Triptolide enhances the sensitivity of gastric cancer BGC823 cells to 5-FU by suppressing TLR4 expression
-
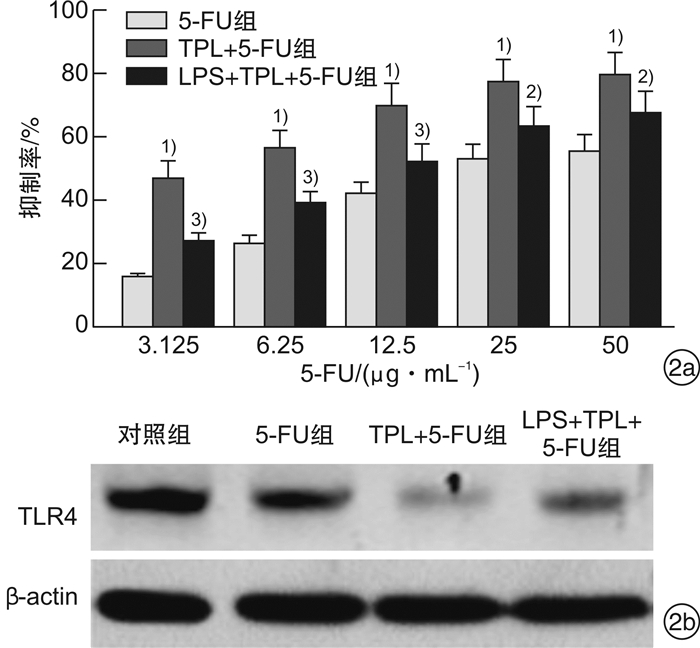
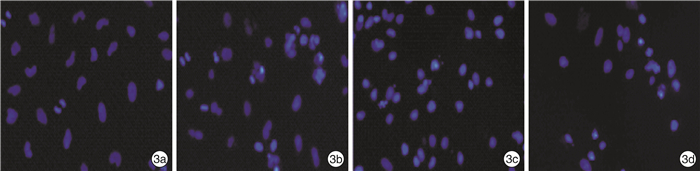
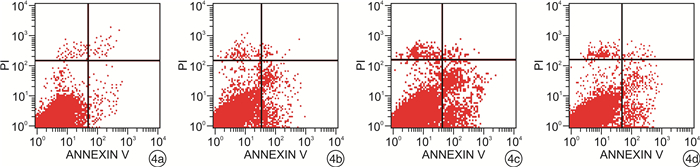
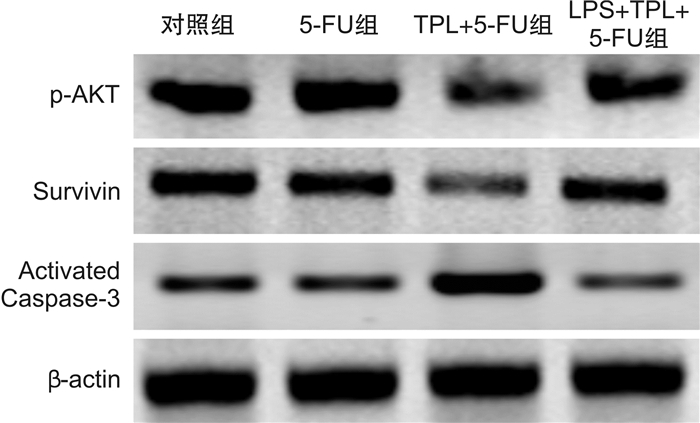
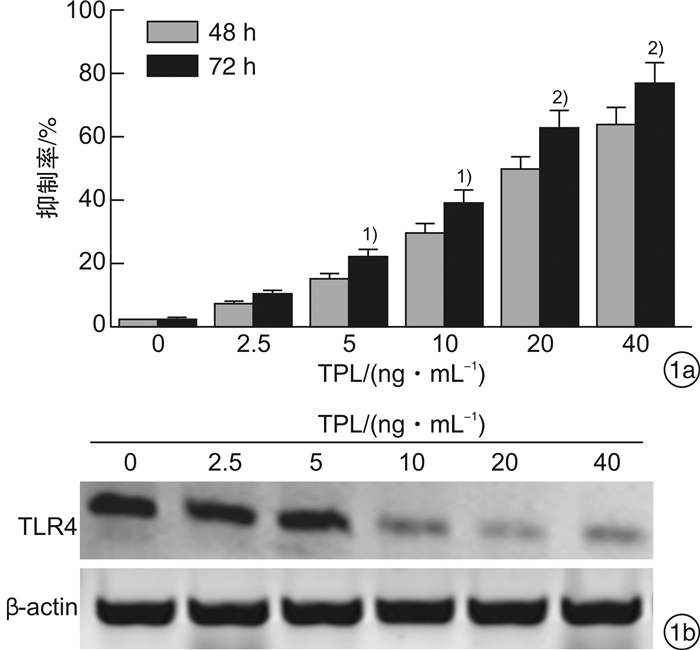
摘要: 目的 观察雷公藤内酯醇(TPL)是否可通过抑制Toll样受体4(TLR4)表达以增强胃癌BGC823细胞对5-FU的敏感性,并分析其相关的下游分子机制。方法 采用CCK-8法检测不同浓度TPL以及TPL联合5-FU对BGC823细胞的增殖的影响。将BGC823细胞分为对照组、5-FU组(仅予5-FU)、TPL+5-FU组以及脂多糖(LPS)+TPL+5-FU组;Hoechst33258染色观察细胞凋亡形态学变化,流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡率,Western blot检测TLR4、磷酸化AKT(p-AKT)、Survivin、活性Caspase-3蛋白表达。结果 TPL可呈浓度-时间依赖性的抑制BGC823细胞增殖。与5-FU组比较,TPL联合5-FU后对BGC823细胞的抑制率明显增加(P< 0.01),其5-FU的半数抑制浓度(IC50)显著降低(P< 0.01)。与5-FU组比较,TPL+5-FU组凋亡细胞数和细胞凋亡率均显著增加(P< 0.01);而LPS+TPL+5-FU组凋亡细胞数以及细胞凋亡率均较TPL+5-FU组显著下降(P< 0.05)。TPL+5-FU组的TLR4、p-AKT、Survivin蛋白表达均较5-FU组下降,而活性Caspase-3蛋白表达增加;与TPL+5-FU组比较,LPS+TPL+5-FU组的p-AKT、Survivin蛋白表达增加,活性Caspase-3蛋白表达减少。结论 TPL具有增强BGC823细胞对5-FU敏感性的作用,其机制与抑制TLR4表达,进而阻断PI3K/AKT通路、下调Survivin表达并促进Caspase-3活化有关。
-
关键词:
- 雷公藤内酯醇 /
- Toll样受体4 /
- 胃癌 /
- 磷酸化AKT /
- 活性Caspase-3
Abstract: Objective To observe whether triptolide (TPL) could enhance the sensitivity of gastric cancer BGC823 cells to 5-FU by inhibiting the expression of Toll like receptor 4 (TLR4), and analyze the related downstream molecular mechanisms.Methods The CCK-8 method was used to detect the effects of different concentrations of TPL and TPL combined with 5-FU on the proliferation of BGC823 cells. BGC823 cells were divided into control group, 5-FU group, TPL+5-FU group and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) +TPL+5-FU group; Hoechst33258 staining was used to observe the apoptosis morphological changes and flow cytometry was used to detect the cell apoptosis rate. TLR4, phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt), Survivin and Caspase-3 protein expression were detected by Western blot.Results TPL could inhibit the proliferation of BGC823 cells in a concentration-time dependent manner. Compared with the 5-FU group, the inhibition rate of the TPL combined with 5-FU group on BGC823 cells increased significantly (P< 0.01), and the half inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 5-FU decreased significantly (P< 0.01). Compared with the 5-FU group, the number of apoptotic cells and apoptosis rate of the TPL+5-FU group were significantly increased(P< 0.01); However, the number of apoptotic cells and cell apoptosis rate of the LPS+TPL+5-FU group were significantly lower than those of the TPL+5-FU group (P< 0.05). The TLR4, p-Akt and Survivin protein expression of the TPL+5-FU group were higher than those of the 5-FU group, and the expression of active Caspase-3 protein increased. Compared with the TPL+5-FU group, the p-Akt and Survivin protein expression of the LPS+TPL+5-FU group increased, but active Caspase-3 protein expression reduced.Conclusion TPL can enhance the sensitivity of BGC823 cells to 5-FU, its mechanism is related to inhibiting TLR4 expression, blocking the PI3K/AKT pathway, down regulating Survivin expression and promoting Caspase-3 activation.-
Key words:
- triptolide /
- Toll like receptor 4 /
- gastric cancer /
- phosphorylated AKT /
- active Caspase-3
-

-
[1] Wang S, Jiang H, Wang J, et al. Superior in vitro anticancer effect of biomimetic paclitaxel and triptolide co-delivery system in gastric cancer[J]. J Biomed Res, 2021, 35(4): 327-338. doi: 10.7555/JBR.35.20210102
[2] Deng QD, Lei XP, Zhong YH, et al. Triptolide suppresses the growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting β-catenin-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2021, 42(9): 1486-1497. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00657-w
[3] Huang G, Hu H, Zhang Y, et al. Triptolide sensitizes cisplatin-resistant human epithelial ovarian cancer by inhibiting the phosphorylation of AKT[J]. J Cancer, 2019, 10(13): 3012-3020. doi: 10.7150/jca.30669
[4] Yang Y, Zhang LJ, Bai XG, et al. Synergistic antitumour effects of triptolide plus gemcitabine in bladder cancer[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 106: 1307-1316. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.083
[5] Zhang S, Yang Y, Weng W, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes chemoresistance to 5-fluorouracil by upregulation of BIRC3 expression in colorectal cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 14. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0985-y
[6] Bates M, Spillane CD, Gallagher MF, et al. The role of the MAD2-TLR4-MyD88 axis in paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(12): e0243715. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243715
[7] Szajnik M, Szczepanski MJ, Czystowska M, et al. TLR4 signaling induced by lipopolysaccharide or paclitaxel regulates tumor survival and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer[J]. Oncogene, 2009, 28(49): 4353-4363. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.289
[8] Sun T, Liu Y, Li M, et al. Administration with hyperoside sensitizes breast cancer cells to paclitaxel by blocking the TLR4 signaling[J]. Mol Cell Probes, 2020, 53: 101602. doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2020.101602
[9] Ma JX, Sun YL, Yu Y, et al. Triptolide enhances the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells to gemcitabine by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2019, 11(6): 3750-3760.
[10] Liu R, Chen Y, Liu G, et al. PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(9): 797. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02998-6
[11] Wang J, Lv X, Guo X, et al. Feedback activation of STAT3 limits the response to PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors in PTEN-deficient cancer cells[J]. Oncogenesis, 2021, 10(1): 8. doi: 10.1038/s41389-020-00292-w
-




 下载:
下载: