis patients(P < 0.05). The degree of esophageal and gastric fundus varices, Child-Pugh grade, MELD score and hepatic vein pressure gradient, a nomogram model for predicting the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding in decompensated cirrhosis patients was established in combination with their respective influence weights based on independent predictors obtained from the results of multivariate analysis. The calibration curve showed that the predicted value of the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding in decompensated cirrhosis patients was in good agreement with the actual observation value(P>0.05).Conclusion Hepatic venous pressure gradient can be used to accurately assess the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding in decompensated cirrhosis patients. The nomogram model has a high predictive value based on independent predictors.
-

-
表 1 肝静脉压力梯度与肝硬化失代偿期患者临床特征的相关性
X±S 临床特征 例数(n=112) 肝静脉压力梯度/mmHga) t P 年龄/岁 0.957 0.276 ≤55 45 15.7±4.6 >55 67 16.0±4.2 性别 2.787 0.018 男 76 16.7±4.5 女 36 15.2±4.2 肝硬化病因 1.617 0.196 病毒性 79 16.2±4.7 非病毒性 33 15.6±4.3 腹水 0.854 0.348 是 80 16.2±4.8 否 32 15.7±4.6 食管胃底静脉曲张程度 5.788 <0.001 轻度 23 14.7±3.8 中度 40 16.2±4.1 重度 49 17.9±4.8 白蛋白/(g/L) 1.657 0.134 ≤28 67 16.3±4.7 >28 45 15.8±4.6 总胆红素/(mmol/L) 1.094 0.234 ≤41 48 15.7±4.5 >41 63 16.2±4.7 凝血酶原活动度/% 1.876 0.094 ≤75 76 16.1±4.3 >75 36 15.7±4.3 Child-Pugh分级 4.974 <0.001 B级 69 15.5±4.3 C级 43 17.5±4.9 MELD评分/分 3.789 <0.001 ≤14 57 15.4±4.6 >14 55 16.9±4.9 注:a)1 mmHg=0.133 kPa。 表 2 两组患者的临床资料比较
例,X ± s 临床资料 消化道出血组(n=42) 无消化道出血组(n=70) t/χ2 P 临床资料 消化道出血组(n=42) 无消化道出血组(n=70) t/χ2 P 年龄/岁 1.644 0.298 白蛋白/(g/L) 1.945 0.239 ≤55 16 29 ≤28 21 46 > 55 26 41 > 28 21 24 性别 5.789 0.024 总胆红素/(mmol/L) 1.243 0.365 男 20 56 ≤41 16 32 女 22 14 > 41 26 38 肝硬化病因 1.879 0.254 凝血酶原活动度/% 4.674 0.041 病毒性 25 54 ≤75 35 41 非病毒性 17 16 > 75 7 29 腹水 0.876 0.467 Child-Pugh分级 9.967 0.002 是 30 50 B级 12 57 否 12 20 C级 30 13 食管胃底静脉曲张程度 7.899 0.004 MELD评分/分 7.895 0.007 轻度 2 21 ≤14 15 44 中度 12 28 > 14 27 26 重度 28 21 肝静脉压力梯度/ mmHg 17.7±4.9 13.4±3.3 5.668 < 0.001 表 3 影响肝硬化失代偿期患者消化道出血的多因素logistic回归分析
自变量 β S.E. Wald χ2 P OR 95%CI 肝静脉压力梯度 1.378 0.337 11.677 <0.001 4.136 1.563~7.663 食管胃底静脉曲张程度(中度) 0.483 0.118 6.221 0.013 1.568 1.135~3.869 食管胃底静脉曲张程度(重度) 1.287 0.356 13.875 <0.001 3.967 1.768~6.774 MELD评分 0.895 0.127 4.234 0.038 2.645 1.078~4.889 Child-Pugh分级 1.145 0.238 7.488 0.011 3.859 1.248~7.865 -
[1] 王月兴, 邓丽娟, 曾凡清, 等. 血清铁蛋白水平与肝硬化失代偿患者死亡率的相关性研究[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2022, 30(3): 217-220, 226. https://zxyxh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2022.03.08
[2] Ou M, Tian Y, Zhuang GQ, et al. QTc interval prolongation in liver cirrhosis with upper gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. Med Clin(Barc), 2021, 156(2): 68-75.
[3] 曹阳, 贺晓烨, 李雯莉, 等. 肝硬化合并门静脉海绵样变性流行病学调查[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2022, 30(6): 437-442. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2022.06.10 https://zxyxh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2022.06.10
[4] Kezer CA, Gupta N. The Role of Therapeutic Endoscopy in Patients With Cirrhosis-Related Causes of Gastrointestinal Bleeding[J]. Curr Gastroenterol Rep, 2018, 20(7): 31. doi: 10.1007/s11894-018-0637-6
[5] Fouad TR, Abdelsameea E, Abdel-Razek W, et al. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding in Egyptian patients with cirrhosis: Post-therapeutic outcome and prognostic indicators[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 34(9): 1604-1610. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14659
[6] 彭麟, 李兴泉, 李建华, 等. 鱼肝油酸钠联合普萘洛尔对肝硬化消化道出血的疗效及对应激反应的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2021, 21(8): 1572-1575. doi: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2021.08.038
[7] Jakab SS, Garcia-Tsao G. Evaluation and Management of Esophageal and Gastric Varices in Patients with Cirrhosis[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2020, 24(3): 335-350. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2020.04.011
[8] 张明艳, 王广川, 黄广军, 等. 833例次肝静脉压力梯度测定临床分析[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2018, 26(4): 266-270. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2018.04.007
[9] 陈炜, 李煜, 车莹, 等. 肝静脉压力梯度对乙肝肝硬化食管胃静脉曲张患者内镜治疗疗效的影响[J]. 中国医师杂志, 2022, 24(5): 662-666. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn431274-20220412-00312
[10] Zhou LL, Wang GC, Zhang MY, et al. Nomogram for hepatic venous pressure gradient in patients with cirrhosis[J]. J Dig Dis, 2021, 22(8): 488-495. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.13033
[11] 林志鹏, 陈斯良, 赵剑波. 乙型肝炎肝硬化患者肝静脉压力梯度与门静脉压力梯度相关性及临床价值[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2019, 28(2): 120-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2019.02.004
[12] Shao RY, Li ZW, Wang JT, et al. Hepatic venous pressure gradient-guided laparoscopic splenectomy and pericardial devascularisation versus endoscopic therapy for secondary prophylaxis for variceal rebleeding in portal hypertension(CHESS1803): study protocol of a multicenter randomised controlled trial in China[J]. BMJ Open, 2020, 10(6): e030960. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-030960
[13] Villanueva C, Albillos A, Genesca J, et al. β blockers to prevent decompensation of cirrhosis in patients with clinically significant portal hypertension(PREDESCI): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial[J]. Lancet, 2019, 393(10181): 1597-1608. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31875-0
[14] Khanna R, Sarin SK. Idiopathic portal hypertension and extrahepatic portal venous obstruction[J]. Hepatol Int, 2018, 12(Suppl 1): 148-167.
[15] Vaishnav M, Biswas S, Anand A, et al. Hepatic venous pressure gradient predicts further decompensation in cirrhosis patients with acute esophageal variceal bleeding[J]. Diagnostics(Basel), 2023, 13(14): 2385.
[16] Baiges A, Hernandez-Gea V. Management of Liver Decompensation in Advanced Chronic Liver Disease: Ascites, Hyponatremia, and Gastroesophageal Variceal Bleeding[J]. Clin Drug Investig, 2022, 42(1): 25-31.
[17] Jachs M, Hartl L, Simbrunner B, et al. Carvedilol Achieves Higher Hemodynamic Response and Lower Rebleeding Rates Than Propranolol in Secondary Prophylaxis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 21(9): 2318-2326. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.06.007
[18] Khalifa A, Rockey DC. Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding in Patients With Cirrhosis-Etiology and Outcomes[J]. Am J Med Sci, 2020, 359(4): 206-211. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2020.01.007
[19] Jindal A, Bhardwaj A, Kumar G, et al. Clinical decompensation and outcomes in patients with compensated cirrhosis and a hepatic venous pressure gradient ≥20 mmHg[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2020, 115(10): 1624-1633. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000653
[20] D'Amico G, Morabito A, D'Amico M, et al. New concepts on the clinical course and stratification of compensated and decompensated cirrhosis[J]. Hepatol Int, 2018, 12(Suppl 1): 34-43.
[21] Garcia de Paredes A, Manicardi N, Tellez L, et al. Molecular profiling of decompensated cirrhosis by a novel microRNA signature[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2021, 5(2): 309-322. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1642
[22] Shalimar VM, Elhence A, Kumar R, et al. Outcome of Conservative Therapy in Coronavirus disease-2019 Patients Presenting With Gastrointestinal Bleeding[J]. J Clin Exp Hepatol, 2021, 11(3): 327-333. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2020.09.007
[23] Warnes TW, Roberts SA, Smith A, et al. Portal pressure is of significant prognostic value in primary biliary cholangitis[J]. Liver Int, 2023, 43(1): 139-146. doi: 10.1111/liv.15289
[24] Hofer BS, Simbrunner B, Bauer DJM, et al. Acute hemodynamic response to propranolol predicts bleeding and nonbleeding decompensation in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2022, 6(9): 2569-2580. doi: 10.1002/hep4.2021
[25] Villanueva C, Albillos A, Genesca J, et al. Bacterial infections adversely influence the risk of decompensation and survival in compensated cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75(3): 589-599. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.04.022
[26] Xia YF, Tie J, Wang GC, et al. Individualized portal pressure gradient threshold based on liver function categories in preventing rebleeding after TIPS[J]. Hepatol Int, 2023, 17(4): 967-978. doi: 10.1007/s12072-023-10489-x
[27] 王继涛, 祁小龙. 肝静脉压力梯度在肝硬化外科手术中的应用现状及前景[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2021, 20(10): 1113-1116. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20210831-00424
[28] 蒋帆荣, 颜华东. 基于肝静脉压力梯度测定的代偿期肝硬化患者临床显著性门静脉高压的相关危险因素分析[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2021, 29(10): 995-1000. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20210829-00437
[29] Cueto-Robledo G, Tapia-Paredes A, Garcia-Cesar M, et al. Evaluation of Hepatic Hemodynamics(Hepatic Venous Pressure Gradient)During Right Heart Catheterization: A Comprehensive Review[J]. Curr Probl Cardiol, 2022, 47(9): 101278. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2022.101278
[30] Ma JQ, Gong XM, Luo JJ, et al. Impact of intrahepatic venovenous shunt on hepatic venous pressure gradient measurement[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2020, 31(12): 2081-2088. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2020.08.027
-




 下载:
下载: